![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three key principles of Information Security? |
i. Confidentiality ii. Integrity iii. Availability |
|
|
What are the five building blocks of Information Security? |
i. Confidentiality ii. Integrity iii. Availability iv. Authentication v. Non-repudiation |
|
|
Describe the following key objective:
Confidentiality |
Is the protection of communications or stored data against interception and reading by unauthorised persons. |
|
|
Describe the following key objective:
Integrity |
Enusuring that information should only be able to be modified by those who are authorised to do so.
Relies on hash algorithms which convert a block of data into a much smaller piece of data as output (a digest or "hash"). If the original data changes, the hash would be different. |
|
|
Describe the following key objective:
Availability |
Means that data is accessible and services are operational despite possible disruptive events such as power supply cuts, natural disasters, accidents or attack. |
|
|
Describe the following Information Security building block:
Authentication |
Is the confirmation of the asserted identity of entities or users. |
|
|
Describe the following Information Security building block:
Non-repudiation |
The concept of ensuring that no party involved in a communication can deny its participation. |
|
|
What is a PKI and how is it useful?
|
PKI; Public Key Infrastructure
Binds public keys with user identities using a digital certificate issued by a certification authority (CA).
Allows secure communications on an insecure public network.
|
|
|
Describe six steps that would be carried out when establishing an information security management system (ISMS) for an organisation. |
i. Identify information assets, their security requirements and value. ii. Identify, assess and treat information security risks. v. Select/implement relevant controls to manage unacceptable risks. vi. Monitor/maintain/improve effectiveness of controls. |
|
|
Why does an organization need Information Security Management (ISM)? |
To protect their assets, whether these be information, systems, networks or people.
These are valuable assets and therefore it is important to address their perceived risk exposure. |
|
|
What is an ISMS and why do companies need them? |
ISMS; Information Security Management System
i. To achieve greater assurance that its information assets are adequately protected against threats on a continual basis. ii. To maintain a structured/comprehensive framework for identifying/assessing risks, applying controls, etc. iii. To continually improve its control environment. iv. To effectively achieve legal/regulatory compliance. |
|
|
What is a digital certificate? |
A digital certificate is a signed message vouching that a particular name is associated with a public key. |
|
|
What is an IDS and how is it useful? |
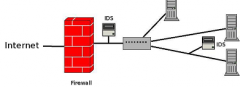
IDS; Intrusion Detection System A device or software application that monitors network or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations and produces reports to a management station.
|
|
|
What are the five types of Intrusion Detection Systems? Briefly describe each. |
i. Network based IDS; sensors located at choke points often in the DMZ or network borders. ii. Protocol based IDS; sensors located at front end of a server, monitoring packets between server/client. iii. Application based IDS; sensors sit within group of servers (e.g. web server -> database), analysing application specific protocols (e.g. SQL queries). iv. Host based IDS; sensor is a software element monitoring all activity on 'host' machine. v. Hybrid IDS; combines the above approaches. |
|
|
What is the difference between passive and reactive IDS? |
Passive: IDS sensor detects/ logs potential security breaches & sends alert to the console.
Reactive: Also known as Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), responds to suspicious activity by resetting the connection/reprogramming firewall to block network traffic from offending source. |
|
|
Describe the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. |
Symmetric Encryption: The decryption key is the same as the encryption key.
Asymmetric Encryption: The keys are different. There is a public and private key, the former of which is openly shared with everyone. |
|
|
What is a digital signature? |
A digital code (generated and authenticated by public key encryption) which is attached to an electronically transmitted document to verify its contents and the sender's identity. |

