![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the five types of chemical substances?
|
1. atomic
2. molecular 3. covalent lattice 4. ionic 5. metallic |
|
|
What did Niels Bohr assumed to explain the Rydberg equation?
|
His assumption is based on the understanding that electrons can only have discrete energies because only certain wavelength of light are absorbed.
|
|
|
What was the problem with Niels Bohr's assumption?
|
He assumed that electronics have a particle like characteristic rather than wave-like.
|
|
|
Why must polar coordinates be used?
|
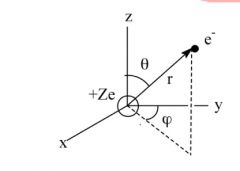
It's used because the system chosen must be consistant with the symmetry of an atom. It needs spherical symmetry.
r=distance from the nucleus Y=is the angle of the projection from the y-axis |
|
|
What does the Schrodinger's Equation explain?
|
It relates the total energy of the electron to the wavefunction for the electron
|
|

What are some boundary conditions for the Schrodinger's Equation?
|

|
|
|
What determines the energy level of electrons?
|
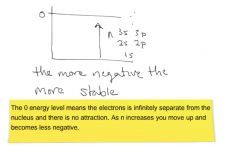
Only n
6g vs 7p 7p is higher energy b/c 7>6 even though g has more electrons that p |
|
|
What does ψ stand for in the Schrodinger's equation?
|
The value of ψ has not direct physical significance. It is a measure of the amplitude of the wavefunction at that particular point in space and may have a positive or negative sign.
|
|
|
What does ψ^2 stand for in the Schrodinger's equation?
|
The value of ψ^2 is related to the probability of finding the electron at a particular point in space.
|
|
|
How can one determine the number of lobes?
|

Remember that n>l if l>n then there is no lobes.
ex. 4h n=4 l=5 (0,1,2,3,4,5:::s,p,d,f.g.h) there will be no lobes b/c n<l Some d and higher orbitals, such as dz2 may have fewer nodes because they are combinations of two orbitals |
|
|
How can one determine the number of nodes?
|

Some d and higher orbitals, such as dz2 may have fewer nodes because they are combinations of two orbitals
|

