![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do you see in active colitis?
|
Acute/active:
PMNs Pus in the crypts Glowouts of the crypts-->invasion of the lamina propria Chronic: Macrophages Lymphocytes Plasma cells |
|
|
What's associated with more severe IBD?
|
Ulcers!
|
|
|
What are the complications of uncontrollable IBD?
|
Hemorrhage
Diarrhea |
|
|
What's always involved in ulcerative colitis?
|
Rectum
|
|
|
What's the definition of left sided colitis?
|
Colon is involved all the way up to the splenic flexure
|
|
|
What macroscopic changes happent ot he colon in ulcerative colitis?
|
Loss of transverse folds
Severe hemorrhage Pseudopolyps (made up of inflamed cells) Mucosal granularity |
|
|
What are some histologic signs of ulcerative colitis?
|
No 2 crypts are same size, shape, going in same direction: THEY LOOK FUNKY!
Plasmacytosis |
|
|
What's the endpoint of ulcerative colitis?
|
Atrophy: complete loss of crypts
Destruction of the nerves that result in a loss of nervous function in the colon-->MEGACOLON! |
|
|
What are the causes of pseudomembranous colitis?
|
C. difficile overgrowth due to giving broad spectrum antibiotics
|
|
|
Whta are complications of ulcers from ulcerative colitis?
|
Many large ulcers: uncontrollable hemorrhage/diarrhea
Undermining ulcers: inflammatory pseudopolyps Broad, deep ulcers: megacolon - A BIG COLON! |
|
|
What is the definition of Crohn's disease?
|
Chronic ulcerating disease classically involving the small intestine (but can involve any part) that in its fully developed state, involves the whole gut wall.
|
|
|
What's the choice location of Crohn's?
|
Terminal ileum
|
|
|
What are the types of ulcers in Crohn's diease?
|
Aphthous: shallow
Linear: run along bowel longitudinally Fissure: perpendicular, deep ulcers-->fistulas |
|
|
What is a characteristic histologic finding of Crohn's?
|
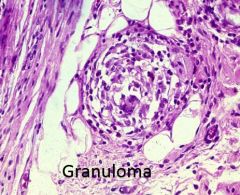
|
|
|
What is a complication of crohns that causes strictures?
|
Proliferation of the mucsularis mucosae-->stricutres
|
|
|
What happens to strictured/diseased intestines?
|
Mesenteric fat wrapping
|
|
|
What are causes of intesitnal ischemic colitis?
|
Arterial hypoperfusion due to low flow, arterial blockage
Venous outflow obstruction: congestio and hemorrhage |
|
|
What is the cause of ischemia in toxic megacolon?
|
Venous outflow obstruction
|
|
|
How do you distinguish between ischemic injury and IBD?
|
Ischemic:
Lack of inflammatory cells "Pinkish" color Submucosal edema Atrophic patches |
|
|
How do you tell something is pseudomembranous colitis on a slide?
|
IT LOOKS LIKE A VOLCANO OF PUS!
|
|
|
What are the inflammatory colitises that don't cause distortion?
|
Lymphocytic
Collagenous |
|
|
Grossly, how do you see lymphocytic colitis?
|
You don't!
It's a microscopic diagnosis. |

