![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Natural defenses of the Nervous System: |
-Skull and vertebrae -Microglial cells and macrophages -Restricted entry into brain (BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER) for: ~ microorganisms ~medications, including most antibiotics ~immune system |
|
|
Nervous System Diseases Both bacteria and viruses and parasites can cause: |
-Meningitis: inflammation of the meninges= membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord -Encephalitis: inflammation of the brain |
|
|
Nervous System Diseases: |
Viruses: --Rabies --Poliomyelitis Neurotoxins --Tetanus |
|
|
Bacterial Meningitis "HSN" |
-Haemophilus influenzae - Streptococcus pneumoniae -Neisseria meningitidis |
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae: |
type b -infants, newborn -also, E.coli, streptococcus agalactiae=group B strep) |
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae: |
-Children 1 month- 4 years - Elderly |
|
|
Neisseria meningitides: |
College students |
|
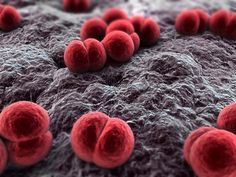
Streptococcal Meningitis |
Streptococcus pneumoniae -GRam + DIPLOCOCCI -Virulent strains are ENCAPSULATED -Children age 1 month -4 years -Elderly ** SUBUNIT VACCINE OPSONIZING*** |
|
|
Meningococcal Meningitis in College Students: |
Neisseria meningitidis -Enters through nasal cavity (droplets) -Incidence=2,500 Americans/year ---10-15% die, up to 20% long-term disabilities -Subunit vaccine: induces OPSONIZING antibody to capsule |
|
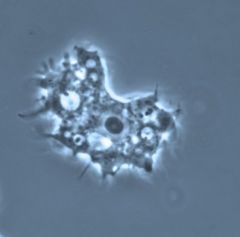
Naegleria Meningoencephalitis A rare infection "Brain-Eating Amoeba" |
-Naegieria fowleri -Small-free living amoeba -Found in fresh water -can be normal flora -Protozoan feeds on bacteria but if introduced into the CNS can feed on human tissue |
|
|
Naegleria Meningoencephalitis specs: |
-acquired from hot tubs, warm ponds and ground water at high temperature -children and young adults -initially infects the nasal mucosa -abrupt onset of symptoms 3 to 10 days after exposure to water ---Sever headache, fever, stiff neck, dementia and coma |
|
|
Naegleria Meningoencephalitis damage to humans: |
-Destroys brain and spinal tissue -death occurs within 10 days of the onset of clinical signs ---NO TREATMENT -Chlorine kills the organism in spas and pools -Mortality rate of > 95% |
|
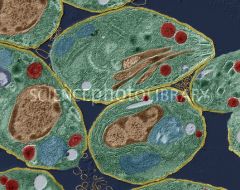
Toxoplasmosis |
--Toxoplasma gondii --flagellated protozoan parasite --infects over 200 species of bird and animals ----PRIMARY RESERVOIR IS CATS - infection usually handled by immune system |
|
|
How is Toxoplasmosis acquired? |
From contaminated meat or ingestion of oocysts in cat feces *** causes serious disease in developing fetus --liver damage --brain abnormalities --blindess -Serious disease in people with AIDS * Prevention: no raw meat, no contact with cat litter |
|
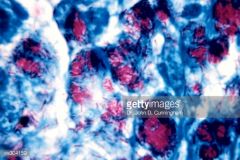
Hansen's Disease: Leprosy |
--- Mycobacterium leprae * Disease of skin and nerves * Change of pigmentation, loss of sensation * Slow progressing * Transmits poorly * Droplet or skin contact |
|
|
Mycobacterium leprae: |
**** Causative Agent of Hansen's Disease:Leprosy*** -Acid fast bacterium -slow growth -strict parasite -multiplies in macrophages -prefers cool areas of body -long course, drug cocktail |
|
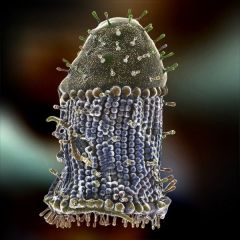
Rabies |
-Viral infection from bite of a "furious" rabid animal: *Animal rabies: Wandering, aggress, biting, salivating -Virus travels from the bite to the brain, via nerves -Thus, variable latent period **A fatal zoonotic disease --Human "dumb" rabies: fever, confusion, anxiety, encephalitis, death |
|
|
Rabies: transmission--> |
Bite --> virus grows in muscle --> virus enters sensory nerve ending --> virus travels to cord, brain --> virus grows in brain, changes behavior --> virus travels to salivary gland and is secreted |
|
|
Animal Reservoirs of Rabies: |
Skunk Fox Coyote Raccoon |
|
|
Diagnosis of Rabies |
-Performed via a POST-MORTEM autopsy on animals -Observing neuronal brain cells with intracytoplasmic inclusions (Negri bodies) -Identification of Rabies Strain -(Bat, Skunk, etc...) |
|
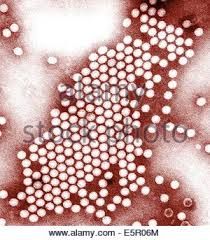
Paralytic Poliomyelitis |
-Neurotropic viral infection acquired by ingestion -Paralytic spinal cord infection -Effective vaccine (PV -1,2,3) -Unvaccinated children are at risk in parts of the world like India, Africa |
|
|
The unique stages of infection and pathogenesis of poliomyelitis |
Poliovirus, an "Enterovirus" has an icosahedral capsid shell that protects it from digestion. |
|
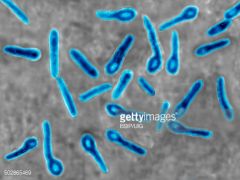
Clostridium tetani, a soil organism and the causative agent of tetanus, have a unique tennis racket morphology. |
Bacterial invasion, release of bacterial TOXIN and symptoms: Rigid paralysis |

