![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cranial or superior |
Toward the head end of the body |
Head |
|
|
Rostral or nasal |
Toward the tip of the nose (head only) |
|
|
|
Caudal or inferior |
Toward the tail end of the body |
|
|
|
Dorsal or posterior |
1)Toward the back 2)front of forelimb and hindlimb from carpus and Tarsus distally |
|
|
|
Ventral or anterior |
Toward the belly |
|
|
|
Medial |
Toward the median plane |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the median plane |
|
|
|
Deep (internal) |
Toward the center (whole body or part) |
|
|
|
Superficial (external) |
Toward the surface (whole body or part) |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Toward the body (extremity) |
|
|
|
Distal |
Away from the body (extremity) |
|
|
|
Palmar |
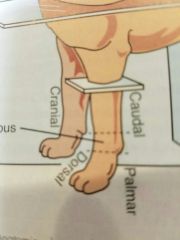
Back of forelimb from carpus distally |
|
|
|
Plantar |
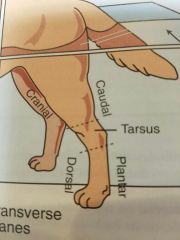
Back of hindlimb from Tarsus distally |
|
|
|
Barrel |
Trunk of the body- Formed by the rib cage and the abd |
|
|
|
Brisket |
Area at the base of the neck b/t the front legs that covers the cranial end of the sternum |
|
|
|
Cannon |
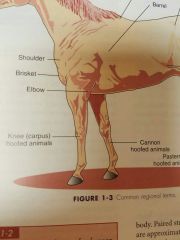
Large metacarpal or metatarsal bone or hoofed animals |
|
|
|
Fetlock |
Joint b/t cannon bone (large metacarpal/metatarsal) and the proximal phalanx of hoofed animals |
|
|
|
Flank |
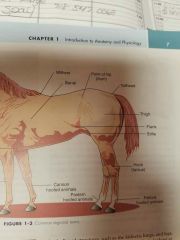
Lateral surface of the abd b/t the last rib and hind legs |
|
|
|
Hock |
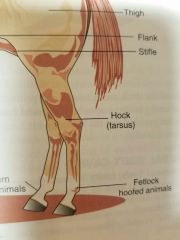
Tarsus |
|
|
|
Knee |
Carpus of hoofed animals |
|
|
|
Muzzle |
Rostral part of the face formed mainly by the maxillary and nasal bones |
|
|
|
Pastern |
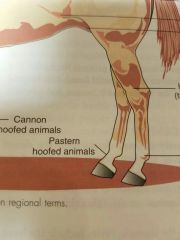
Area of proximal phalanx of hoofed animals |
|
|
|
Poll |
Top of the head b/t the bases of the ears |
|
|
|
Stifle |
Femorotibial/femoropatellar joint equivalent to human knee |
|
|
|
Tailhead |
Dorsal part of the base of the tail |
|
|
|
Withers |
Area dorsal to scapulas |
|
|
|
Bilateral symmetry |
The left and right halves are mirror images of each other |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Composed only of cells Covers and protects (surface) |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Composed of living cells and non-living intercellular substances Binds cells and structures together and supports the body |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Movements
Skeletal (voluntary) Cardiac (heart/involuntary) Smooth muscle (organs) (involuntary) |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Composed of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells Transmits information around body Coordinates and controls activities |
|
|
|
Adipose tissue |
Fat |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
Maintenance of a dynamic equilibrium in the body Dynamic- implies activity, energy, and work Equilibrium- refers to balance |
|
|
|
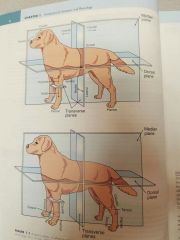
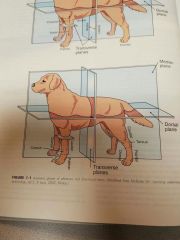
What are the four anatomic planes of reference? |
Sagittal plane Median plane Transverse plan Dorsal plane |
|
|
|
Anatomy |
The forms and structure of the body and it's parts (what things look like and where they are located) |
|
|
|
Physiology |
The functions of the body and it's parts (how th ok nasty work and what they do) |
|
|
|
Microscopic anatomy |
Microscopic anatomy deals with structures so small we are microscope to see them clearly |
Cells and tissue |
|
|
Macroscopic anatomy (gross anatomy) |
Deals with body parts large enough to be seen with the unaided eye |
Organ, muscle and bones |
|
|
Regional anatomy |
The study of an individual region of the body Ex. The neck region would include all the cells, tissues, blood vessels, nevers, muscle, organs, and the bones present in the neck |
|
|
|
Systemic anatomy |
The study of an individual system of the body Ex. Nervous system, Skeletal system as separate topics |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
Contains the brain and spinal cord The central nervous system |
|

