![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the major characteristics of the phylum arthropoda? |
exoskeleton, jointed appendages, bilaterally symmetrical, open circulatory systems, complete digestive tracts, protosomes |
|
|
What are the major characteristics of the class insecta? |
3 sections - head, thorax, abdomen 6 legs- one per thorax section 1 pair antennae wings |
|
|
Insects are the most succesful terrestrial animals. What are the key features of insects that have contributed to their success? |
1. getting on land first -> little competition 2. wings -> flight, easier and faster to disperse 3. small -> able to occupy more niches 4. versatile body plan -> able to occupy more niches 5. very fast, prolific reproduction -> adapt & evolve rapidly |
|
|
How does the cuticle tackle the problem of dessication? |
the waxy coating helps keep water in so the insect doesn't dry out |
|
|
What system does an insect use for gas exchange? what are the openings to this system called? |
tracheal system. the openings are called spiracles |
|
|
What are the 2 main layers of the cuticle? what is the difference between them? |
endocuticle-reabsorbed prior to moulting exocuticle - sceleterised (hard & rigid) shed during moulting |
|
|
How does the structure of the cuticle contribute to its strength without becoming too heavy? |
the chiten is layered in different directions to give it strength in all directions |
|
|
What are the 2 major modes of locomotion used by most adult insects? |
walking & flying |
|
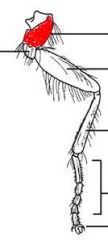
name the highlighted section |
coxa |
|
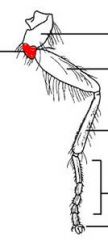
name the highlighted segment |
trochanter |
|
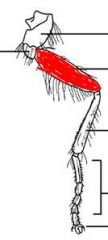
name the highlighted section |
femur |
|
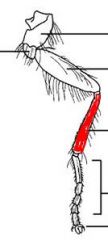
name the highlighted section |
tibia |
|
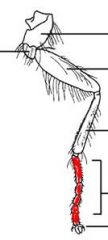
name the highlighted section |
tarsal segments |
|
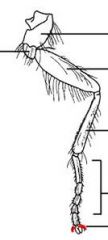
name the highlighted section |
pretarsus |
|
|
What other functions can a leg play besides walking? |
running, jumping, swimming, digging, protection, grasping, pollen basket (bees) |
|
|
What are some orders that are very accomplished fliers? |
diptera, lepidoptera, hymenoptera, coleoptera, ephemeroptera, odonata, orthoptera, hemiptera |
|
|
some primitive insects have no wings and their ancestors never had wings, name some apterous insects |
collembola, protura, diplura, thysanura |
|
|
some insects don't use both sets of wings for flight, give some examples |
coleoptera - forewings are a protective shell diptera- hind wings are halteres |
|
|
What is an ocellus and how does its structure differe from a compound eye? |
ocelli are sensory organs that sense circadium rythems and do not produce full images |
|
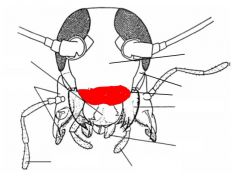
name the highlighted area |
cyplus |
|
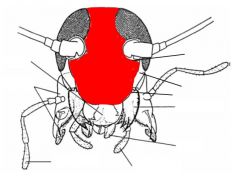
name the highlighted area |
frons |
|
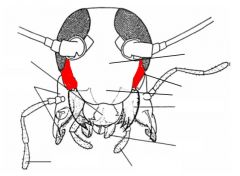
name the highlighted area |
gena |
|
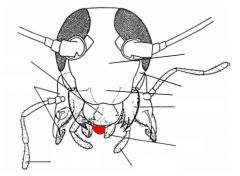
name the highlighted area |
hypopharynx |
|
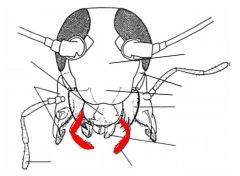
name the highlighted area |
labial palps |
|
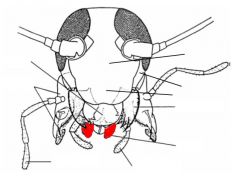
name the highlighted area |
labium |
|
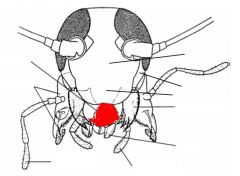
name the highlighted area |
name the highlighted area |
|
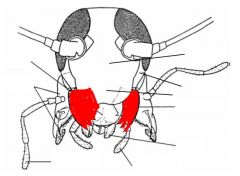
name the highlighted area |
mandibles |
|
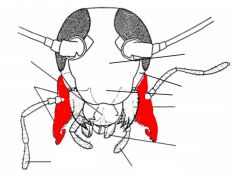
name the highlighted area |
maxillae |
|
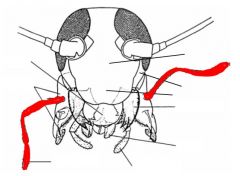
name the highlighted area |
maxillary palps |
|
|
How do insects exchange gasses via their tracheal system? |
diffusion |
|
|
How does an insects tracheal system and method of exchanging gasses limit their size? |
diffusion is slow, so the longer the trachea are, the less effective diffusion is. Therefore the insect needs to remain small to effectively exchange gasses. |
|
|
How do some larger insects improve the efficiency of gas exchange? |
They actively pump air through their tracheal system, so more air can make it to the end of the trachea |
|
|
What is the function of the rings of chitin around the trachea |
they prevent the trachea from collapsing |
|
|
what function does the fat body play? |
storing energy reserves |
|
|
What is the function of the salivary glands and salivary bladder? |
release saliva to start digestion outside the body |
|
|
what is the function of the esophagus? |
transport the food to the crop |
|
|
what is the function of the crop? |
food storage |
|
|
what is the function of the proventriculus? |
grinding of food |
|
|
what is the function of the gastric caecae? |
increase surface area for secretion and absorption |
|
|
what is the function of the midgut? |
digestion and absorption |
|
|
waht is the function of the malphigian tubules? |
responsible for getting rid of nitrogenous wastes |
|
|
what is the function of the rectum? |
water and salt re-absorption |
|

name the highlighted area |
anus |
|

name the highlighted area |
crop |
|

name the highlighted area |
esophagus |
|
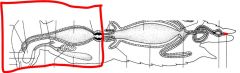
name the highlighted area |
foregut |
|
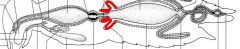
name the highlighted area |
gastric caecae |
|
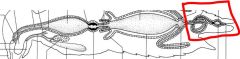
name the highlighted area |
hindgut |
|

name the highlighted area |
intestine |
|

name the highlighted area |
malphigian tubules |
|
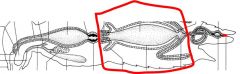
name the highlighted area |
midgut |
|
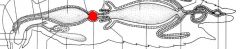
name the highlighted area |
proventriculous |
|

name the highlighted area |
rectum |
|

name the highlighted area |
salivary duct and salivary glands |
|
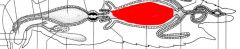
name the highlighted area |
ventriculous |
|
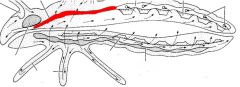
name the highlighted area |
dorsal vessel - aorta |
|
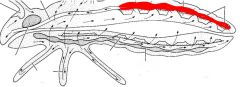
name the highlighted area |
dorsal vessel - heart |
|
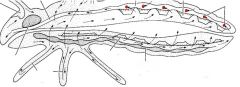
name the highlighted area |
ostia |
|
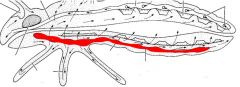
name the highlighted area |
ventral nerve chord |
|
|
Why do some insects not have a dentricle? |
If they have a liquid diet their food does not need to be ground up so their is no need for the dentricle |
|
|
Describe an insects nervous system |
numerous ganglia line the ventral nerve chord, 3 are fused to make the brain, the more advanced an insect is the fewer ganglia it has and the more fusion there is |
|
|
Open circulatory system |
there are no capilaries, "blood" fills the free space in the insect |
|
|
haemoceol |
cavity that is filled with haemolymph |
|
|
haemolymph |
insect blood, does NOT transport gasses |
|
|
what are the functions of an insects circulatory system? |
transport (not of gasses), pressure, defense and support |
|
|
Air sac |
sacs connected to the tracheal system that are full of air to provide extra energy for flight as well as "space to grow" in larva & nymphs |
|
|
Antennae |
appendages on the head that smell and taste |
|
|
apodeme |
piece of cuticle that serves as a muscle attachment |
|
|
chitin |
protein that makes up the cuticle |
|
|
cibarium |
space anterior to the true mouth cavity |
|
|
cuticle |
the exoskeleton of an insect |
|
|
dermal gland |
glands that excrete a waxy coating to the surface of the cuticle |
|
|
epicuticle |
top waxy gland of the cuticle |
|
|
filter chamber |
where the gut is looped in the insect to get rid of excess fluid in insects with a liquid diet |
|
|
frass |
liquid and solid waste from an insect |
|
|
gill |
found on spiracles in aquatic insects |
|
|
notum |
dorsal portion of an insects thoracic segment |
|
|
ovipositor |
where the female lays her eggs from |
|
|
peritrophic membrane |
covers the ventriculous, allows nutrients and waste to pass through |
|
|
prognathous |
The long axis of the head is horizontal and in line with the long axis of the insects body. The mouthparts are directed forwards |
|
|
resilin |
elastomeric protein found in many insects and arthropods |
|
|
proboscis |
lock mouth parts on insects (ex. butterflies), adapted from mandibles |
|
|
stemmata |
simple eyes found on larva |
|
|
taenida |
rings of chitin surrounding the trachea |
|
|
tagmosis |
the specialized grouping of segments (ex. head, thorax, abdomen) |
|
|
sclerite |
the hard part of the exoskeleton |

