![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
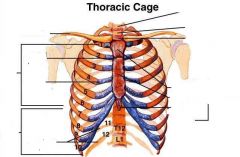
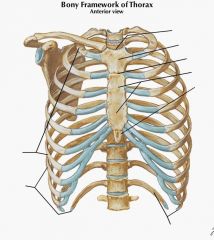
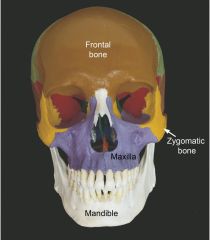
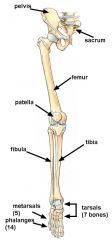
Name the following diagram.
|
|
|
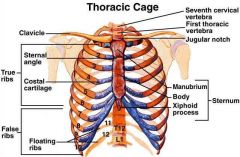
Thoracic cage, how many:
Ribs? True ribs? False ribs? Floating ribs? Label the diagram
|
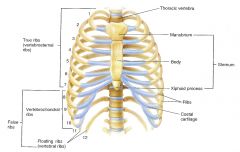
12 ribs; 1-7 true; 8-10 false; 11-12 floating;
|
|
|
Features of the anatomical position |
Reference position; Face forward; Arms at side; Palms forward; Feet pointing forward; |
|
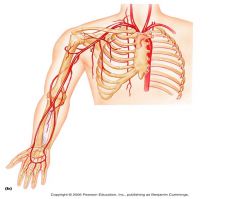
State the meaning of the following anatomical Position terms:
Subclavian; Axillary; Brachial; Radia;; Ulnar; |
Serving the neck and arm (used for blood vessels); Directly under joint where arm connects to shoulder (underarm); relating to the arm; relating to the radius; Relating to the ulna (elbow bone) |
|
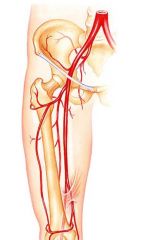
What is the meaning of the term "Profunda femoris"? |
Deep femoral artery |
|
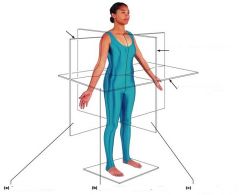
Name the following Planes and Sections |
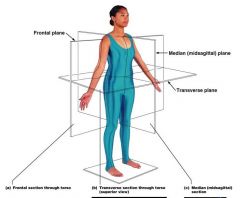
|
|
|
State the functions of:
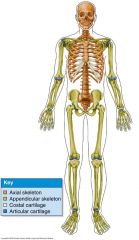
a) Axial skeleton b) Appendicular skeleton |
a) Support and protection b) Locomotion |
|
|
What are the two fundamental divisions of the skeleton? |
Axial, and Appendicular skeleton |
|
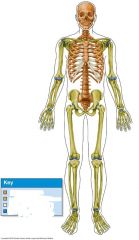
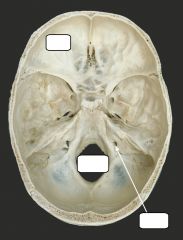
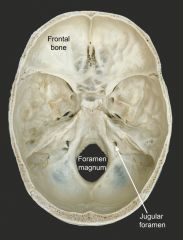
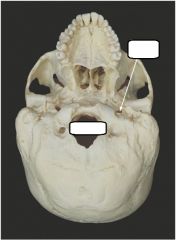
What is denoted by the colour scheme? |
|
|
|
What makes up the Axial skeleton? |
skull; ribs, sternum; vertebrae |
|
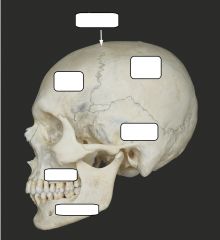
|

|
|
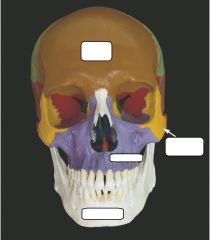
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
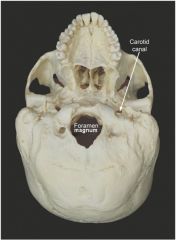
|
|
|
To which thoracic vertebrae is the second floating rib connected to? |
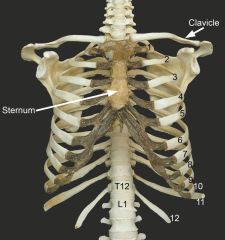
Second floating rib = rib 12, so Thoracic vertebrae 12
|
|
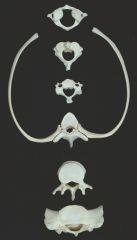
NB: |
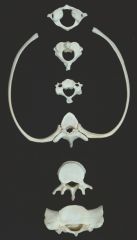
Atlas Axis Cervical vertebrae Thoracic vertebrae Lumbar vertebrae Sacral vertebrae |
|

|
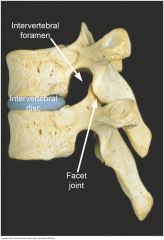
|
|

|
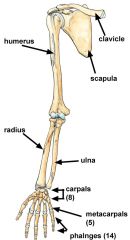
Carpals - wrists Metacarpals - hand phalanges - fingers |
|
|
What are the names given to the joints in the hand? |
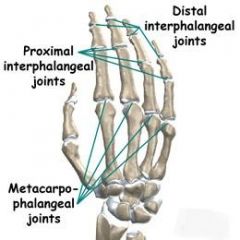
Radiocarpal joint - between radius and carpal
RadioUlnar joint - between radius and ulna |
|
|
What is the pelvic girdle made up of? |
Pelvis and sacrum (but sacrum part of axial skeleton) |
|
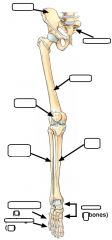
|
|
|
|
Joint classification, how?
Expand on your answer |
Structural classification (connecting tissue and presence/absence of synovial cavity)
Functional classification (amount of movement) |
|
|
Give the 3 structural classification of joints |
fibrous cartilaginous synovial |
|
|
Give the 3 functional classifications of joints |
synarthroses (immovable) amphiarthroses (partially m.) diarthroses (freely m.) |
|
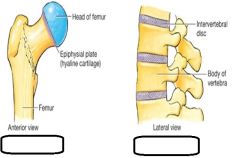
Type of joint? |
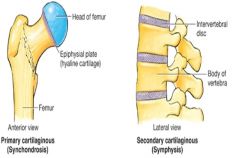
Synchondrosis and Symphysis are (Cartilaginous + amphiarthroses) |
|
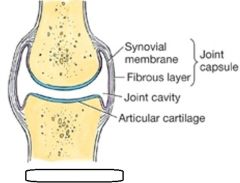
Type of joint? |
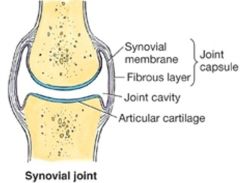
|
|
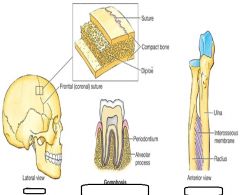
Type of joint? |
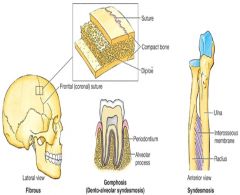
Syndesmosis are (fibrous and amphiarthroses) |
|
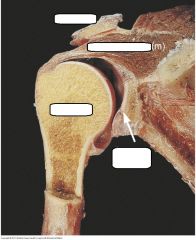
|
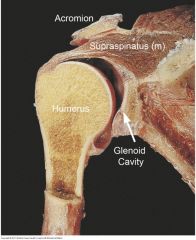
acromion of scapula (bone prominence at top of shoulder blade) |
|
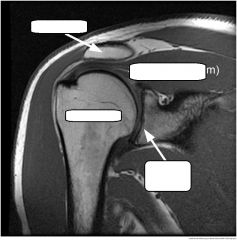
|
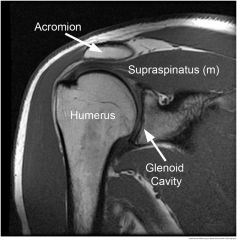
supraspinatus muscle abducts arm at shoulder. runs at superior part of the scapula |
|
|
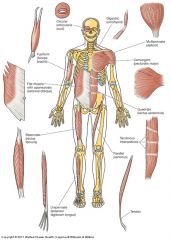
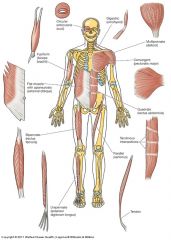
|
|
|
Characteristics of Muscles? |
Movement and posture role;
Direct attachment to bones, or indirectly via tendons and fascia (fibrous tissue layer);
Different arrangement of muscle fibres and overall muscle shapes |
|
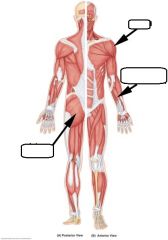
|
|
|
|
rule of thumb for remembering flexion and extension |
flexion always forward until the knees and below |
|
|
Example of possible range of movement from anatomical position? |
flexion, extension; Abduction, adduction; Lateral rotation, medial rotation; Circumduction; Supination, pronation (hands); Dorsiflexion, plantaflexion (feet); Eversion, inversion (feet); Protrusion, retrusion (jaw); Elevation, depression (shoulders); |

