![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 classifications of cardiomyopathies
|
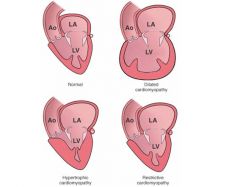
hypertrophic
alcohol-related idiopathic dilated restrictive |
|
|
some inherited multi-system diseases with cardiac involvement
|
Marfan's
myotonic dystrophy Muscular dystrophy Ehlers-Danlos Loeys-Dietz |
|
|
define cardiomyopathies
what do they predipose to |
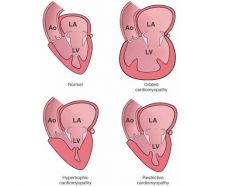
chronic disease, usually inherited, of myocardium--> enlarges, thickens, stiffens, weakens
--> arrhythmias & HF |
|
|
commonest type of cardiomyopathy
|
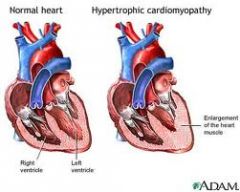
hypertrophic
|
|
|
cardiomyopathies can develop 2° to what
|
ischaemia
valve abnormalities HTN inflam systemis---metabolic---drugs---alcohol |
|
|
S&Ss cardiomyopathies
|
SYMPS: faitgue---dyspnoea---po oedema---palpitations/ arrhythmia----syncope.
SIGNS: ↑HR jerky pulse, ↓BP, ↑JVP, displaced apex |
|
|
IXs for cardiomyopathies
|
ECG, CXR, Echo, cardiac catheterisation
?iron studies, genetic testing, TFTs, Holter monitoring |
|
|
how does dilated cardiomyopathy usually present on CXR
ECG feature |
CXR- cardiomegaly, po oedema
ECG- LBBB |
|
|
pathological effects of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
obstruct LV outflow= ↓EF
↓coronary perfusion MR rhythm disturbances stiff/ relaxes poorly = S4 |
|
|
heart sounds heard in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
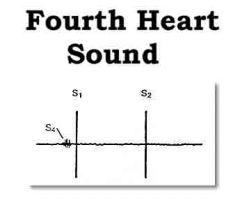
S4 - stiff, non-compliant ventricle, late filling
|
|
|
arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies - where do arrhythmias usually originate
|
LV/RV (sometimes atria)
|
|
|
arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy ECG findings- & what specific feature
|
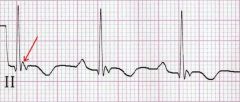
T wave inversion
QRS>1s EPSILON waves - long & low afterpotentials |
|
|
what type of cardiomyopathy are EPSILON waves found in the ECG
|
arrythmogenic
|
|
|
what's restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
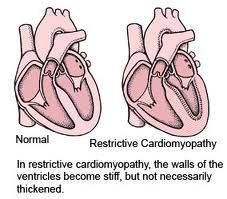
walls become stiff (not necessarily thickened)
resist filling = ↓EDV normal EF |
|
|
which 3 cardiomyopathies show an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance
|
Hypertrophic
dilated arrhythmogenic |
|
|
pharmacological treatment of cardiomyopathies include? (6)
|
ACEIs---Diuretics----BBs---rate-limiting CCBs
anticoagulants anti-arrhythmics |
|
|
separate management for arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies
|
rate-control
RFCA for VT ICD for high risk pt's |
|
|
4 important complications of cardiomyopathies
|
long QT syndrome
Primary electrical diseases Brugada syndrome SCD (sudden cardiac death) |
|
|
what's long QT syndrome
triggers onset age |
congenital
syncope, seizures, SCD, asymp prone to VT, torsades de pointes triggers: high adrenergic tone, sudden auditory stimuli, swimming, sleep age: teens! |
|
|
treatment for inherited long QT syndrome/ complication of cardiomyopathies
|
low risk- lifestyle & BB's
high risk- lifestyle + ICS + BBs |
|
|
what's brugada syndrome (complication of cardiomyopathies)
who does if effect |
cardiac Ca channel mutation
risk VT/VF, AF can present with long QT young men |
|
|
treatment for brugada syndrome (complication of cardiomyopathies)
|
symptomatic/ FH- ICD
|

