![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an image?
|
Continuous function that maps FROM:
> the reals in m dimensions (e.g. x, y, z co-ordinates or x, y co-ordinates and the frame number t in an image sequence) TO: > the reals in n channels (e.g. Red, Green, Blue colour values, or Hue, Saturation, Intensity values) |
|
|
What is aliasing?
|
The effect of taking sparser samples for an image
|
|
|
How is anti-aliasing achieved?
|
Filtering out frequencies above Nyquist limit
|
|
|
What is the Nyquist limit?
|
The Nyquist frequency is TWICE the maximum frequency present in a signal
|
|
|
What is the minimum frequency of sampling we can get away with without losing information?
|
The Nyquist frequency
|
|
|
What is quantisation?
|
Representing the values of a continuous function f(x) as discrete values
|
|
|
Continuous version of CONVOLUTION
|
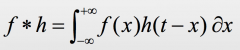
f * h = ∫ f(x).h(t−x) ∂x
(between -∞ and +∞) |
|
|
Discrete version of CONVOLUTION
|
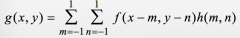
|
|
|
Discrete version of CORRELATION
|
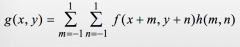
|
|
|
Give an example of a low pass filter kernel and its effect on an image
|
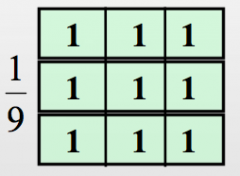
SMOOTHS IMAGE
|
|
|
Give an example of a high pass filter kernel and its effect on an image
|
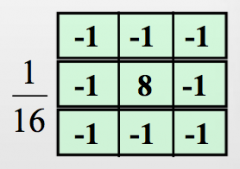
SHARPENS IMAGE
|
|
|
State the relationship between convolution and multiplication in the spatial and frequency domains
|
Convolution in spatial domain = multiplication in frequency domain and vice versa
|
|
|
Describe the process of low/high pass filtering using Fourier transform
|
- Transform image to Fourier space
- Remove low/high frequencies (a gradual removal of increasing/decreasing frequencies is a 'Butterworth' low/high pass) - Transform back to spatial domain |
|
|
Give the parametric equation that can be used to represent a 2D line
|
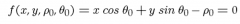
|

