![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
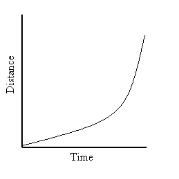
What does this graph show?
|
Non-linear Acceleration
|
|
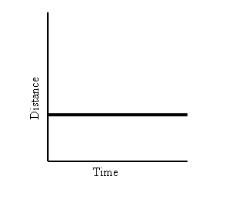
What does this graph show?
|
An object at rest (not moving)
|
|
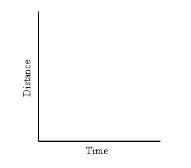
What type of graph is this?
|
Speed. D/T
|
|
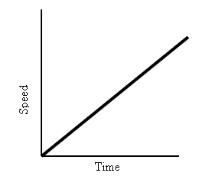
What does this graph show?
|
Constant Linear Acceleration
|
|
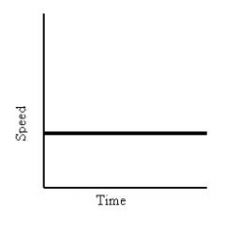
What does this graph show?
|
Constant Speed
|
|
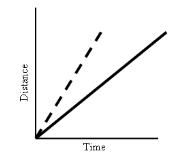
What does this graph show?
|
Constant Speed
|
|
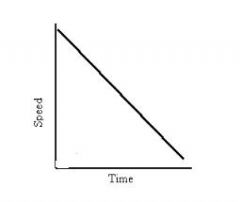
What does this graph show?
|
Deceleration/slowing down
|
|
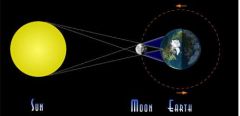
What type of eclipse is shown?
|
Solar Eclipse
|
|
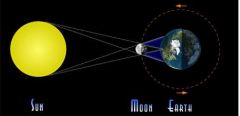
What phase of the moon is shown? How much light will we see on the moon?
|
New moon, we will see no light reflecting on the moon-the sky will be dark.
|
|
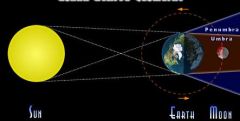
What type of eclipse is pictured?
|
Lunar Eclipse-Earth is casting a shadow on the moon. This is the most frequently seen type of eclipse, because the Earth casts a bigger shadow.
|
|
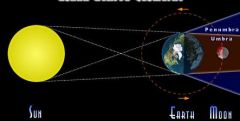
What phase of the moon is pictured? How much light would you see reflected by the moon?
|
This is the full moon orientation. You would see the whole face of the moon illuminated.
|
|

What is the ring of rocks shown called? Between which two planets is it located?
|
Asteroid Belt, found between Mars and Jupiter.
|
|

What is this thing? Which way does its tail point? What is it made out of?
|
Comet-the tail always points away from the Sun. It's made out of ice and rock.
|
|

What is this shooting star really called? What is it most likely made out of?
|
Meteor-probably Iron (Fe).
|
|
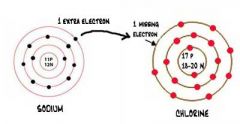
What type of bonding is pictured? What type of elements are involved in this type of bonding? What are the properties of this type of bond? What state of matter will you find it as at room temperature?
|
Ionic bonding-transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal. The metal becomes positive and the non-metal becomes negative. They have high melting and boiling points. They are solids at room temperature and are brittle (easy to break). They are considered weaker bonds.
|
|
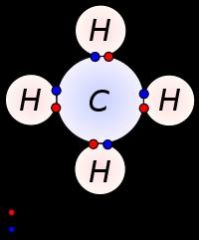
What type of bond is pictured? What types of elements are involved in this type of bonding? What are the characteristics of this type of bond?
|
Covalent, a non-metal is sharing electrons with another non-metal. These bonds have low melting/boiling points so they are found as liquids or gasses at room temperature.
|
|
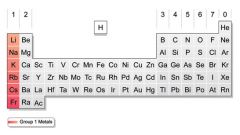
What is the name of the group that is highlighted on the periodic table? What makes this group so special? What are the properties of this group?
|
Group 1 Alkali Earth Metals. They are the most reactive elements on the periodic table, as they only need to lose 1 electron to become stable. They are soft, shiny, and pretty much explosive.
|
|
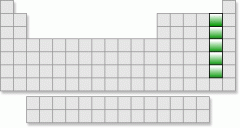
What is this group called? What are their properties? Why are they important?
|
Halogens-the most reactive non-metals. They have 7 valence electrons and only need one more to have a full valence level with 8.
|
|
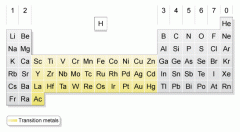
What do you call the elements highlighted above? What makes them important?
|
Transition metals, groups 3-12. They are the metals that are used to make everyday products.
|
|
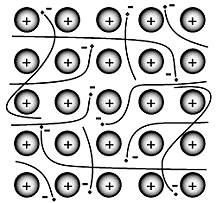
What type of structure is shown? What type of bond is this where electrons can travel freely?
|
Crystal lattice/matrix. It's a metallic bond.
|
|
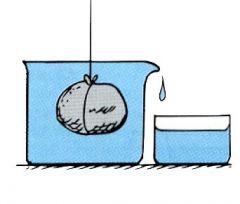
How much water is displaced?
|
An amount equal to the volume of the rock.
|
|
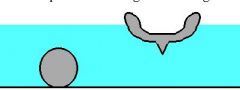
What does the buoyant force equal? Why does the ball sink and the ship hull float when they are the same mass?
|
Buoyant force equals the weight of the water displaced. In the case of the ship hull that's floating buoyant force equals the weight of the ship hull or it wouldn't float. The ship hull displaces more water than the ball as it has a larger volume so it floats.
|
|

What do you call a mixture in which the particles are big enough to settle out?
|
Suspension
|
|
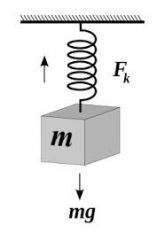
In this example, what force is labeled Fk in the upward direction?
|
Elastic Tension because the object is stretching the spring as it hangs down.
|
|

What type of force is shown in the spring?
|
Elastic Compression force, as you are compressing (squishing) the spring.
|
|
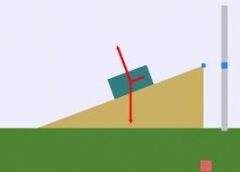
What is the upward force pictured? What is the downward force pictured?
|
The upward force is Normal Force aka Elastic Compression Force
The downward force is weight or gravity |
|

What is the atomic number of the element that is pictured?
What is the atomic mass of the element that is pictured? What is the charge of the element pictured? |
Atomic Number:11
Atomic Mass: 23 Charge: +1 |
|
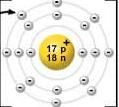
What is the atomic number of the element that is pictured?
What is the atomic mass of the element that is pictured? What is the charge of the element pictured? |
Atomic Number 17
Atomic Mass 35 Charge -1 one more Electron than Proton |
|
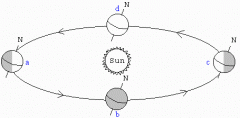
What events are pictured at a and c?
What events are pictured at b and d? |
A + C Winter and Summer Solstice
B + D Spring and Fall Equinox |
|
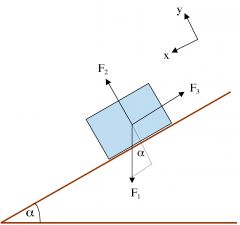
What are F1, F2, and F3?
|
F1 Gravity/Weight
F2 Normal Force F3 Friction |
|
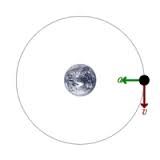
What two forces combine to form an orbit?
|
Gravity pulling in-ward and inertia going in a straight line.
|
|
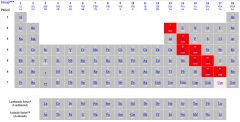
What type of elements are highlighted?
|
Metalloids
|
|
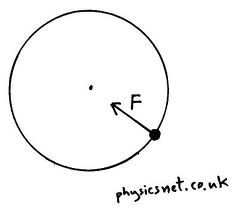
The force that makes things spin in a circle
|
Centripetal Force
|
|
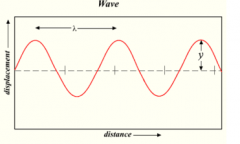
What quality is labeled y?
What quality is labeled lambda (the squiggly one) |
Y=Amplitude=wave height
Lambda= Wave Length |
|
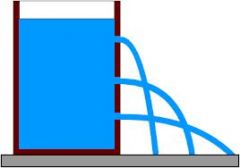
Why does the water squirt out farther on the bottom?
|
Pressure increases with depth because of all of the weight of the liquid on top.
|

