![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
mn>0 |
m>0 n>0 Or m<0 n<0 |
|
|
mn<0 |
m>0 n<0 Orm<0 n>0 |
|
|
a/b > 0 |
(a/b)*b² >0
ab>0 |
|
|
√a√b |
√ab |
|
|
(√a) / (√b) |
√(a/b) |
|

To rationalise |
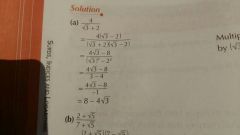
|
|
|
B = A² |
logaB = 2 |
|
|
logaA |
1 |
|
|
loga1 |
0 |
|
|
logPQ |
LogP + Log Q |
|
|
Log P/Q |
LogP-Q |
|
|
LogP² |
2logP |
|
|
General term for Arithmetic progression |
a + (n-1)d |
|
|
General term for Geometric sequence |
ar^(n-1) |
|
|
Arithmetic progression Sn |
= n/2(2a + (n-1)d) = n/2(a+l) |
|
|
r<1 |
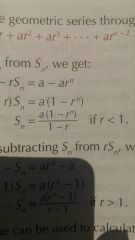
|
|
|
r>1 |
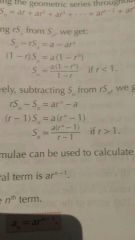
|
|
|
Geometric sequence sum to infinity |
A/r-1 |
|
|
To find the coordinates of the point of intersection |
Simultaneous equations |
|
|
general form of the equation of a circle |
(x –(- g))² + (y -(– f))² = r² x²+y²+2xg+2yf+f²+g²=r² x²+y²+2xg+2yf+c=0 |
|
|
In the general form of the equation of circle C= |
f²+g²-r² |
|
|
gradient of a tagent |
(x+g)/(y+f) |
|
|
gradient of a normal |
(y+f)/(x+g) |
|
|
Equation of a straight |
y=mx+c |
|
|
point gradient form |
Y-y= m(x-x) |
|
|
magnitude of a vector |
√(x²+y²) |
|
|
Unit vector |
(xi+yj) / √(x²+y²) |
|
|
a•b |
(i×i)+(j×j) |a||b|cosX= √[(x-x)²±(y-y)²] √[(x-x)²±(y-y)²] cosX |
|
|
a•b=0 |
Perpendicular |

