![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three major induction agents?
|

|
|
|
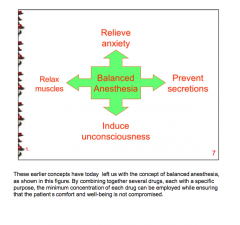
What are the four components of balanced anesthesia? |
|
|
|
True or false: All of the intravenous anesthetic agents are highly lipid soluble.
How does this affect injection ability?
What are two major side effects?
|

|
|
|
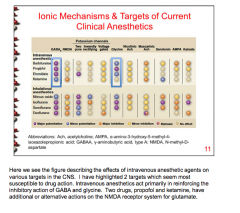
What two neurotransmitters seem most susceptible to drug action by intravenous agents? |
|
|
|
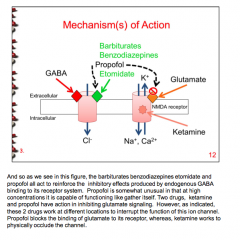
What are the mechanisms of action of barbiturates, benzodiazepines, propofol, and etomidate? |
|
|
|
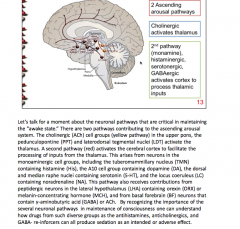
What are the two ascending arousal pathways? Draw them out. |
|
|
|
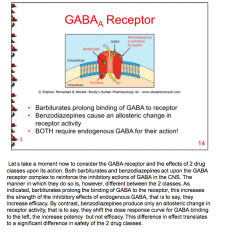
What drugs prolong binding of GABA to receptor? What drugs cause allosteric change in receptor activity? What do both require? |
|
|
|
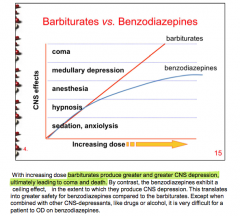
Why are benzodiazepines safer to use than barbiturates? |
|
|
|
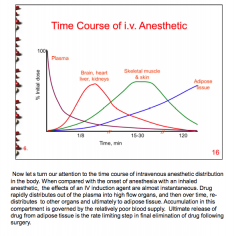
Which produces after onset (intravenous or inhaled anesthetic)? |
|
|
|
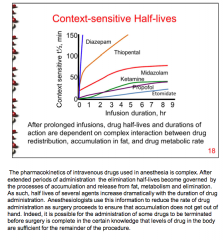
After prolonged infusions, what do drug half-lives and durations of action depend on? |
|
|
|
Draw the pathway of the CV response to IV anesthetics: |
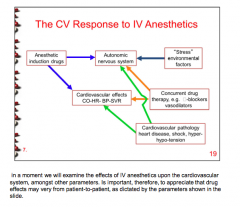
|
|
|
Which drug has an effect on CBF, CMRO2, ICP, MAP HR, and CO but no effect on RR and Ve?
Which drug affects only heart rate? |
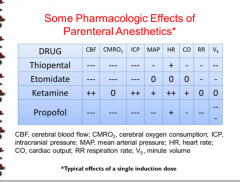
|
|
|
What important drug class is the quintessential CYP enzyme inducer? What can they exacerbate?
Which drug has antiemetic properties and can cause ______ infusion syndrome?
Which drug causes inhibition of steroidogenesis?
Which drug has an analgesic effect, keeps pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes, can be used as a bronchodilator, and causes hallucinations? |
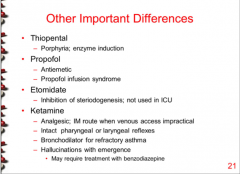
|
|

|

|
|

What is shown here? What is a problem in caring for these patients? |
Propofol infusion syndrome Diminished responsiveness to cario-active drug support |
|
|
When are benzodiazepines useful?
What is the specific antagonist?
Diazepam, lorazepam, and midazolam. Which has the longest (shortest) half-live? Which is rapidly inactivated, which has 3 active metabolites, and which is conjugated for elimination? |
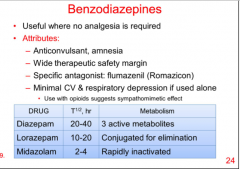
|
|
|
Draw midolazam effect on heart rate and myocardial contractility.
Use venodilation, cardiac output, venous return, portal bloodflow, blood mobilization from spleen and intestines in addition. |
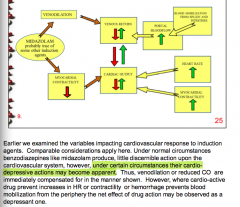
|
|
|
What are some adverse cardiovascular effects from opiate use in anesthesia? |
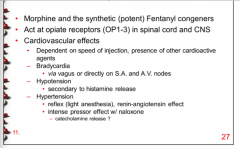
|
|
|
Can opiate use cause respiratory depression and loss of responsiveness to rising CO2?
What are the opiate antagonists? What are the effects of opiates on muscles, cranial bloodflow and pressure?
What overdose triad? |

|
|
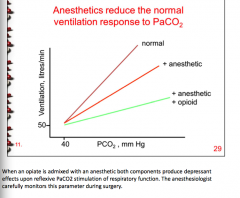
|
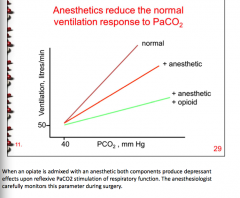
|
|
|
What is neurolept-analgesia/anesthesia?
What drugs are used in the combinations?
|
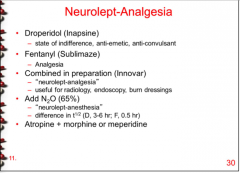
Pain relief and state of indifference Patient is responsive to command but is not compromised by situational anxiety.
|
|

What does this describe?
How must it be administered? |
Remifentanil = a new opioid class
Administer via IV |
|
|
What opioid is ideal for long-lasting analgesia? What is the 20 minute drug for a 20 minute procedure?
Differences in adverse effects between the two? |

|
|

What is this the clinical diagnosis of? What drug causes it? |

Malignant hyperthermia: Succinylcholine |
|
|
What are triggers of malignant hyperthermia? Which drugs are considered safe to use?
What is the treatment? |

|

