![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The range of exposure intensities an image receptor can accurately detect determines its __________.
|
dynamic range
|
|
|
Film screen image receptors have a _______ dynamic range when compared to digital image receptors.
|
narrow
|
|
|
Which type of image receptor can accurately detect very low and very high exposure intensities.
|
Digital
|
|
|
These are used to convert radiographs recorded on conventional film into digital images.
|
film digitizers
|
|
|
Name the class of radiography that instantly produce digital images following exposure.
|
Direct digital
|
|
|
True or False
With conventional film image, the image is not permanent and further adjustments can still be made. |
False
A restriction to conventional film image is that the image is permanent and further adjustments cannot be made. |
|
|
Name some drawbacks of conventional film-screen imaging.
|
processing time
image is permanent, no changes possible limited contrast resolution (difficulty in recognizing differences between tissues of nearly identical subject contrast) archiving limitations/issues |
|
|
What are the similarities of digital and conventional imaging
|
1.)Exposure Factor selection
2.)Accurate positioning 3.)Accessory devices such as grids and collimators are still used 4.) A latent image is still produced, and is processed to form a manifest image |
|
|
True or False
In digital imaging, moderately underexposed or overexposed images will still be of acceptable diagnostic quality. |
True
Because digital image receptors can respond to a wider range of x-ray exposures. |
|
|
is the response of the image receptor in digital imaging curvilinear or linear.
|
linear
|
|
|
A matrix is a combination of _______ and _________
|
rows and columns
|
|
|
What is a pixel?
|
The smallest component, (picture element) of the matrix.
|
|
|
What does FOV stand for?
|
Field of view
|
|
|
increasing the matrix size _________ the # of pixels.
|
increases
|
|
|
A larger matrix has more pixels and better ____________ ?
|
spatial resolution
|
|
|
____________ is a combination of zeros and ones to process and store computer information.
|
Binary Number System
|
|
|
What is a computers basic unit of information?
|
A bit
|
|
|
When FOV is decreased, what happens to the resolution
|
Resolution improves
|
|
|
Pixels representing highly attenuating tissues (like bone) are assigned a (low/high) value for higher brightness.
|
Low
|
|
|
Digital imaging typically involves which three conceptual steps.
|
1.) Image Acquisition
2.) Image Processing 3.) Image Display Remember *( A public display ) of affection |
|
|
In digital fluoroscopy the exit radiation is absorbed by the ___________ and converted into electrons.
|
input phosphor
|
|
|
in digital fluoroscopy, once the exit radiation is absorbed by the input phosphor, and converted into electrons, where is it sent next?
|
to the output phosphor
|
|
|
in digital fluoroscopy, name the sequence of events that exit radiation goes through in order to be transmitted to the television monitor
|
1.) Input phosphor
2.) Converted in electrons 3.) Output phosphor 4.) Released as Visible light 5.)Television camera converts to electronic video signal for transmission to the television monitor |
|
|
Name some advantages of digital imaging as compared to Film screen imaging
|
-Images acquired and displayed quickly
-transmission of images, processing of images, interpretation of images on a display monitor, stored, retrieved via electronic means -Provide greater dynamic range -Greater contrast resolution |
|
|
A larger matrix has *(more/less) pixels?
|
more
|
|
|
If you are looking at an x-ray, and your FOV (field of view) is decreased what happens to the images resolution
|
The resolution is improved
(because as long as it's the same picture with the same matrix size you can see pixels better when they are farther away, and as your field of view is decreased (like zooming out on a photo) you see it better. |
|
|
What is a high attenuating tissue? Why is it high attenuating?
|
Bone
Because it makes x-rays lose intensity a lot faster than air. |
|
|
How is the numerical value of a pixel determined.
|
relative attenuation of x-rays passing through the corresponding volume of tissue
(like the value for bone is low because it's harder for x-rays to pass through bone, and low value = high brightness (low density) |
|
|
bit depth simply means the __________ of bits in each pixel.
|
number
|
|
|
What controls the exact pixel brightness and the precision with which the exit radiation is recorded?
|
The bit depth
|
|
|
Name the four main principles involved in Computed Radiography.
|
1.) The radiation exits the patient and interacts with the imaging plate.
2.)Photon intensities are absorbed by the photostimulable phosphor (PSP) 3.)Some of the energy is released as luminescence (visible light) 4.) Energy is captured in the plate to produce a latent image |
|
|
In CR, the imaging plate is put into a reader which converts the _______ image into a ________ image.
|
analog
digital |
|
|
In CR, once the imaging plate is placed in the reader, it is scanned with a ____________ which ________________.
|
helium - neon laser which releases stored energy into visible light
|
|
|
What does PMT stand for?
|
photomultiplier tube
|
|
|
What's the role of the photomultiplier tube in CR?
|
In the reader, it collects, amplifies, and converts light to an electrical signal.
|
|
|
True or False
Photostimuable phosphors can be reused up to 10,000 times before they need to be replaced. |
True
|
|
|
What does ADC stand for?
|
Analog - to - digital converter
|
|
|
Explain how the reader in CR erases the imaging plate before it is returned to service.
|
it is exposed to an intense white light to release any residual energy
|
|
|
What indicates the level of x-ray exposure received by the CR imaging plate.
|
numerical exposure indicator
|
|
|
Why is it important for the radiographer to consider the numerical exposure indicator.
|
because exposure errors affect the quality of the image and the exposure dose to the patient.
|
|
|
What percentage of underexposure may produce noisy images.
|
50% or greater
|
|
|
How does the radiographer know the expected range of x-ray exposure sufficient to produce a quality image
|
Each CR system specifies the expected range of x-ray exposure needed to produce a quality image.
|
|
|
What are the advantages of using a CR system?
|
1.) It's compatibility with existing FS equipment
2.) Higher dynamic range versus film screen |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of using CR.
|
1.) The amount of time needed for processing and image readout
2.) increased x-ray exposure when trying to achieve comparable image quality to film screen methods. |
|
|
following exposure, using a DR system, when are images available?
|
almost instantly
|
|
|
how are DR images processed?
|
by a computer workstation
|
|
|
What is a limitation of the charged coupled device.
|
limited to small field of view applications
|
|
|
When using a CCD, each pixel element functions as a __________, which stores a charge proportional to the intensity of incident light.
|
capacitor
|
|
|
___________ is a solid state array of light sensitive sensor elements, such as that found in digital cameras.
|
CCD
charged - coupled device |
|
|
in order for a CCD to function as an x-ray detector, it must be coupled with a _______________
|
scintillator
|
|
|
Flat panel digital receptors are constructed using _____________ arrays below a layer of attenuating material which converts x-rays into electrical charge.
|
TFT ( thin film transistor)
|
|
|
In Flat Panel Direct Capture Systems, what three things are already integrated into the flat panel device?
|
signal storage
signal readout digitizing electronics |
|
|
What are the advantages of flat panel direct capture systems?
|
1.) highly dose efficient
2.) provide quicker access to higher resolution compared with FS and CR |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of flat panel direct capture systems?
|
1.)incompatibility with existing equipment
2.)difficulty in mobile imaging |
|
|
The first image that is seen after acquiring a digital image is based on the _________ for that image.
|
histogram
|
|
|
Why is it important for the radiographer to indicate the correct radiographic prodecure?
|
So that the correct algorithm is performed
|
|
|
Following histogram analysis of a digital image, __________ provide a method of altering the image to change the display of the digital image.
|
LUT's look up tables
|
|
|
LUT's alter the ______ and _______ of an image.
|
brightness and contrast
|
|
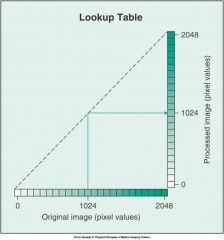
What does this graph represent
|
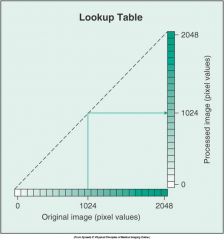
no pixel value change because of the straight line.
|
|
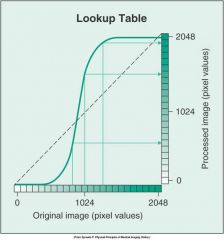
What does this graph represent
|
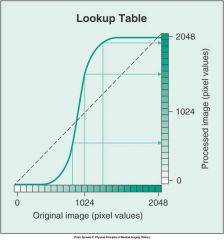
pixel value change because of the curved line
|
|
|
Once the image has been processed in a digital format it can be
A. displayed on a monitor (CRT) or (LCD) B. printed on film C. sent to a distant location D. Stored on magnetic tape or optical disk. E. All of the above |
E. all of the above
|
|
|
Visualizing a digital image of similar quality to a conventional film image requires that the display monitor have high spatial resolution, how many lines must a monitor have to achieve this?
|
1024 lines
2048 preferred |
|
|
_______ is manipulation by the radiographer or the radiologist for soft-copy viewing.
|
post-processing
|
|
|
a post-processing technique that can remove superimposed structures so that the anatomic area of interest is more visible
|
subtraction
|
|
|
A post-processing technique that alters the pixel value to increase image contrast.
|
contrast enhancement
|
|
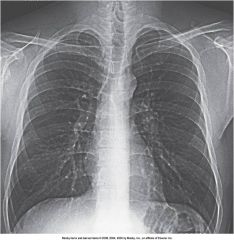
This image demonstrates an ____________ postprocessing technique
|
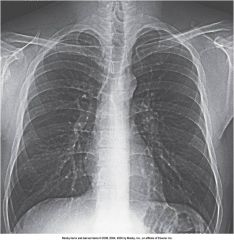
edge enhancement
|
|
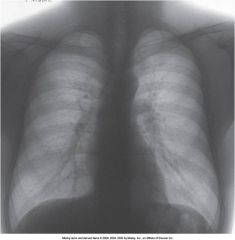
This image demonstrates a ______________ postprocessing technique.
|
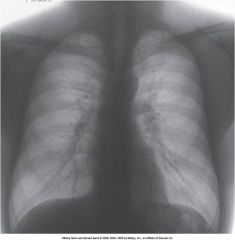
Black and White reversal postprocessing technique.
|
|
|
Which post processing technique suppresses image noise (quantum mottle).
|
Smoothing
|
|
|
Which postprocessing technique reverses the grayscale from the original image.
|
black/white reversal
|
|
|
Which post processing technique may degrade spatial resolution.
|
Smoothing
|
|
|
Which post-processing technique improves visibility of small, high contrast structures.
|
Edge enhancement
|
|
|
image noise may be slightly increased while using this post-processing technique.
|
edge enhancement
|
|
|
While the computer can adjust for under or overexposure, the radiographer should choose exposure factors based on __________ .
|
ALARA
|
|
|
Underexposure affects ________ and overexposure affects _________.
|
quantum mottle
patient dose |
|
|
when technologists inadvertently increase dose to avoid the appearance of noise in underexposed images.
|
dose creep
|
|
|
This sets the midpoint of the range of densities visible in the digital image.
|
Window level
|
|
|
greater window level > = (what type of brightness)
|
greater brightness
|
|
|
(less) < level = (what type of brightness)
|
less brightness
|
|
|
WIDE window width displays __________ with lower contrast differences
|
more densities
|
|
|
NARROW window width shows __________ with more differences from one another thus higher contrast.
|
fewer densities
|
|
|
Long Scale contrast = _______ window width
|
Wide window width
|
|
|
Short scale contrast = ________ window Width
|
Narrow window width
|
|
|
Manipulating ______ for desired level of contrast is not required with digital imaging because the computer can adjust the radiographic contrast.
|
kVp
|
|
|
_________ varies the range of densities visible
|
window width
|
|
|
How can a radiographer correct noise in digital imaging?
|
by increasing the mAs (photons)
|
|
|
The contrast resolution of the human eye is limited to about ________ shades of gray.
|
32
|
|
|
If the entire range of densities is displayed on an image (wide window width) the image has ________ contrast.
|
lower
|
|
|
When a smaller range of densities is displayed on an image (narrow window width) the image has ________ contrast.
|
higher
|
|
|
True or False
quantum mottle will always be visible on the radiographers monitor |
False
|
|
|
What can a radiographer refer to when trying to determine if an image has quantum mottle?
|
exposure index number in CR
|
|
|
What does PACS stand for.
|
picture archival and communication system
|
|
|
Why is it helpful to integrate RIS
(radiology information systems, HIS (hospital information systems), and PACS. |
So that images, patient data, and interpretations can be viewed simultaneously by people at different workstations.
|
|
|
a communication standard for sharing information between PACS and imaging modalities.
|
DICOM (digital imaging and communication in Medicine)
|
|
|
What does DICOM stand for
|
digital imaging and communication in medicine
|
|
|
a communication standard for medical information
|
HL7
|
|
|
How many bits are in a byte?
|
8
|
|
|
Recording Radiographic images as numerical data is _____________
|
Digital imaging
|

