![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
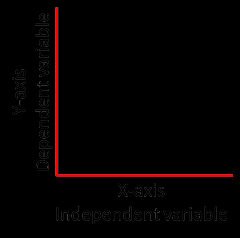
Independent variable |
a variable (often denoted by x ) whose variation does not depend on that of another |
A |
|
|
Dependent variable |
a variable (often denoted by y ) whose value depends on that of another.
|

|
|
|
Controlled variable |
the one element that is not changed throughout an experiment, because its unchanging state allows the relationship between the other variables being tested to be better understood.
|

|
|
|
Hypothesis |
a proposition made as a basis for reasoning, without any assumption of its truth. |

|
|
|
Data |
facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis |

|
|
|
Conclusion |
the end or finish of an event or process |

|
|
|
Qualitative observation |
The opposite is a quantitative observation, such as the weight or length of an object |
|
|
|
Quantitative observation |
Uses five senses |
|
|
|
Inference |
An estimated guess |
|
|
|
Valid |
f an argument or point) having a sound basis in logic or fact; reasonable or cogent
|

|
|
|
Trial |
A run through |

|
|
|
Line graph |
compare two variables. Each variable is plotted along an axis . A line graph has a vertical axis and a horizontal axis. So, for example, if you wanted to graph the height of a ball after you have thrown it, you could put time along the horizontal, or x-axis, and height along the vertical, or y-axis. |
|
|
|
Bar graph |
a diagram in which the numerical values of variables are represented by the height or length of lines or rectangles of equal width. |
|
|
|
Pie chart |
a type of graph in which a circle is divided into sectors that each represent a proportion of the whole. |
|
|
|
Data table |
Adding Columns to a DataTable. Describes how to define the columns of a table using DataColumn objects. Creating Expression Columns. Explains how the Expression property of a column can be used to calculate values based on the values from other columns in the row. |
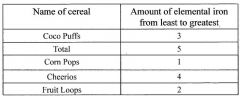
|
|
|
Convex lenses |
A convex lens is a converging lens. When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens the refracted rays converge at one point called the principal focus. The distance between the principal focus and the centre of the lens is called the focal length.
|
|
|
|
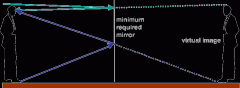
Plane mirror |
A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat (planar) reflective surface. For light rays striking a plane mirror, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal (an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface). |
|
|
|
Color filter |
a photographic filter that absorbs light of certain colors.
|

|
|
|
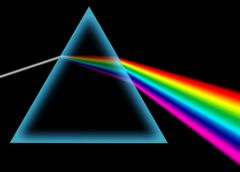
Prism |
A prism that refracts light |
|
|
|
Slinky spring |
Slinky is a toy; a precompressed helical spring invented by Richard James in the early 1940s.
|

|

