![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
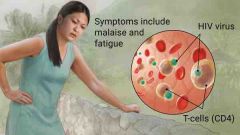
AIDS/HIV |
a disease in which there is a severe loss of the body's cellular immunity, greatly lowering the resistance to infection and malignancy. |
|
|
|
Allergy |
a damaging immune response by the body to a substance, especially pollen, fur, a particular food, or dust, to which it has become hypersensitive.Anti |

|
|
|
Antibiotic |
a medicine (such as penicillin or its derivatives) that inhibits the growth of or destroys microorganisms. |
|
|
|
Antibody |
a blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen. Antibodies combine chemically with substances that the body recognizes as alien, such as bacteria, viruses, and foreign substances in the blood. |
|
|
|
Antigen |
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies. |
|
|
|
B-Cells |
a lymphocyte not processed by the thymus gland, and responsible for producing antibodies. |
|
|
|
Dendritic Cells |
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as accessory cells) of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. |
|
|
|
Fever |
an abnormally high body temperature, usually accompanied by shivering, headache, and in severe instances, delirium. |
|
|
|
Histamine |
a compound that is released by cells in response to injury and in allergic and inflammatory reactions, causing contraction of smooth muscle and dilation of capillaries. |
|
|
|
Immunity |
the ability of an organism to resist a particular infection or toxin by the action of specific antibodies or sensitized white blood cells. |
|
|
|
Immunology |
the branch of medicine and biology concerned with immunity. |
|
|
|
inflammation |
a localized physical condition in which part of the body becomes reddened, swollen, hot, and often painful, especially as a reaction to injury or infection. |
|
|
|
interferon |
a protein released by animal cells, usually in response to the entry of a virus, that has the property of inhibiting virus replication. |
|
|
|
Lymph Nodes |
ach of a number of small swellings in the lymphatic system where lymph is filtered and lymphocytes are formed. |
|
|
|
Lymphocyte |
a form of small leukocyte (white blood cell) with a single round nucleus, occurring especially in the lymphatic system. |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
a large phagocytic cell found in stationary form in the tissues or as a mobile white blood cell, especially at sites of infection. |
|
|
|
Natural Killer Cell |
a lymphocyte able to bind to certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without the stimulation of antigens, and kill them by the insertion of granules containing perforin. |
|
|
|
Pathogen |
a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease |
|
|
|
Pus |
a thick yellowish or greenish opaque liquid produced in infected tissue, consisting of dead white blood cells and bacteria with tissue debris and serum. |
|
|
|
Pyrogen |
substance, typically produced by a bacterium, that produces fever when introduced or released into the blood. |
|
|
|
Spleen |
an abdominal organ involved in the production and removal of blood cells in most vertebrates and forming part of the immune system. |
|
|
|
T-Cells |
a lymphocyte of a type produced or processed by the thymus gland and actively participating in the immune response. |
|
|
|
Thymus |
a lymphoid organ situated in the neck of vertebrates that produces T cells for the immune system. The human thymus becomes much smaller at the approach of puberty. |
|
|
|
Tonsil |
either of two small masses of lymphoid tissue in the throat, one on each side of the root of the tongue. |
|
|
|
Toxin |
an antigenic poison or venom of plant or animal origin, especially one produced by or derived from microorganisms and causing disease when present at low concentration in the body. |
|
|
|
Vaccine |
a substance used to stimulate the production of antibodies and provide immunity against one or several diseases, prepared from the causative agent of a disease, its products, or a synthetic substitute, treated to act as an antigen without inducing the disease. |
|
|
|
Phagocyte |
a type of cell within the body capable of engulfing and absorbing bacteria and other small cells and particles. |
|

