![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Information system (IS) Definition |
An information system is a group of components that interact to produce information. The components can be described in a five-component framework, consisting of hardware, software, data, procedures and people. |
|
|
|
Enterprise System (ES) Definition |
ESs represent a specific category of information systems, they build on pre-packaged industry best practices, embedded in standardised product software and target large scale integration of data and business processes across all company functional areas and beyond company borderlines. |
|
|
|
Types of ESs |
1) Information-centric - business intelegence 2)Process-centric - supply chain management - entetprise resource planning - customer relationship management 3)People-centric - groupware - portals |
3 |
|
|
Types of ISs |
1) Business-to-customer (B2C) - Direct engagement with customers/consumers 2) Business-to-business (B2B) - Enabling business networks 3) Enterprise Systems (ES) - Focusing on company internal processes |
3 |
|
|
Role of integration in IS |
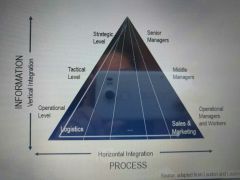
|
|
|
|
Three Tier Architecture |

1) User Interface Tier - provides different ways to access information - receives input & displays output - can access functions from the application tier, but not the database tier
2) Application Tier - contains all algorithms for manipulation of objects, e. g. analysis and processing of data - processes the logic & makes calculations - can access functions from the database tier to store data Database Tier - handles all tasks about data storage and access - stores and manages data - can only be accessed from the application tier
|
|
|
|
Hardware (definition) |
Hardware includes all physical components of an application system. This includes computer as well as networking technology |
|
|
|
Networking technology (definition ) |
Networking technology covers all components required to establish computer networks |
|
|
|
IPO+S Model |
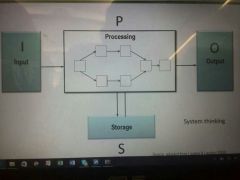
|
|
|
|
Von Neumann Architecture + Key elements |
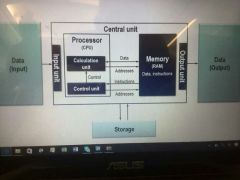
Key elements:
> Processor (central processing unit, CPU) - control unit - calculation unit
> Memory (RAM) - each memory cell is serially numbered (adress) - volatile storage - only maintains data when powered |
|
|
|
Software (definition) |
Software consists of clearly defined instructions that upon execution, instructs hardware to perform the tasks for which it is designed |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Software |
- intangible - no wear out - aging trough alternative innovations - no physical restrictions for changes - easy to replicate |
|
|
|
Classification of Software by function |
System software - controls and manages access to the hardware Application software - must work trough the system software - end-users primarily use application software |
|
|
|
Network (definition) |
A network is a linkage of different devices, which enables a communication between these devices |
|
|
|
Simple computer network |
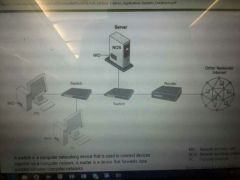
|
|
|
|
Client-Server Architecture simple |
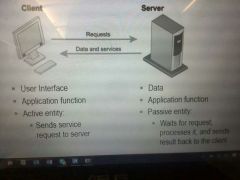
|
|
|
|
Client-Server Architecture (cont.) |
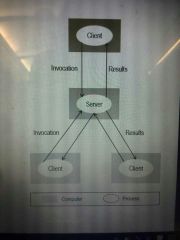
See hint |
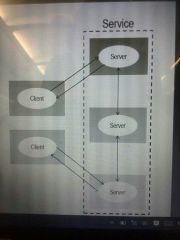
|
|
|
Types of computer networks |
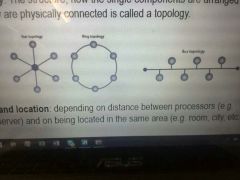
Differ in size & topology
topology: |
|
|
|
Packet Switching |
Packet switching is a method of slicing digital messages into parcels (packets) along different communication paths as they become available, and then resembling the packets at their destination |
|
|
|
Weakness of the spreadsheet approach |
- no search for multiple sets possible - difficult to create reports from different files and share data sets - each user has the same view - single person access - easy to delate, overwrite, move data - minutes possibility to control, access data - difficult to integrate data stored in different seets and files - formulas are embedded in seets - data redundancies (same data stored in different files) - limited numbwr of rows and colums |
|
|
|
Advantages of databases |
- centralised developement/maintainance - prevent redundancies and inconsistency - simplified and scalable access - multi-user support - prevent loss of data (backup) - security |
|
|
|
Data (def) |
Data are recorded facts and numbers |
|
|
|
Information (def) |
Information is data presented in a meaningful contest and processed by aggregating, comparing or similar operations |
|
|
|
Components of a Database system |
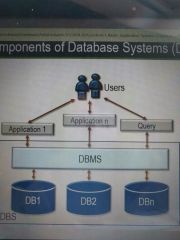
|
|
|
|
Charakteristics of database systems |
- data is stored centraly and organized - applications need to go through the DBMS - applications and queriea are independent from actual storage and organization of the data - multiple user can access the same data in parallel - еnforce constrains - data independancy - multi-user access - integrity - security - efficiency |
|
|
|
Layer model DB |
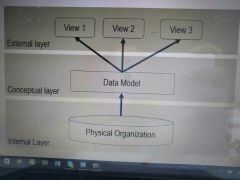
The conceptual layer describes the entities, their relationships and assosiated data The external layer provides a view in the conceptual layer. It is a subset of the overall data model. |
|
|
|
The relational database model |
The dominent database model is the relational database model which is based upon tables of data (called relations) All current DBMS products are based in it. |
|
|
|
Foreign keys |
Foreign keys are attributes of a relation R1 which create a relationship to another relation R2 |
|
|
|
Structured query language SQL |
The database language use to interact with rational databases is the SQL |
|
|
|
No SQL Databases |
- no user of relational model - open source - schameless |
|
|
|
Categories of NoSQL Data Models |
1)Key-value model 2) Document model 3)Column-family model 4)Graph model |
|
|
|
What is a requirement |
1) a condition or capability needed by user to solve a problem or achive an objective 2) a condition or capability that must be met or possesst by a system or system components to satisfy a contract, standard, specification or other formaly imposed docoment 3) a document representation of a condition or capability as in 1) or 2) |
|
|
|
Types of requirements |
1) user requirements - in natural language - written for customers 2) system requirements - detailed description of the system's functions services and operational constraints - defines what should be implemented 1) functional requirements - define the provided services - describe the system functionality, behavior and reactions 2) Non-functional requierments - specification of quality of services - comstraints on the services |
|
|
|
Categories of non-functional requirements |
Usability reliability performance maintainability Security |
|
|
|
Requirements engineering |
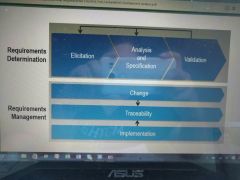
|
|
|
|
Project definition |
A project is a temporary endeavour having a defined beginning and end undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives usually to bring about beneficial change or added value which are pursued by progressive elaboration |
|
|
|
Project management definition |
Project management is the application of a structured process including initiating planning executing monitoring and controlling and closing activities in order to accomplish the project's objectives |
|
|
|
Phases of a project |
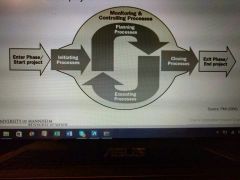
|
|
|
|
The Project's critical path |
A critical path generally is the sequence of scheduled activities that determines the duration of the project. It is the longest path trough the project |
|
|
|
Organizational structures |
1) Centralized - brings together all staff, hardware software data and processing into a single location Decentralized - the components are scattered in different locations to address local business needs 2) Decentralized- the components are scattered in different locations to address local business needs3)Federalism- a combination of centralized and decentralized structures 3)Federalism - a combination of centralized and decentralized structures |
|
|
|
5 major categories of IT decisions |
1) Principles 2) IT Arcitecture 3) IT infrastructure strategies 4) business application needs 5) IT investment and prioritizing |
|
|
|
Insourcing |
Insourcing is when a firm provides IS services or develops IS in its own in-house IS organization- "make" decision |
|
|
|
Outsourcing |
The purchase of a good or service that previously was or could be provided internally but is now provided by outside vendors |
|
|
|
Onshoring or inshoring |
Performing Outsourcing work domestically |
|
|
|
Three normative theories of business ethics |
1) Stockholder Theory - maximize stockholder wealth in legal and non-fraufulent manners 2) Stakeholder Theory - maximize benefits to all stakeholders while weighing costs to competing interests 3) Social contract - create value for society in a manner that is just and non-discriminatory |
|
|
|
Levels of culture |
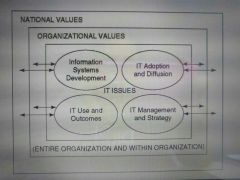
|
|
|
|
Review |

|
|
|
|
Telecommuting |
Telecommuting or teleworking is a work arrangement with employers that allows employees to work from home |
|
|
|
Components of TCO |
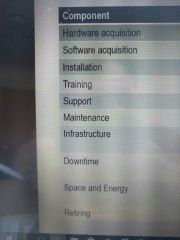
|
|
|
|
Basic cost structures when managing IT |
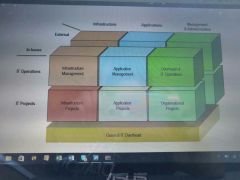
|
|
|
|
Silo perspective and Business process perspective |

|
|
|
|
User centered design |
User centered design is a universally applicable proces to develop usable systems background Inc the whole design process information about the people who will use the productIt is based on three principles1) early focus on users and tasks2) empirical measurement3) iterative design It is based on three principles 1) early focus on users and tasks 2) empirical measurement 3) iterative design |
|
|
|
IT Governance |
IT governance focuses on how decision rights can be distributed differently to facilitate centralized, decentralized or hybrid models of decision making Another perspective on IT governance - it is not about what decisions are actually made but who is making the decisions - the accountability |
|
|
|
The 3 organizational structures |
1) centralized - brings together all staff hardware, software, data and processing into a single location 2) Decentralized - the components are scattered in different locations to address local business needs 3) Federalism - a combination of centralized and decentralized structures |
|
|
|
What DB, DBS and DBMS |
DB - the database is a collection of related data DBS - database systems record facts and numbers - data, in a way that enables the production of information DBMS - the database Management Systems provides a set of services to create, access and maintain that databases |
|
|
|
System analysis |
An in-depth study of end-user information needs. Typically involves a detailed study of - information needs of a company and end user - activities, resources and products of Information Systems currently being used - information system capabilities required to meet the information needs of business stakeholders |
|
|
|
Strategic alignment model |
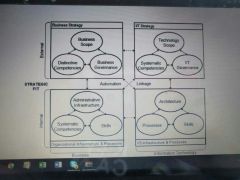
|
|
|
|
It Department in the phase of transition |
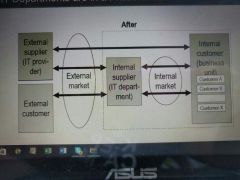
|
|

