![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
immunolglobins, aka antibodies are a family of _______ that bind to a _______range of __________with great strength.
They are the components of the __________ response. |
glycoproteins bind to a wide range of antigenic structures with great strength
both adaptive and humoral responses |
|
|
|
What are the five isotypes of antibody?
What is the functional role of antibody? specific for Membrane bound antibodies? |
igMADGE
They fucntion in the recognition phase of humoral immunity, Membrane bound are B cell receptors for antigens |
|
|
|
What is the function of antibodies in the effector phase of humoral immunity?
role in adaptive immunity? |
Antibodies are produced in a secreted form b antigen stimulated cells- they in turn are the only mechanism of adaptive immunity against extracellular organisms
|
|
|
|
What are the two phases of humoral immunity that are particular to antibodies?
|
The recognition phase and the effector phase
|
|
|
|
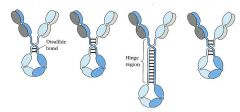
The basic structure of an Antibody contains _____ # chains, named_____
What chains are connected? What connects them? |
four polypeptide
light heavy light to heavy heavy to heavy in middle, both via disulfide bonds |
|
|
|
What area of the antibody allows it to play twister with receptors/antigens?
|
the Hinge region
|
|
|
|
Heavy and light chains can be divided into what two types of regions?
What is the significant difference in types? |
Constant and Variable
Variable region has a variability in AA sequences |
|
|
|
What area of the antibody is responsible for antigen binding?
Clone cells have varying____. Antibody diversity is generated when and where? |
The combined Variable areas of both H and L chains
Variable regions generated during the B cell development in the bone marrow |
|
|
|
What areas of which chains determine the class of antibody?
What is significant of the same region of the opposite chain? |
The constant regions of the the Heavy chain
The Constant of Light has 2basic AA sequences that have the same function Kappa (60%) and lambda (40%) |
|
|
|
Antibodies are limited to binding _______ antigen (s)
|
2- b/c have two different poles with codes/receptors
|
|
|
|
What is a supergene family?
What is the "motif" in consideration when organizing supergene families? What does this suggest? |
Proteins that contain one or more domains that share a homolgous sequence
beta-pleated sheets stabilized by disulfide bonds They evolved from a common precursor |
|
|
|
What fragments are created from the cleavage of antibodies via Papain? Then What?
What about clevage by Pepsin? Where are the cleaves? |
Papain cleaves just inferior to the hinge region, creates two Fab (Antigen Binding Fragments) from the superior portion, the inferior portion is now the Fcr (Constant Fragment) of only heavy chain.
Pepsin cleaves inferior to the disulfide bond between the two heavy chians Leaving a Bivalent fragment still bound via disulfide and have hinge regions |
|
|
|
what are the two natural distribution types of antibodies?
|
Cell-Surface and Secreted
|
|
|
|
Cell surface antibodies are on the surface of what cells? how are they attached?
What do they do while they are there? |
They are on B lymphocytes, they are integral membrane glycoproteins, antigen receptors
They are also activators of particular immune cells with Fc receptors (monocytes, NK cells, Mast cells |
|
|
|
What secretions contain secreted forms of antibodies?
Explain Antiserum |
Mucosal Secretions
Interstitial fluid of tissues Plasma Antiserum is from the antibodies that remained in serum after a blood clot and are available in a detectable amount |
|
|
|
What are the biological effector functions of immunoglobins?
|
NO ABCD
Neutralization Opsonization ADCC B-lymphocyte activation Complement activation Degranulation of Mast Cells |
|
|
|
BCell Activation
Step 1 __________ acts as a BCR in complex with a disulfide linked _________ called _______ Step 2, this functions as the _______ pt of the BCR complex Step 3, the BCR gets _________ by antigen and activated!!! |
Membrane bound Immunoglobin (Antibodies) function as BCR in complex with disulfide linked heterodimer called Igalpha/Igbeta
this functions as the signaling portion crosslinking of BCR by antigen = activation |
|
|
|
Complement Activation
Certain_______ acivate the classical pathway of compliment, which is an important defense against _______. Neutralization is: How do antibodies promote neutralization? |
Complement Activation
Certain classes of antibodies acivate the classical pathway of compliment, which is an important defense against bacterial infection. Neutralization is: inactivation of a microbial product or counteraciton of a microorganisms infectivity How do antibodies promote neutralization? Binding to bacterial and viral surfaces prohibit attachment to surfaces. Inhibits colonization, viral infection |
|
|
|
Explain the four steps of opsonization:
First the bacteria are considered slippery, which means: Second: ______ bind to bacteria, and are received via their _______ at _______ on a macrophage or __________. Third:When bound the complex is phagocytosed and the slippery bacteria children are viciously slaughtered while their parents watch in horror |
Explain the four steps of opsonization:
First the bacteria are considered slippery, which means, they have slippery capsules that aren't detected by macrophages. Second: antibodies bind to bacteria, and are received via their Fc at FcReceptor on a macrophage or Neutrophil. Third:When bound the complex is phagocytosed and the slippery bacteria children are viciously slaughtered while their parents watch in horror |
|
|
|
ACDC... um ADCC
This is considered the bridge between ________ immunities. Several cell types are naturally ________ against cells presenting ______ on their surfaces. This applies to both ______ and _______/ |
Antibody Dependent Cell mediated Cytotoxicity
ACDC... um ADCC This is considered the bridge between humoral and cell-mediated immunities. Several cell types are naturally cytotoxic against cells presenting antibodies on their surfaces. This applies to both cells and microbes. |
|
|
|
What are the five cell types that actively participate in ADCC?
|
MMNNE
Mono Macro Neutro Nat'ral Eosin |
|
|
|
Explain Mast cell and Basophil degranulation
What Immunoglobin is in the membrane? What starts the whole shabang? Then what happens? |
IgE
Bacteria bind to the antibodies on the surface of the cell, The antibody/bacteria complex gets cross-linked This sends an unexplained message to discharge granules from the cell |
|
|
|
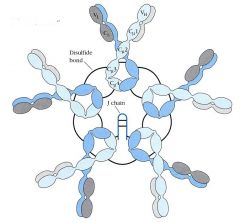
IgM
__% total serum antibody shape: plays role in ________ first antibody secreted during __________ Potent activator of _________ Serves as antigen receptor on _________ cells in the ________Form |
IgM
5-10 total serum antibody shape: pentagon plays role in neutralization first antibody secreted during primary response Potent activator of compliment Serves as antigen receptor on naive B cells in the monomeric Form |
|
|
|
IgG is the beast
|
yes
|
|
|
|
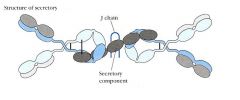
IgA
____% total secreted antibody __% total serum antibody produced in ____ Secreted during _______ response or _______ response Predominant class in _________ secretions including |
IgA
>50% total secreted antibody 10-15% total serum antibody produced in MALT Secreted during Memory response or late Primary response Predominant class in external secretions including saliva tears, breast milk, mucus, neutralizes antibody at mucosal surfaces |
|
|
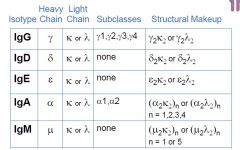
M
A D G E |
Mew
Alpha Delta Gamma Epsilon |
know these characteristics
Kappa or Gamma A and G have subclasses |
|
What Ig
%serum antibody Serum 1/2 life Role Special Points |
What Ig- IgM
%serum antibody 5-10% Serum 1/2 life- 5 days Role- neutralization Special Points 1-can trnasport across epithelium 2-first secreted during primary response 3-Potent activator of compliment 4-serves as antigen receptor on naive B cells (in the monomeric form) |
|
|
What Ig
%serum antibody Serum 1/2 life Role Special Points |
What Ig- IgG
%serum antibody- 80% Serum 1/2 life-25 days Role- neutralization Special Points -sensitizes NK cells for killing -predominant antibody in Memory response (late primary also) - crosses placenta -opsonizes antigens for phagocytosis -activates classical complement pathway |
|
|
What Ig-
%serum antibody Serum 1/2 life- Role- Special Points |
What Ig- IgA
%serum antibody- 10-15%, over .5 of total Serum 1/2 life- 6 days Role- Memory response and external secretions Special Points- in saliva, tears, breast milk, mucus, -important neutralizing antibody at mucosal surfaces |
|
|
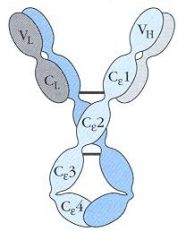
What Ig-
%serum antibody Serum 1/2 life Role Special Points |
What Ig- IGE
%serum antibody <1% Serum 1/2 life- 2-3 days Role- Bind IgE receptors on FceR complex on baso/mast. Secreted during memory response and late primary Special Points -Triggers secretion of inflammatory mediators when crosslinked by antigen (allergen) -Parasite defense via ADCC activation of eosinophils |
|
|
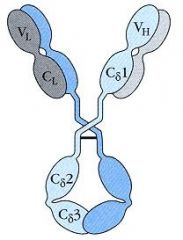
What Ig
%serum antibody Serum 1/2 life Role Special Points |
What Ig- IgD
%serum antibody <1% Serum 1/2 life 3 days Role- BCell acitvation Special Points -Not sure what it does as a secreted immunoglobin, -along w/ IgM, serves as a membrane bound antigen receptor on naive (unactivated) B cells |
|
|
|
IgG has four subclasses with different biological activity
However, |
We don't need to memorize the differences
|
|
|
|
_________ Deficiency
-Most common primary immunodeficiency - caused by a block in ______ |
Selective IgA Deficiency
-Most common primary immunodeficiency - caused by a block in B cell differentiation |
|

