![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do treatments differ in patients whose goal is to cure the cancer versus those whose goal is to improve QOL?
|
The willingness to put up with side effects of treatment.
|
|
|
What two scales guide cancer treatment in terms of how aggressive to be?
|
"ECOG Performance scale (0 - 4) - 4 being the worst
Karnofsky scale (0-100) - 0 being the worst " |
|
|
What are the different levels of the ECOG scale?
|

|
|
|
What is the common system that grades chemotherapy side effects?
|
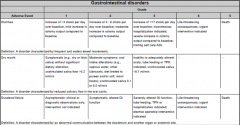
"NCI CTC version 4.0 - National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria
Grade 4 is life threatening." |
|
|
What is myelosupression? When can it occur after chemotherapy treatment? What cells are affected in the short term and long term?
|
"Bone marrow toxicity occurring 7-10 days after chemo.
Decreased platelets - leads to bleeding Decreased WBCs - leading to febrile neutropenia Long term - leukaemia" |
|
|
What are some GI side effects of cancer treatment? Why do these happen?
|
"Oral mucositis
Esophagitis Nausea/vomiting Anorexia/weight loss Diarrhea/urgency/bowel incontinence This occurs because the GI cells are rapidly dividing and get targeted by chemo." |
|
|
What lung, heart and CNS toxicities can occur due to cancer treatment?
|
"Lung - interstitial pneumonitis
Heart - Decreased ejection fraction, MI CNS - peripheral neuropathy, seizures" |
|
|
What kinds of hormonal toxicities can occur due to cancer treatment? (give 3 each for men and women)
|
"Women - estrogen deprivation
Hot flushes, sweats, amenorrhea, osteoporosis, infirtility Men - testosterone deprivation Hot flushes, ED, decreased libido, gynecomastia, infertility" |
|
|
How should you manage nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy treatment?
|
"Prophylactic anti-emetic drugs!
What are the three classes?" |
|
|
What are some other anti-emetic drugs used in other areas of medicine outside of chemotherapy treatment?
|
"1) H-1 Antagonists (antihistamines) - Gravol
2) Dopamine Receptor Antagonists - haloperidol 3) Multiple Neuro‐receptor Antagonist - olanzapine, cannabinoids 4) Adjuctives - benzos, ginger" |
|
|
What are the two patterns of bone metastases?
|
"1) Lytic (myeloma, breast cancer)
2) Blastic (prostate cancer)" |
|
|
Bone pain at night is suspect for what?
|
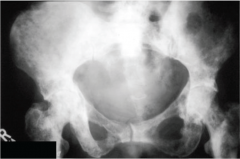
"Red flag for bone mets.
What are good modalities for evaluating bone mets? Pictured: Blastic bone disease (sclerotic)" |
|
|
How are bone mets treated?
|
"Orthopedic intervention (surgery)
Radiation Pain management Bone protectants (bisphosphonates)" |
|
|
Describe two types of bone resorption inhibitors.
|
"1) Bisphosphonates - inhibit osteoclastic bone resorption
2) RANK ligand inhibitors - monoclonal antibody to a protein that acts as a signal for bone resorption" |
|
|
What are four cancer-related oncologic emergencies?
|
"1) Hypercalcemia
2) Spinal cord compression 3) Superior vena cava obstruction 4) Bleeding" |
|
|
What are 5 treatment induced oncologic emergencies?
|
"1) Infusion reactions (during chemo)
2) Febrile neutropenia 3) Bleeding 4) Diarrhea 5) Radiation pneumonitis" |

