![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Macrocylic metallocofactors (4)
|
Cobalamin (Co)
Tetrapyrroles (Ni) Porphyrins (Fe) Chlorophyll (Mg) |
|
|
Metal clusters
|
Fe-S (Fe4S4, Fe2)
FeMoCo Cu2, mixed metal clusters |
|
|
Single metal sites
|
Non-heme iron
Cu2+ mostly structural sites: Ca2+, Zn2+ |
|
|
The Cobalamin cofactor
|
- 3 States, most reduced is Cb(1)
- (1,3) are active, (2) is inactive - Vitamin B12 - Catalyzes three reaction types: - Intramolecular rearrangements - Reductions of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides (DNA synthesis) -Methyl group transfers (assisted by tetrahydrofolate) |
|
|
General Mechanism for AdoCbl-Dependent Rearrangement Reactions
|
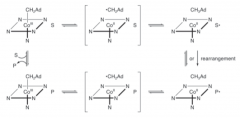
C-Co bond to generate 5’-DA radical
The 5’DA radical mediates H abstraction from substrate to form the intermediate 5’-DA and substrate radical. |
|
|
Summary: Two Roles of Cobalamins
|
Adenosyl cobalamin = adenosyl radical
Methyl cobalamin = methyl donor |

