![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 levels that found the matrix of IPE? |
Global. International. State/social Individual
|
|
|
What are the 4 structures that found the matrix of IPE? |
Production/trade Money/finance Knoweldge/Technology Security |
|
|
What are the 3 dominant paradigms in IPE? |
Economic (competitive liberalism/neoliberalism) Mercantilism Structuralism |
|
|
Within the 3 dominant paradigms in IPE, what component is the drier, and what is the driven?
(neoliberalism, mercantilism, structuralism) |
In neoliberalism, markets/econ drives politics. In mercantilism, politics drives markets. In structuralism, economics drives politics. |
|
|
How is a collective/social pressure/force defined, and an example of such? |
a.) If an individual is forced to act in a way he would not normally choose or b.) if the general action is in line with choice but traits/features are not in line with interests/preferences.
Examples: A.) Military service yes or no B.) military service yes, but fewer/longer months |
|
|
The mechanisms of the market theoretically and to a large extent practically contribute measures that help to (1) eliminate private force over the weak (as propagated by Hobbes) (2) and, more or less. escape the collective pressure by the state. However, if the market fails, what are the 3 options, that an individual can apply to show her/his dislike? |
1. Exit the collective/in-group 2. Voice (protest/opposition) 3. Exit and voice
Be able to discuss each options transaction costs. |
|
|
Which (3) conditions apply to the application of the polluter-pays-principle? |
(1) Negative externalities exist (2) These negative externalities must interfere with the property rights of the harmed third party. (3) If the owner of an asset is using it according to his property rights and harming a third party, then the harmed third party has to induce a change in the behavior to the owner through compensation |
|
|
Which parties/players are involved in the political decision making process? |
(1) voter-consumer/taxpayers (2) politicians (3) civil servant/bureaucrats |
|
|
Which issues inflict on the economic efficiency of the government thus harm the public interest? |
1. The power of special interests 2. The shortsightedness effect 3. Rent seeking costs 4. Lack of signals and incentives to promote operational efficiency |
|
|
Explain the issues inflicting on the economic efficiency of the government for The power of special interest |
an issue that generates substantial personal benefits for a small number of constituents while imposing a small individual cost on a large number of other voters. |
|
|
Explain the issues inflicting on the economic efficiency of the government for The shortsightedness effect |
Issues that yield clearly defined current benefits at the expense of future costs that are difficult-to-identify |
|
|
Explain the issues inflicting on the economic efficiency of the government for Rent seeking costs |
Actions by individuals and interest groups designed to restructure public policy in a manner that will either directly or indirectly redistribute more income (rents) to themselves. |
|
|
Explain the issues inflicting on the economic efficiency of the government for Lack of signals and incentives to promote operational efficiency |
Absence of the profit motive reduces the incentive of producers to keep costs low. |
|
|
What are the differing concerns of neoclassical economics and IPE? |
Neoclassical economics is primarily concerned with efficiency and the mutual absolute benefits of economic exchange IPE is particularly interested in the distribution of benefits from market activities. |
|
|
Why do state-centric scholars of IPE argue that it is difficult to attain international (economic) cooperation? |
Because state-centric scholars of IPE give more importance to the relative benefits/gains: this implies that economic actors are attentive not only to absolute gains but also to the size of their own gain relative to benefits/gains of other actors. |
|
|
Why do we say there is a clash between the logic of the market and the logic of the state? (Two reasons). |
logic of the market is to locate economic activities wherever they will be most efficient and profitable
logic of the state is to capture and control the process of economic growth and capital accumulation in order to increase the power and economic welfare of the nation |
|
|
What is the hypothesized impact of participating in the international economy? |
That the international economy has a positive impact on international political affairs, because it moderates the self-centered behavior of states. |
|
|
Which 2 preconditions ought to exist to the creation of effective international regimes and solutions to the compliance problem ? |
(1) A strong international leadership (hegemon) (2) An effective international governance structure |
|
|
According to Olson (1995), why would we need a hegemon? |
It is difficult for a country to reduce trade barriers unilaterally in the absence of external pressures exerted by a powerful state. The world works better when there is a hegemon that finds its own self interest in seeing that various international collective goods are provided. |
|
|
Give a simple definition for an institution, remember North. |
System of generally accepted formal rules and informal rules, which are governing the human behavior and which are structuring incentives in view of a common objective. |
|
|
Which 3 components does Ostrom distinguish with regard to defining an institution? |
(1) rule component, which is generally known (2) Information component, which reduces strategic insecurity (3) enforcement respectively sanction component |
|
|
If having a choice between different institutions dealing with transferring assets, which institution should be the preferred and why? |
The preferred is the institution that (1) minimizes transaction costs and (2) delineates property rights (PRs) in the most specific and predictable way.
This is because the institution with the lowest transaction costs is the most efficient one with regard to welfare maximization and when property rights are well defined then transaction costs with regard to allocating assets are low, which again serves efficiency. |
|
|
Three important aspects of property rights theory are (1) transferability (2) exclusiveness (3) universality.
How can you define universality? |
Universality implies that each and every asset/resource ought to be the property of at least one (natural or legal) body. |
|
|
From the important aspect of property right theory known as universality, how can we learn from the prisoner game dilemma? |
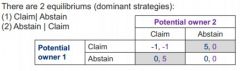
|
|
|
Give examples of insecure property rights on assets/resources. (5) |
• Fewer investments in productivity maintaining activities • Fewer inputs in productivity increasing activities • Thereby a reduced value of the asset/resource • Missing access to credit markets because insecure asset/resource can not be used as collateral • Reduced capacity to carry risks |
|
|
What are the main points of the Coase Theorem? (6) |
1. Property rights are necessary 2. the first distribution of property rights is not relevant for efficient allocation. 3. property rights are sufficiently specified and complete information is given 4. the affected parties can freely transfer their rights. 5. market participants can solve external effects that are arising from the property rights distribution. 6. The state does not have to intervene. |
|
|
What was Hardin’s (1968) recommendation to overcome the issue that he coined as the “tragedy of the commons”? |
1. Nationalization of property rights - state installs rules on how to use assets/resources
2. Privatization of property rights, including universality, transferability and exclusiveness |
|
|
Mention the most important principles of early-modern mercantilism (3) |
• Economic policies of the state in the national economy, with an interventionist notion, especially in foreign trade
• Duty of the state is to enhance and maintain both national wealth and national power
• Applies protectionist policies to protect, promote domestic manufacturing industries, particularly with regard to exporting these goods |
|
|
Give a ‘neutral’ brief definition of capitalism. |
Capitalism describes an economic system in which the means of production are privately owned and operated for profit. |
|
|
If we add the term ‘laissez faire’ to capitalism, what does it imply? (3) |
• Gov. should interfere minimally with the free and efficient workings of the market
• Gov. has a responsibility to create the proper environment for free economic exchange
• Protect private property rights & enforce contracts |
|
|
Which factors contributed to the success of the UK under the reign of Queen Victoria (19th century) as economic ‘workshop of the world’?. (4) |
Several parallel factors contributed to the success story: 1. The Victorian period is also called ‘age of individualism’, indicating that particularly the better-off shifted away from the tutelage of the church (and thus the Queen) and concentrated on bettering their own economic situation. 2. A primary approach to improve the economic situation was to replace labor with machines (take-off industrialization) to shift the profit border outwards. 3. The economic philosophy of ‘laissez-faire’ also falls into this period. 4. In order not to bring up the population against the Church (= Queen), the Queen let the entrepreneurs engage in the structural change starting the industrialization era. |
|
|
Is an efficient allocation of resources necessarily an equitable (fair) allocation of resources? |
Only achieved if income is distributed in an equitable manner – which case in markets thriving for efficiency.
As a side note, distributive justice is associated with structuralism – with all its flaws. |
|
|
What are the main modern (recent) structuralist theories and what are their main ideas? |
Dependency Theory
Modern world system (MWS) theory
Neo-imperialism
|
|
|
Describe the main points (4) of dependency theory |
1. there are core and peripheral countries. 2. Domestic elites in the peripheral countries ally with international capitalists. 3. As a result, instead of protecting their country and seeking independence, periphery leaders allow the economic exploitation by international capitalists in core countries to continue. 4. This (3) is often referred to as economic neocolonialism |
|
|
Describe the main points of (MWS) modern world system theory (3) |
1. Structurally 3 functional areas: capitalist core states, agricultural periphery, and semi-periphery with labor intensive economic structures. 2. International division of labor makes nation-states mutually dependent on economic exchange. 3. The core states dominate the other states through unequal exchange for the purpose of extracting cheap raw materials and not just for dumping surplus production. |
|
|
What makes FDI (foreign direct investments) attractive? (2) |
1. Locational advantages - specific country charecterisitics that provide opportunity to provide such as natural resources
2. Market imperfections - Horizontal or vertical integration |
|
|
Name 3 positive impacts of FDI to host countries. |
1. FDI can transfer savings from one country to another.
2. MNCs can bring technology and managerial expertise
3. MNCs can enable host-country producers to gain access to marketing |
|
|
Name 3 negative impacts of FDI to host countries. |
1. MNC make decisions about how resources will be used in the host country
2. MNC may reduce, rather than increase, the amount of funds available for investment
3. MNC might also drive established host-country firms out of business |
|
|
Name 3 MNC/FDI regulations by host countries |
1. Blocking FDIs in some sectors of the economy
2. Requiring that the majority of the domestic affiliate is owned by local shareholders
3. Requiring that domestic affiliate to purchase a certain percentage of its inputs from domestic suppliers |
|
|
Explain in your own words the principal-agent framework from institutional economics, which Humphreys et al. 2007 |
....? |
|
|
What are common aspects characterizing governance of a state? (4) |
Governance …
1. refers to the exercise of political power (procedures & policies) to manage a nation’s affairs 2. also includes procedures that regulate the actions of non-governmental and private-sector players 3. also includes political processes at supranational level and relevant regional organizations 4. can only be understood in the light of the specific historical, cultural, social and economic context |

