![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Intelligence test |
A method for assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others |
Uses numerical scores |
|
|
Mental Age |
A measure of intelligence test performance |
Devised by Binet |
|
|
Standford-Binet |
The widely used American version of Binet's orginal intelligence test. |
|
|
|
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) |
Ratio of mental age to chronological age multiplied by 100 |
=ma/ca x 100 |
|
|
Intelligence |
Ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations |
Mental quality |
|
|
Factor Analysis |
Statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test |
Used to identify different demensions of performance that underlie one's total score |
|
|
General Intelligence |
A general intelligence factor |
|
|
|
Savant Syndrome |
Condition in which a person otherwise Limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill |
Has a special skill like to drawing |
|
|
Emotional Intelligence |
The ability to perceive, express, understand, and regulate emotions |
Critical part of social intelligence |
|
|
Creativity |
The ability to reduce the novel in valuable ideas |
Celeste |
|
|
Aptitude Test |
A test designed to predict a person's future performance |
Everyone takes this test in Divergent |
|
|
Achievement Test |
A test designed to assess what a person has learned. |
Reflects |
|
|
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) |
Most widely used intelligence test |
Contains verbal and performance subtests |
|
|
Standardization |
Defining meaningful scores by comparison |
|
|
|
Normal curve |
Most scores fall near the average and fewer scores lie near the extremes |
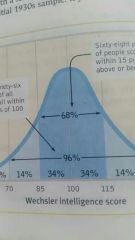
Bell-shaped curve |
|
|
Reliability |
Test yields consistent results |
|
|
|
Validity |
The extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to |
|
|
|
Content Validity |
Extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of Interest |
Driving test that samples driving tasks |
|
|
Criterion |
The behavior that a test is designed to predict |
Use in defining whether the test has predictive validity |
|
|
Predictive Validity |
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict |
Criterion-related validity |
|
|
Mental Retardation |
Condition of limited mental ability indicated by an intelligence score below 70 and difficult and adapting to the demands of life |
|
|
|
Down Syndrome |
A condition of retardation and associated physical disorder is caused by an extra chromosome in one's genetic makeup |
|
|
|
Stereotype threat |
A self confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype |
|

