![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Mediated immunity is the effector function of what cells?
CMI serves as the defense mechanism against _________, that affect what cells? |
T lymphocytes
defense mechanism against microbe that survive and replicate within phagocytes and non phagocytes |
|
|
The effector phase of CMI is initiated by________?
Defects in CMI result in an increase succeptibility to infection by ______. |
Recognition of antigens by T cells
Intracellular Microbes |
|
|
Response to microbes within phagosomes of phagocytes is done by what cells?
Response to extracellular microbes including fungi and bacteria, is mediated by what cells? Response to helminthic parasites and various allergens is mediated by what cells? Response to microbes that infect and replicate within cells is mediated by what cells? |
TH1 (the "big 1" phagocytes)
TH17 (european 7 looks like F) TH2 (2 looks like a worm) CTL (cytotoxic T Lymphocyte -definition based) |
|
|
TH1
TH17 TH2 CTL |
Response to microbes within phagosomes of phagocytes is done by what cells?
Response to extracellular microbes including fungi and bacteria, is |
|
|
DiGeorge syndrome is a _________ defect caused by _________ of ____________.
Absence of or abnormal _________, __________, leading to _______ with cardiac and _________anomalies |
Digerorge syndrome is a congenital defet causd by a deletion in a portion of chromosome 22 characterized by absence or abnormal theymus, absence or abnormal parathyroids (leading to hypoparathyroidism, as well as cardiac and facial anomalies.
|
|
|
pathological characteristics of DiGeorge syndrome include
Variable _____ cell counts, Increased succeptibility to ________ infections, ________ response to skin test antigens (these tests assess _______ function) Subject to ________ due to hypocalcemia Prognosis is often ________ |
Variable T Cell counts
Increased succeptibility to opportunistic infections decreased response to common skin test antigens, tests assess T Cell function, Tetany due to hypocalcemia, poor prognosis |
|
|
The two main types of Tcells are ___ and ___.
TCR expressed by _____ T cells recognizes its antigen displayed _______. TCRs are necessary and specific, each t cell has _________ TCR created during maturation |
The two main types of Tcells are Th and Tc.
TCR expressed by all T cells recognizes its antigen displayed in the MHC molecule TCRs are necessary and specific, each t cell has its unique TCR created during maturation |
|
|
Cytosolic peptides are degraded by _______ and ultimately displayed in class ______ MHC to ______ cells.
-Exogenous peptides are degraded by _________ and ultimately displayed in class ______ MHC to _____ cells. |
Cytosolic peptides are degraded by proteosomes and ultimately displayed in class I MHC to CTL cells.
-Exogenous peptides are degraded by Phago-lysosomes and ultimately displayed in class Class II MHC to TH cells. |
|
|
T Cell activation occurs in _____ tissues and requires _____ activation signals
These signals come from the interaction of a ________ cell with the _______, which is most likely a ______ cell. |
could I be any more vague?
T Cell activation occurs in secondary lymphoid tissues and requires two activation signals These signals come from the interaction of a naive T cell with the APC, which is most likely a Dendritic cell. |
|
|
What are the five steps of Tcell activation ending with Effector functions?
|
Antigen Recognition
Activation Clonal Expansion Differentiation Effector Functions |
|
|
TCell Activation First signal:
binding of TCR complex (which is made up of TCR and _________) on the T cell to the _______/______ complex. when it binds then Receptors _____ and______ also bind to the ____. The "adhesion" that occurs is due to what molecules? |
TCell Activation First signal:
binding of TCR complex (which is made up of TCR and CD3 and lambda? chains on the T cell to the MHC/peptide complex. when it binds then Receptors CD4 andCD8 also bind to the MHC. The "adhesion" that occurs is due to what molecules?- due to CAM mediation |
|
|
T-cell activation Second Signal
Binding of B7 (molecules _____) on the APC with _____ on the T cell. Interaction between ______ leads to activation of the T cells. |
T-cell activation Second Signal
Binding of B7 (molecules CD80/86) on the APC with CD28 on the T cell. Interaction between the two signals leads to activation of the T cells. |
|
|
Each TCell activation segment's Receptors/ligand
Signal Transduction (2)- Antigen recognition- Adhesion- |
Each TCell activation segment's Receptors/ligand
Signal Transduction (2)- CD 4, CD3, CD28w/CD80/86 Antigen recognition- TCRw/Class II MHC/peptide Adhesion- LFAw/ICAM1 |
|
|
Why are dendritic cells the APC that activates naive T cells in a primary immune response?
-Constitutively expresses __________. -they don't have to be activated via cytokines from _____ . Macrophages, however need to be activated by ________ before they express ________ |
MHC, B7
T cells/macrophages or NK cells IFN-gamma, MHC and B7 |
|
|
B7 cell receptor found on _____ is responsible for?
It is exressed _______. |
Dendritic cell
Costimulation Constitutively |
|
|
_______ are more effective at stimulating effector T cells that have migrated _________, because they were _______ activated in the __________ by the __________.
|
Macrophages are more effective at stimulating effector T cells that have migrated into the tissue sites of infection, because they were previously activated in the lymphatics by the dendritic cells
|
|
|
_______ happens when the second signal is absent. It is by definition:________.
Only ______ can provide ________ to T cells, which reduces the amount of cells that could _______ a ____ cell. |
ANERGY happens when the second signal is absent. It is by definition: a state of unresponsiveness.
Only APCs can provide costimulation to T cells, which reduces the amount of cells that could activate a t cell. |
|
|
Binding of the ______ (which are?) aggregates signaling motifs on the ______side of the _________, triggering several ___________pathways in the T cell.
|
Binding of the two activation signals (B7-CD28, TCR/MHCw/peptide) aggregates signaling motifs on the cytosolic side of the receptors, triggering several signal transduction pathways in the T cell.
|
|
|
The signal motifs of a T cell trigger several transcution pathways that result in 3________, which are
___,____,____. |
Transcription factors
NFAT NF-kB AP-1 |
|
|
The four steps in TCell activation begining with signal and ending with transcription factors are?
|
-Initiation of TCR mediated signals
-Biochemical intermediates -active enzymes -transcription factors |
|
|
In Tcell activation, The three transcription factors bind to the____and initiate transcription of the ____gene.
-Also, the T cell will express a __________ , named____, -____is NECESSARY for ____cell activation! |
The three transcription factors bind to the DNA and initiate transcription of the IL-2 gene.
Also, the T cell will express a high affinity IL-2 receptor = IL-2R, IL-2 is NECESSARY for T cell activation! |
|
|
Two drugs that can target Tcell activation signal transduction pathways, thereby inhibiting T cell activation.
These drugs bind to ______, these complexes inhibit ______, thereby preventing active ______ generation. -Without ______, transcription of the ________ gene will not occur. -These drugs (and others) are important in _________ therapy. |
Cyclosporin
Tacrolimus (FK506) These drugs bind to proteins (FYI: cyclophilin and FKBP12, respectively); these complexes inhibit calcineurin, thereby preventing active NFAT generation. Without NFAT, transcription of the IL-2 gene will not occur. These drugs (and others) are important in immune suppression therapy. |
|
|
Antigen-activated T cells synthesize ___ and also expresses ______,aka:______, forming a high affinity ______.
-IL-2 binding to the high affinity IL-2R stimulates: -Survival – by stimulating production of ______ (an __________ protein) -Clonal proliferation – by stimulating production of _____ and degradation of _____ (aka____) |
Antigen-activated T cells synthesize IL-2 and also expresses CD25 = IL-2R, forming a high affinity IL-2R.
-IL-2 binding to the high affinity IL-2R stimulates: -Survival – by stimulating production of Bcl-2 (an antiapoptotic protein) -Clonal proliferation – by stimulating production of cyclins and degradation of p27 (a CKI) |
|
|
One way to enhance the activation of T cells is to administer______,
-Isolate T cells (and some NK cells) from tumor -These are known as ______= _____cells -Exogenously administer ___ to ___ cells, which will stimulate their proliferation -Place ____ cells back into patient to help fight the tumor |
One way to enhance the activation of T cells is to administer IL-2; this is done in the treatment of some cancers
Isolate T cells (and some NK cells) from tumor These are known as tumor infiltrating lymphocytes = TIL cells Exogenously administer IL-2 to TIL cells, which will stimulate their proliferation Place TIL cells back into patient to help fight the tumor |
|
|
Antigen-activated T cells express two additional receptors:
1.________ that will function in the activation of: a____, b______ 2. ______ (aka:_____) : Within a few days after activation all activated T cells will express _____. This also binds to _____ on the _____; binding results in _______ of ___ cell proliferation |
Antigen-activated T cells express two additional receptors:
1.CD40L (CD154)that will function in the activation of: macrophages, B cells. 2. CTLA-4 (CD152): ), all activated T cells will express CTLA-4. CTLA-4 also binds to B7 (CD80/86) on the APC; binding results in inhibition of T cell proliferation |
|
|
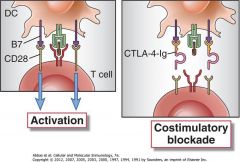
Abatacept is a fusion protein composed of the extracellular domain of ______ and the ___ of ____
-______domain binds B7 on the APC, preventing B7 from binding to ______, the_____extends the half-life of the drug. -This drug prevents the APC from delivering the ______ needed for T cell activation, this block is called a ______ |
Abatacept (Orencia®) is a fusion protein composed of the extracellular domain of CTLA-4 and the Fc region of IgG1.
CTLA-4 domain binds B7 on the APC, preventing B7 from binding to CD28; the IgG1 extends the half-life of the drug. This drug prevents the APC from delivering the second signal needed for T cell activation = it functions to block B7-CD28 costimulation (costimulatory blockade) |
|
|
After proliferation, the clonal population of antigen-specific T cells will further differentiate into either an _______ or a _____ cell:
|
After proliferation, the clonal population of antigen-specific T cells will further differentiate into either an effector T cell or a memory T cell:
|
|
|
-________: short-lived cells responsible for the immune response to the antigen. If the activated T cell was a naïve T cell, this results in generation of a _______ immune response.
-Two main types :_____ and ______ -_________: long-lived cells that respond to _________ with ________ sensitivity. Will generate a _________ immune response when activated. |
Effector T cells: short-lived cells responsible for the immune response to the antigen. If the activated T cell was a naïve T cell, this results in generation of a primary immune response.
Two main types of effector T cells: helper and cytotoxic Memory T cells: long-lived cells that respond to subsequent challenge with heightened sensitivity. Will generate a secondary immune response when activated. |
|
|
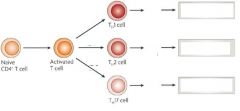
Helper T cells – upon activation, helper T cells can further differentiate into one of ____ primary subsets, which are ___ ___ ___, each _______, and playing a specific role in _____.
|
Helper T cells – upon activation, helper T cells can further differentiate into one of three (four) primary subsets, TH1,2,17 THreg, each secreting distinct cytokines and playing a specific role in host defense
|
|
|
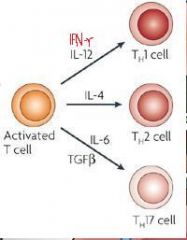
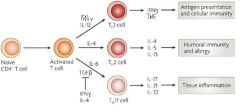
Mature, naïve CD4+ T cells differentiate into EITHER a _, a _, or a _ cell when stimulated by ___ + ____ (often cytokines) to proliferate and differentiate.
-Which subset develops depends on the ___ present during the ______ Type of antigen Antigen For TH1: Antigen For TH2: Antigen For TH17: -Cytokines for TH1 differentiation: -Cytokines for TH2 differentiation: -Cytokines for TH17differentiation: |
Type of antigen
-For TH1: Various intracellular pathogens -For TH2: Parasites and allergens -For TH17: Various extracellular bacteria and fungi -Cytokines -IL-12 and IFN- → TH1 -IL-4 → TH2 -IL-6 and TGF-β → TH17 |
|
|
TH1 cell differentiation is driven by two cytokines: _____ and ______
______ is secreted from activated macrophages and dendritic cells, in response to __________. ______ is secreted by ____ & TH1 cells |
TH1 cell differentiation is driven by two cytokines: IL-12 and IFN-
IL-12 is secreted from activated macrophages and dendritic cells, in response to intracellular microbes. IFN- is secreted by NK & TH1 cells |
|
|
______ is secreted by NK & TH1 cells.
-First, NK cells secrete _____ upon stimulation via ______; the two cytokines together promotes TH differentiation into ____ cells. -_____will also augment phagocyte killing mechanisms and ________! -Upon T cell stimulation, TH1 cells also secrete _____, further promoting TH1 cell development (which is called _______). |
IFN- is secreted by NK & TH1 cells.
First, NK cells secrete IFN- upon stimulation with IL-12 (recall L8); this IFN-, along with IL-12, promotes TH differentiation into TH1 cells This IFN- will also augment phagocyte killing mechanisms and antigen presentation! Upon T cell stimulation, TH1 cells also secrete IFN-, further promoting TH1 cell development (amplification). |
|
|
TH2 cell differentiation is driven by the cytokine ____
-secreted from ____in response to _______. |
TH2 cell differentiation is driven by the cytokine IL-4.
IL-4 is secreted from mast cells (and possibly other cellular sources, such as eosinophils)in response to helminths and allergens. |
|
|
IL-4 is also secreted as an autocrine growth factor by ____ and ___ in the absence of ___ and _______ (signals)
|
IL-4 is also secreted by activated TH cells and TH2 cells
In the absence of IL-12 and IFN-, activated helper T cells will secrete IL-4, promoting their own differentiation into TH2 cells and continue to secrete IL-4 (amplification) IL-4 is functioning as an autocrine growth factor |
|
|
TH17 cell differentiation is driven by _____ and ______
______= a pro-inflammatory cytokine released by ______ and _____ in response to ______ and ____.. -_______is an anti-inflammatory cytokine released by many cell types, often at _________. -These two cytokines result in T cell secretion of _____, which has ______ action, promoting the differentiation of ____cells. |
TH17 cell differentiation is driven by two cytokines: IL-6 and TGF-β
IL-6 = a pro-inflammatory cytokine released by dendritic cells and macrophages in response to bacteria and fungi. Recall Lectures 7-8 FYI: IL-1 may also participate TGF-β is an anti-inflammatory cytokine released by many cell types, often at mucosal surfaces. Promotes TH17 development in conjunction with pro-inflammatory cytokines! These two cytokines result in T cell secretion of IL-21, which has autocrine action, promoting the differentiation of TH17 cells. |
|
|
Effector T cells “home” to regions of ______ (within the _____) by recognizing ___ and ______ on ________ cells.
-If the effector T cell recognizes its antigen in the periphery (via ______ interaction), the T cell is retained in the tissues and is “activated” or stimulated to perform its effector function. |
Recall, effector T cells “home” to regions of infection or injury (within the peripheral tissues) by recognizing chemokines and CAMs on inflamed vascular endothelial cells.
If the effector T cell recognizes its antigen in the periphery (via TCR-MHC interaction), the T cell is retained in the tissues and is “activated” or stimulated to perform its effector function. |
|
|
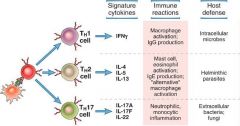
The primary function of effector TH1 cells is _______.
-The signature cytokine secreted by effector TH1 cells is ________. -They also produce ____ and ____ -TH1 cells activate ____,____,____ -TH1 cells stimulate B cell production of _______. |
The primary function of effector TH1 cells is phagocyte-mediated defense against intracellular microbes or tumor cells.
The signature cytokine secreted by effector TH1 cells in response to intracellular infections or tumor cells is IFN-. oBut TH1 cells also produce IL-2 and TNF. TH1 cells activate macrophages, NK cells, and TC cells TH1 cells stimulate B cell production of opsonizing antibodies |
|
|
The four major functions of Th Cells
|
TH1-Mediated Activation of Macrophages
TH1-Mediated Stimulation of B Cells TH1-Mediated Activation of CTLs TH1-Mediated Augmentation of Inflammation |
|
|
TH1 Activation of Macrophages:
-Effector TH1 cells secrete ____and _____, the ligand for _____ that is expressed by APCs. Both of these augment the___ and _______ functions of macrophages |
Effector TH1 cells secrete IFN- and also express CD40L (CD154) = the ligand for CD40 that is expressed by APCs.
Both IFN- and the CD40-CD154 binding interaction augment the APC and phagocytic functions of macrophages |
|
|
TH1-Mediated Stimulation of B Cells
______ secreted by effector TH1 cells also functions in the stimulation of B cells: results in the B cells producing _____ antibodies via ________. These antibodies are good _______and can activate _______ |
TH1-Mediated Stimulation of B Cells
IFN- secreted by effector TH1 cells also functions in the stimulation of B cells. IFN- results in the B cells producing IgG antibodies via class-switching Details on this process in Lectures 14-15 IgG antibodies are good opsonins and can activate complement |
|
|
TH1-Mediated Activation of ____s
-Effector TH1 cells also participate in the activation & differentiation of naïve _______ into effector _____ (often referred to as ______, ). 1-Effector TH1 cell secretes ____ and ____ that can augment TC cell activation. 2- Effector TH1 cells can augment _____ activity via ______ binding to become more effective at activating TC cells. |
TH1-Mediated Activation of CTLs
Effector TH1 cells also participate in the activation & differentiation of naïve TC cells into effector TC cells (often referred to as CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes). Panel A: Effector TH1 cell secretes IL-2 and IFN- (“cytokines” in the figure) that can augment TC cell activation. Panel B: Effector TH1 cells can augment APC activity via CD40-CD40L binding to become more effective at activating TC cells. |
|
|
TH1-Mediated Augmentation of Inflammation
-Effector TH1 cells also secrete ____, which acts on the vascular endothelium to increase expression of ____ and production of _____. -This will promote the ___ and _____ of WBCs from the _____ into and through the _____. -If the pathogen is resistant to the ________ chronic inflammation can occur. |
TH1-Mediated Augmentation of Inflammation
Effector TH1 cells also secrete TNF, which acts on the vascular endothelium to increase expression of CAMs and production of chemokines. This will promote the extravasation and chemotaxis of WBCs from the vasculature into and through the tissue spaces. If the pathogen is resistant to the phagocyte’s intracellular killing mechanisms, chronic inflammation can occur. |
|
|
Functions of Effector TH2 cells
-The primary function of effector TH2 cells is ______, but they also participate in ______. -The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH2 cells are ____. |
Functions of Effector TH2 cells
The primary function of effector TH2 cells is in defense against helminths, but they also participate in allergic reactions. The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH2 cells in response to helminths and various allergens are IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5 |
|
|
The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH2 cells in response to helminths and various allergens are __, __, and ___
-____ stimulates B cells to class-switch to ____. ____ activates ____ to degranulate. ___ with____ stimulates peristalsis and increased mucus secretion in the gut as well as ______ activation of _______. |
The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH2 cells in response to helminths and various allergens are IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5
IL-4 stimulates B cells to class-switch to IgE (FYI: and IgG4) IL-5 activates eosinophils to degranulate IL-4 and IL-13 stimulates peristalsis and increased mucus secretion in the gut as well as alternative activation of macrophages |
|
|
Effector TH2 cells secrete___and ____ that stimulate macrophages differently than ___from ___ cells.
-TH2 cells stimulate macrophages to synthesize factors that promote ____ and _____ in ______. -These “alternatively activated” macrophages also secrete ____ cytokines that suppress ______ and a ____ cell response |
Effector TH2 cells secrete IL-4 and IL-13 that stimulate macrophages differently than IFN- from TH1 cells.
TH2 cells stimulate macrophages to synthesize factors that promote collagen synthesis and fibrosis in chronic parasitic diseases and allergies These “alternatively activated” macrophages also secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines that suppress “classically activated” macrophages and a TH1 cell response |
|
|
Functions of Effector TH17 cells
-The primary function of effector TH17 cells is to____. -The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH17 cells are ___ and ___. |
Functions of Effector TH17 cells
The primary function of effector TH17 cells is to induce neutrophilic inflammation to destroy extracellular bacteria and fungi. The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH17 cells in response to extracellular bacteria and fungi are IL-17 and IL-22 |
|
|
The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH17 cells in response to extracellular bacteria and fungi are ___ and ____
-___ stimulates the production of ____ and _______ to recruit _____ and also stimulates the production of _____ (e.g., _____) -IL-22 ________ -TH17 cells are important in the pathogenesis of many _______ diseases |
The signature cytokines secreted by effector TH17 cells in response to extracellular bacteria and fungi are IL-17 and IL-22
IL-17 stimulates the production of chemokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines to recruit PMNs and also stimulates the production of anti-microbial peptides (e.g., defensins) IL-22 promotes epithelial integrity TH17 cells are important in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory diseases |
|
|
Function of Effector TC Cells = CTLs
-CTLs function to kill target cells that are infected with _____ or has _______. -Effector CTLs recognize infected or tumor cells via _____ interaction; recognition of ____ by the effector CTL triggers its killing capabilities. -Killing requires ____ between the ______. -____ one CTL can bind to any given target cell -Two mechanisms are used by the CTL to kill target cells -Both induce ___ |
Function of Effector TC Cells = CTLs
CTLs function to kill target cells that are infected with an intracellular organism or has become transformed (cancer). Effector CTLs recognize infected or tumor cells via TCR-MHC Class I interaction; recognition of antigen by the effector CTL triggers its killing capabilities. Killing requires cell-to-cell contact between the CTL and the target cell. More than one CTL can bind to any given target cell (the image shows three CTLs attached to one tumor cell) Two mechanisms are used by the CTL to kill target cells Both induce apoptosis in the target cell Tumor cell |
|
|
Mechanism of CTL Killing: Degranulation
1.Degranulation =______ -_______: pore forming protein Granzymes: _________ -______monomers insert and polymerize, forming a channel for ______ to enter and activate an __________ pathway. |
Mechanism of CTL Killing: Degranulation
Perforin monomers insert and polymerize, forming a channel for the granzymes to enter and activate an apoptotic (caspase) pathway. 1.Degranulation = release of granular contents: Perforin: pore forming protein Granzymes: serine esterases |
|
|
Mechanism of CTL Killing: Fas-FasL
2.Fas-FasL interaction between the____ and _____ -____ cells express Fas receptors -______ cells express FasL. The Fas-FasL interaction activates the ______ pathway. |
Mechanism of CTL Killing: Fas-FasL
2.Fas-FasL interaction between the CTL and the target cell All of our nucleated cells express Fas receptors Only activated CD8+ T cells (CTLs) express FasL. If a CTL recognizes its antigen displayed in Class I MHC and binds to the target cell, there is now sufficient time for FasL to bind to Fas receptors. The Fas-FasL interaction also activates the caspase pathway, stimulating apoptosis. |
|
|
T cell-mediated immune responses to an antigen usually result in the generation of _____ cells specific for that antigen, which may ________.
-These cells are responsible for _____responses when the same antigen is encountered again. -Mediate___ immune responses. -For each type of T cell, there are ___ subsets of these cells. |
T cell-mediated immune responses to an antigen usually result in the generation of memory T cells specific for that antigen, which may persist for years, even a lifetime.
These memory T cells are responsible for more rapid and amplified responses when the same antigen is encountered again. Mediate secondary immune responses. For each type of T cell, there are two subsets of memory cells |
|
|
Central memory T cells (TCM)
-Home (go) to _________ -Proliferate quickly on exposure to antigen and generate ________. |
Central memory T cells (TCM)
Home to secondary lymphoid tissue Proliferate quickly on exposure to antigen and generate many effector T cells (and memory cells) |
|
|
Effector memory T cells (TEM)
-Home to ______ -Secrete cytokines upon ____ and proliferate ______. -Provides for a _____ response -The prolonged maintenance of these memory T cells is ____ dependent. -Constitutive expression of ____ -Support _____proliferation |
Effector memory T cells (TEM)
Home to peripheral tissues, especially mucosal surfaces Secrete cytokines upon antigenic stimulation but don’t proliferate much Provides for an Initial rapid response 38 The prolonged maintenance of these memory T cells is cytokine-dependent Constitutive expression of IL-7 Support low-level proliferation |
|
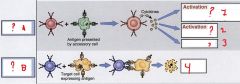
Fill this out
|
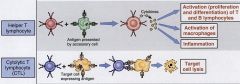
|
|
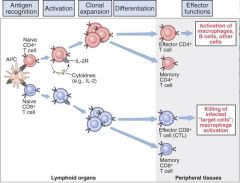
look at this and think about it
|
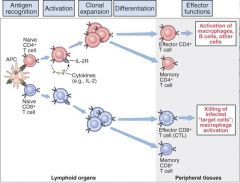
|
|
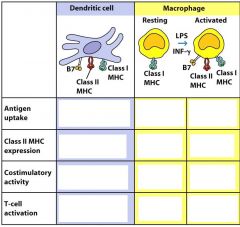
Fill this out
|
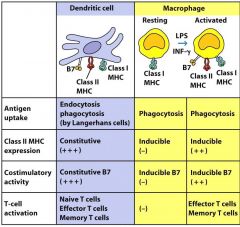
|
|
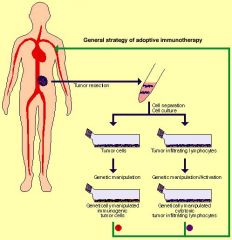
Explain the theory of adoptive immunotherapy
|
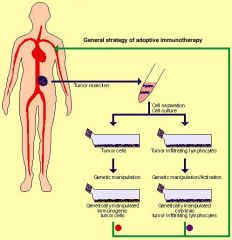
|
|
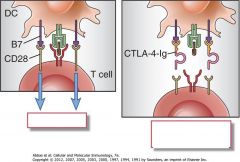
Fill in these boxes
|
|
|
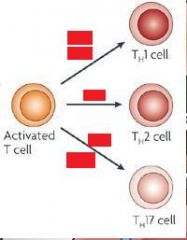
Label these red boxes
|
|
|
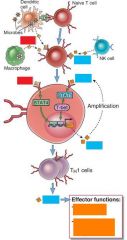
Label the colored boxes
|
I dont have the picture file?
|
|
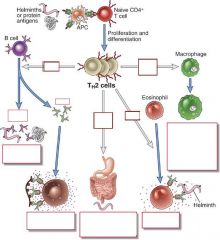
Fill this beast out
|
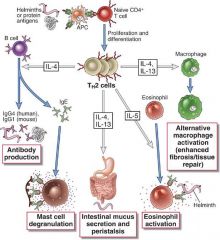
|
|
KNOW THIS ISH!!!
|
|
|
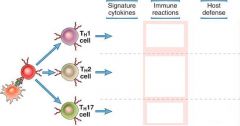
KNow this ISH as well, holy wacamoly!
|
|

