![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A ________ is defined as surface-attached microbial communities encased in a self-produced extracellular matrix. |
biofilm |
|
|
In general, the biofilm matrix consists of ________, ________, and ________. |
polysaccharide proteins DNA |
|
|
Extracellular DNA is released from the bacteria through cell ________. |
lysis |
|
|
________ has an essential role in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development. |
Extracellular DNA |
|
|
Bacterial cells treated with ________ were inhibited from developing a biofilm. |
DNase I |
|
|
The significance of biofilms in nature is exemplified by ________ corrosion, on the surface of ________ in Yellowstone National Park, and ________ treatment plants (beneficial biofilm). |
pipe hot springs sewage |
|
|
The CDC estimates that ________% of bacterial infections are biofilm-based. |
65 |
|
|
Bacteria in a biofilm can be up to ________-fold more resistant to antibiotic treatment. |
1000 |
|
|
Possible mechanisms for antiobiotic resistance include: ________ changes in the bacteria, inactivation of the antibiotics by ________, ________ of the antibiotic, and ________ limitation leading to slow growth. |
phenotypic extracellular polymers sequestration nutrient |
|
|
Biofilm-based infections are ________. |
chronic |
|
|
Biofilms form on ________ and ________ tissue and frequently form on ________. |
dead living medical implants |
|
|
________ biofilm is commonly formed inside catheters. |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
|
|
________ can attach to lung tissue in cystic fibrosis patients. |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from ________ cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single-cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium
|
planktonic |
|
|
The developmental cycle of biofilm formation consists of the following steps: (1) ________ and ________ of bacterial and planktonic cells, (2) ________ on the surface, (3) ________ biofilm, (4) ________. |
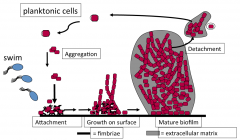
aggregation attachment growth mature detachment |
|
|
________ dishes can be used to grow biofillms. These systems are static, so end-products ________ and this limits growth and viability. |
Microtiter accumulate |
|
|
A biofilm assay consists of overnight ________ of the bacterium, ________, and lastly the culture is ________ allowing time for the bacteria to grow on the surface of the well - creating a biofilm. The biofilm is washed two times in distilled water to remove ________ cells. The wells are filled with dye to stain the biofilm for 15 minutes. |
culture dilution incubated planktonic |

