![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common organism in the vaginal flora and how does it inhibit other organisms growth |
Lactobacillus acidophilus Converts glucose to lactic acid --> hostile environment |
|
|
What is the most common co-infection with gonorrhoea and its prevalence |
clamydia 5% of gonorrhoea infections |
|
|
what are the complications of infection with chlamydia and how are they caused |
pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility (form scarring), chronic pain and ecotopic pregnancy Damage is due to chronic immune activation due to infection, not due to chlamydia trachomatis |
|
|
what are the symptoms of chlamydia in men and women |
it is asymptomatic in 75% of women - presents with pain and mucropurulent discharge if symptoms Men - 50% of time symptomatic - urethritis, white discharge, dysuria |
|
|
what are the symptoms of gonorrhoea infection |
50% of women have symptoms - purlent vagina d/c, pelvic pain men present with penile discharge and dysuria |
|
|
what are the complications of gonorrhoea and why are they formed |
pelvic inflammatory disease (10-20%) of time, infertility, chronic pelvic pain, blood stream infections (1-3%) --> septic arthritis Damage mainly due to chronic immune activation |
|
|
can gonorrhoea be transmitted vertically and if so what is a complication |
yes ophthalmia neonatorum |
|
|
what is the infectious agent in syphillis and how many of them does it take to innoculate 50% of people |
treponema pallidum 60 organisms |
|
|
what are the three stages of syphilis infection |
Primary stage Secondary stage: If the primary notcleared, 7-10 weeks later treponemes spread systemically) Tertiary stage: In 3-30years, if not cleared Symptoms from constant activation of immune system andthus damage: |
|
|
what are the 2 very high risk forms of HPV, the two high risk forms and the two low risk forms |
16, 18 --> 64-79% of cervical cancers 31, 45 - high risk of developing into cervical cancer 6, 11 --> low risk of cervical cancer, but 90% correlation with genital warts |
|
|
what are the 3 stages of HPV infection |
1. Transmittedvia skin to skin contact (sex not required, fingers etc) 2. Enterssquamous cell epithelium (KERATINOCYTES)through micro-abrasions 3. Viralproteins E6 and E7 disruptcell division cycle → virus induces cell to divide → infected cellsoutgrow non infected, may also integrate into genome (even moreexpression and division) → cancer |
|
|
what are the symptoms of herpes simplex virus infection |
Primary lesions 4-7 days after initial infection Usually on penis, vulva and possibly intravaginal Painful genital sores + pain, itching, burning, dysuria,maybe fever, malaise, myalgia Lesions heal over 3-4 weeks |
|
|
what is neonatal herpes and what are its consequences |
herpes of the neonate due to vertical transmission skin and eye disease, cognitive impairment, organ dysfunction, death |
|
|
how does inoculation of invasive aspergillous occur, its complications and symptoms |
inhalation of IA spores pneumonia, sinusitis, haemoptysis, chest pain and headache |
|
|
what are the radiography signs of invasive aspergillous |
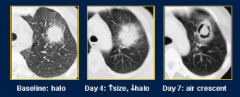
|

