![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
286 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the categories of the Standards?
|
Attribute Standards
Performance Standards Implementation Standards |
|
|
Definition of Internal Auditing
|
An independent assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations.
|
|
|
How does IA help an organization accomplish its objectives?
|
By bringing a systematic disciplined approach to evaluate and improve risk mgmt, control and goverance processes
|
|
|
What is the Professional Practices Framework (PPF)?
|
A full range of guidance for professionals consisting of the following mandatory, advisory & practical categories:
1) Code of Ethics 2) Practice Advisories 3) Development & Practice aids |
|
|
What is the purpose of "The Standards"
|
1) Delineate Basic Principles of IA
2) Framework for providing & promoting value-added activities 3) Establish a basis for evaluating IA performance 4) Foster improved organizational processes. |
|
|
What are the Attribute Standards?
|
1) Addresses the characteristics of organizations and individuals performing IA activities, and
2) Guidance for IA quality 3) Applies to all IA services |
|
|
What are the Performance Standards?
|
Describes the nature of IA activities & provides quality criteria against which the performance of these services can be evaluated
|
|
|
Definition of "Engagement"
|
1) A specific IA assignment, task or review activity
2) May include multiple tasks or activities designed to accomplish a set of related objectives. 3) May deal with industry-specific, regional or specialty services. |
|
|
What are Implementation Standards?
|
They expand on Attribute and Performance Standards and how they apply to types of engagements.
|
|
|
Describe types of Implementation Standards
|
There are multiple sets of Implementation Standards that apply to both Assurance and Consulting services
|
|
|
Definition of "Assurance Services"
|
An objective examination of evidence to provide an independent assessment of risk mgmt, control and governance processes.
|
|
|
Which parties are involved in an Assurance Engagement?
|
Process owner
IA User of the Assessment |
|
|
Define "Consulting Services"
|
Advisory and client-related svc activities, agreed with the client, intended to add value and improverisk mgmt, control and governance processes.
|
|
|
Consulting Svcs involve which two parties?
|
IA
Engagement client |
|
|
What is the intention of an audit activity?
|
1) Provide assurance that internal controls are in place and adequate to mitigate risks.
2) Ensure that org goals are met. |
|
|
What are Practice Advisories?
|
1) Endorsed guidance on best practices for performance of the Standards.
2) non-mandatory 3) Helps to interpret or apply standards. 4) Have ongoing updates 5) Submitted to a formal review process by IIA's Professional Issues Committee. |
|
|
Definition of Internal Audit Activity
|
A team of practitioners that provides independent, objective assurance & consulting svcs designed to add value & improve an organization's operations.
|
|
|
What is the function of the CAE in cases where IA activities are provided by outside svc providers?
|
1) To oversee svc contract
2) oversee quality assurance 3) report to Sr. mgmt & the audit committee of the Board 4) f/u with engagement results |
|
|
What is the IA Charter?
|
A formal document that defines the activity's purpose, authority and responsibility.
|
|
|
What should the IA Charter establish?
|
1) IA's pos'n within the organization
2) Authorize access to records, personnel & properties relevant to the engagement. 3) Define scope of IA activities. |
|
|
What are typical elements of the Audit Charter?
|
1) Mission & scope of IA
2) Accountability of CAE to mgmt & audit committee 3) Independence of IA 4) Responsibilities of CAE & staff 5) Range of authority of CAE & staff 6) Standards of IA practice to be met. |
|
|
Practice Advisory 1000-1
|
= "Internal Audit Charter"
1) IA Charter s/b in writing 2) A written stmnt provides formal communication 3) Facilitates a periodic assessment of the adequacy of IA's purpose, authority & responsibility. |
|
|
Types of engagements by CAE
|
Assurance
Consulting Mixed (blended) |
|
|
What is Practice Advisory 1000.C1-2?
|
"Additional Considerations for Formal Consulting Engagements"
1) Formal consulting engagements 2)Informal 3) Routine activities, i.e. standing committees, etc 4) Special consulting engagements |
|
|
How should a consulting eng. NOT be done?
|
NOT in an attempt to circumvent an Assurance Engagement, however an assurance eng. can become a consulting eng.
|
|
|
What are key documents that support the purpose, authority and responsibility of the audit department?
|
1) IA Charter
2) Function & Responsibility Stmt 3) Policies & Procedures 4) Audit Manual 5) Job Descriptions |
|
|
How to market IA function?
|
1)Brochures
2)Newsletters 3)Publications 4)Audit Open House 5)Advisory Board of Operating Managers 6)Client Training 7)Engagement Documents & Meetings |
|
|
Define Audit Independence
|
Freedom from conditions that threaten objectivity or the appearance of objectivity.
|
|
|
How should threats to audit objectivity be managed?
|
At the level of:
1) Individual Auditor 2) Engagement 3) Functional 4) Organizational |
|
|
Define audit objectivity
|
An unbiased mental attitude that allows internal auditors to perform engagements in such a manor that they have an honest belief in their work product and that no significant quality compromises are made.
|
|
|
Define Attribute Standard 1100 & PA 1100-1
|
"Independence & Objectivity"
IA activity s/b independent & auditors s/b objective |
|
|
Define Attribue Std 1110,
PA 1110-1,& 1110-2 |
"Oranizational Independence"
CAE s/report to a level within the org that allows the IA activity to fullfil its responsibilities. |
|
|
What is Implementation Std 1110.A1?
|
"Assurance Engagements"
IA activity s/b free from interference in determining scope of its work & communicating results. |
|
|
Attribute Std 1120?
|
"Individual Objectivity"
IA auditors s/have impartial, unbiased attitudes & avoid conflicts of interest. |
|
|
Attribute Std 1130?
|
"Impairments to Independence or Objectivity"
If Independence or Objectivity is impaired in fact or in appearance, the details of the impairment s/b disclosed to the appropriate parties |
|
|
Implementation Std 1130.A1 (Assurance Eng.)
|
IA auditors s/not audit operations for which they were previously responsible. Otherwise objectivity is assumed to be impaired.
|
|
|
Implementation Std 1130.A2 (Assurance Eng.)
|
Assurance Eng. for functions over which CAE has responsibility s/b overseen by a party outside of IA activity.
|
|
|
Implementation Std 1130.C1 (Consulting)
|
IA may provide consulting svcs relating to operations for which they had previous responsibilities
|
|
|
Implementation Standard 1130.C2 (Consulting)
|
If IA auditors have pot'l impairments to Independence or Objectivity, relating to proposed consulting svcs, disclosure s/b made to the client prior to accepting the eng.
|
|
|
Show IA Dual Reporting Structure
|
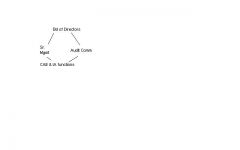
|
|
|
What is meant by functional reporting re: the CAE?
|
FR provides the ultimate source of independence & authority.
|
|
|
Describe PA 1110-2
|
"CAE Reporting Lines"
Provides examples of Governing Authority: -Approve IA Charter -Approve IA Risk Assessment -Approve Audit Plan -Receive Communication from CAE -Approve hiring / firing of CAE & compensation -Ensure resources for IA |
|
|
Describe administrative reporting of the CAE.
|
A.R. facilitates the day-to-day operation of the IA function.
|
|
|
PA 1110-2?
|
Administrative reporting examples including:
-budget & mgmt acctg -HR admin -IA communication & info. flow -admin of P&Ps |
|
|
What are other benefits of dual reporting?
|
Supports:
-appropriate flow of information -access to key executives / mgrs -appropriate reporting of IA results |
|
|
What are ways that the CAE can ensure proper alignment in order to achieve audit independence?
|
-regular & direct comm with board
-Report to sr. Exec w/ stature -Report to audit comm or equiv. -CAE allowed to meet privately w/audit comm |
|
|
What policies w/ help promote objectivity?
|
-IAs s/have no operational responsibilities
-No assurance audit of operations where auditor worked 1 yr. ago. -A policy to enforce code of ethics -IA s/not subordinate judgement to others -No quality compromises -remain objective -avoid conflicts of interest. |
|
|
What can help ensure that objectivity has been followed during an eng.?
|
Ongoing assessment
|
|
|
What practices can help perpetuate individual objectivity?
|
-CAE s/periodically query IA staff re: conflicts of interest.
-IA assignments s/b rotated periodically -IA s/not accept gifts, etc. |
|
|
What are some examples of impediments to objectivity according to the Standards Glossary?
|
Impairments may include:
-personal conflicts of interest -scope limitations -restrictions on access to records, etc. -resource limitations |
|
|
What should the CAE do in the case of impediments in Independence & objectivity?
|
The CAE s/report these situations or reassign the auditor
|
|
|
What are some examples of scope limitations?
|
-defined scope in the Charter
IA's access to records, personnel & properties -Approved engagement work schedule -Performance of necessary procedures -Approved staffing plan -Final budget |
|
|
What should the CAE do in the event of scope limitations?
|
Report them to the board
|
|
|
What are the differerent ways that the IA can be staffed?
|
-in house audit staff
-total outsourcing (on an ongoing basis) -partial outsourcing (ongoing) -co-sourcing w/ external auditors to supplement specialist skills -Subcontracting: External party to source part of an eng.or of a specific Eng. In this case is managed by in-house staff. |
|
|
Attribute Std 1200?
|
Proficiency & Due Prof'l Care
|
|
|
Attribute Std 1210?
|
"Proficiency"
IAs s/possess the knoledge, skills and other competencies needed to perform thier responsibilities. |
|
|
Implementation Std 1210.A2 (Assurance)?
|
IA s/have sufficient knowledge to identify indicators of fraud, but, is not expected to have the same expertise of a person whose primary resp. is detecting & investigating fraud.
|
|
|
Implementation Std 1210.A3?
|
IAs s/h knowledge of key info. of IT risks, controls & available IT-based audit techniques to perform work, however, not all IAs are expected to have the expertise of an IA whose primary resp. is IT auditing.
|
|
|
Define Knowledge
|
A body of information necessary to perform IA activity
|
|
|
Define Skills
|
A level of proficiency needed to perform IA activity
|
|
|
Define Competencies
|
Collective knowledge, skills & abilities & personal attributes that lead to exceptional performance = "critical success factors"
|
|
|
Define Proficiency
|
Facilitates the gathering of sufficient evidence that a control is working.
|
|
|
Define Understanding
|
i.e. IA completes training to learn about a process & the objectives of the organization.
|
|
|
Define "Appreciation"
|
IA is able to recognize indicators of successful activity, opportunities for process enhancements, or potential fraud or red flags.
|
|
|
What should an IA have Proficiency in?
|
-Standards, techniques, & procedures.
-Acctg principles & techniques (if required, or other technical knowledge) |
|
|
What should an IA have an UNDERSTANDING of?
|
Mgmt principles & good business practices
|
|
|
What should an IA have an APPRECIATION of?
|
Subjects such as acctg, econ, commc'l law, tax, finance, quant methods, IT, etc. depending on the nature of the organization.
|
|
|
Why are oral and written skills necessary?
|
-To efficiently communicate & deal with engagement clients to convey:
-Eng objectives -Evaluations -Conclusions -Recommendations |
|
|
What do other essential skill sets include?
|
-In-depth understanding of org's industry
-IA Stds & best practices -Knowledge & skills for implementing & improving processes in Finc'l & operational areas. -Prof'l certifications |
|
|
What is the CAE responsible for in order to ensure a successful outcome of an audit activity?
|
Determining appropriate levels of experience & education depending on scope of work and level of responsibility.
|
|
|
Define "career path"
|
Process by which individuals progress through stages in their career.
|
|
|
Define "Job Analysis"
|
systematic study of a job to determine the activities & responsibilities the job entails.
-including required personal qualifications & conditions under which the job is performed. |
|
|
Define "Job Description"
|
An outcome of a job analysis. a written summary of the most important features of a job, including
-req'd taasks -knowledge -skills -abilities -reporting structure |
|
|
Define "Job Specification"
|
An outcome of a job analysis; written statements that spell out necessary qualifications for the eprson in the job in order to perform it properly.
|
|
|
Define "Performance Appraisal"
|
A method of measuring employee's adherence to performance standards & providing feedback on performance.
|
|
|
Define "Recruiting"
|
The process of identifying potentially qualified employees (internal or external) and encouraging them to apply for job openings.
|
|
|
Define "Retention"
|
Ability to keep talented employees in an organization.
|
|
|
Define "Selection"
|
The process of hiring the most suitable candidate for the job.
|
|
|
What should the outcome of successful staffing be?
|
The IA staff should collectivel possess the knowledge, skills and experience essential to the practice of the profession in the organization.
|
|
|
Why should an annual analysis of an audit dept's knowledge & skill set be performed?
|
To help identify areas of opportunity that can be addressed by continuing professional development, recruiting, or co-sourcing
|
|
|
What are the steps for evaluationg staff professional proficiency?
|
1)Review educational background of IA staff
2) Review staff & mgmt job descriptions 3) Review info. re: req'd special skills 4) Staffing analysis |
|
|
When is co-sourcing & out-sourcing necessary?
|
When unique competencies & special skills are not available to fulfill an audit activity.
|
|
|
What should the CAE do to support of compliment areas in IA where a skill set is not completely proficient?
|
Source from outside the org.
|
|
|
What are the risks to planning or accepting assignments that cannot be staffed competently?
|
Can potentially expose the org. to inadequate evaluation of the effectiveness of risk mgmt, control and governance.
-Provides false assurances that also weaken the role of IA |
|
|
What is the distinction between co-sourcing and out-sourcing?
|
Co-Sourcing: external provider supplements internal staff.
Outsourcing: Takes the IA function and pays outside staff to handle it. |
|
|
What are the ADVANTAGES of co-sourcing and outsourcing?
|
-frees IA resources for other activities
-Provides flexibility -can improve efficiency -can reduce expenses -saves office space -provides coverage of remote locations -improves quality or timeliness of audit work |
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES of co-sourcing & out-sourcing?
|
-possible more cost for specific skills
-loss of in-house capabilities & process control --more pot'l for poor staff morale --requires oversight & coordination to manage -pot'l for privacy & confidentiality issues -loss of IA activities as a training ground for IA staff |
|
|
What should the CAE consider to determine if the outside provider has the necessary knowledge, skills and other competencies?
|
-prof'l certifications, licenses, etc.
-member of prof'l organizations -reputation of the provider -experience in the type of work being contracted for. -relevant education & training -knowledge & experience in the industry |
|
|
What should the CAE consider when assessing the relationship with outside svc providers?
|
-ensure independence & Objectivity are maintained
-determine that there are no conflicts of interests to impede objectivity |
|
|
What Items s/b reviewed with the outside svc provider? -Where should these be documented?
|
-scope & objectives of work
-specific items to be covered -access to records, personnel, property -info. regarding assumptions & procedures -ownership & custody of wkg papers -confidentiality & restrictions =s/b documented in the Engagement Letter |
|
|
What is the area where the services of an outside advisor are often retained?
|
Fraud
|
|
|
Define "Fraud"
|
Any illegal act characterized by deceit, concealmenmt or violation of trust.
-Not dependent on violaence or use of force |
|
|
Describe PA 1210.A2-1 & give examples
|
"Auditor's responsibility related to fraud risk assessment, prevention & detection"
-acceptance of bribes -diversion of profitable business -ebezzlement, cover-up & theft -intentional concealment or misrepresent ation of facts -false claims of svcs or products provided -intentional failure to act when reqired -unauthorized or illegal use of property or IT. |
|
|
Regarding PA1210.A2-1, what are guidelines & guidance of IAs responsibilities?
|
"Detecting fraud during engagements"
-consider fraud in assessment of control design -have sufficient knowledge of fraud to detect red flags -be alert to opportunities that would allow fraud -evaluate the indicators of fraud & determine if further action is necessary -notify appropriate authorities if fraud has occurred. |
|
|
Are all IAs expected to be fraud experts?
|
No, but they are expected to understand enough about internal audit controls to identify opportunities for fraud.
-Ias s/understand fraud schemes, ecenarios & signs that point to fraud. |
|
|
Describe Implementation standard 1210.A3 (Assurance)
|
"IAs s/have knowledge of key IT risks and controls and available audit techniques to perform thier assigned work.
However, not all IAs are expected to have the expertise of an IA whose primary responsibility is IT auditing. |
|
|
Define "Due Professional Care"
|
The application of care & skill expected of a reasonably prudent & competent IA in the same or similar circumstances.
-Due Prof'l care is exercised when audits are performed in accordance with the Standards. |
|
|
What is Attribute Standard 1200?
|
"Proficiency & Due Professional Care"
-eng s/b performed w/proficiency & due prof'l care. |
|
|
What is Attribute Standard 1220?
|
"Due Prof'l Care"
-IAs s/apply the care & skill expected of a reasonably prudent & competent IA. -Due Prof'l Care does not imply infallibility |
|
|
Waht is implementation Standard 1220.A1 (Assurance)
|
IAs s/exercise Due Prof'l Care by considering:
-work needed to complete eng. objectives -Relative complexity, materiality, or significance of matters of assurance eng. -adequacy & effectiveness of risk mgmt, controls and governance processes -probability of significant errors, irregularities, or non-compliance. -cost of assurance vs. benefits |
|
|
What is Implementation Standard 1220.A2 (Assurance)
|
In exercising Due Professional Care, the IA s/consider the use of computer-assisted audit tools & other data-analysis techniques.
|
|
|
Describe Implementation Standard 1220.A3 (aSSURANCE)
|
The IA s/b alert to significant risks that might affect objectives, operations or resources.
-However this does not gty that all significant risks w/b identified. |
|
|
Describe Implementation Std 1220.C1 (Consulting)
|
IAs s/exercise Due Prof'l Care when performing a consulting eng.by considering:
-needs & expectations of clients including the nature, timing & type of comm. of results. -Relative complexity & extent of work needed to achieve eng. objectives. -cost of consulting eng. vs. benefits |
|
|
What are the implications of "Due Prof'l Care?
|
-IAs s/b independent of the activities they audit
-IA s/b performed by people who collectively possess the necessary knowledge, skills & disciplines to conduct the audit properly & objectively -All work must be planned & supervised -Audit reports must be clear, concise, constructive & timely -IAs s/follow up on reported finding to ensure action is taken. |
|
|
Describe PA 1220-1
|
"Due Prof'l Care"
-implies reasonable care & competence, not infallibility or extraordinary performance. -Due care requires the IA to conduct examinations & verifications to an extent that is reasonable, but does not require a detailed review of every single transaction. |
|
|
In exercising Due Prof'l Care, what s/an IA do?
|
-apply care & skill expected of a reasonably prudent & competent IA in the same or similar circumstances & appropriate to the complexity of the eng. being performed.
-be alert to the possibility of internal wrongdoing, errors, omissions, inefficiencies, waste ineffectiveness & conflicts of interest. -be alert to where irregularities are most likely to occur. -identify inadequate controls & recommend improvements. |
|
|
What are "Engagement Objectives"
|
Broad statements, developed by IA, that define intended engagement accomplishments.
|
|
|
Define "risk" from an audit point of view.
-How is it measured? |
Risk is the possibility of an event occuring that will have a negative impact on the achievement of objectives.
-Risk is measured in terms of likelihood and impact. |
|
|
What are examples of NOT exercising Due Prof'l Care?
|
The failure to recognize an indicator, or red flag, of fraud.
-performing an audit of each dept. every three years w/o regard to relative risks or importance of the dept. |
|
|
What are similarities & differences of consulting vs. assurance engagements?
|
Similariries:
-Due Prof'l Care -Relative work -Complexity Differences: -Needs & expectations of clients have increased significance. |
|
|
What is PA 1000.C1-2?
|
Relates to multiple Implementation Standards for consulting eng. Ias s/understand:
-needs of clients, incl. nature, timing & type of comm. -poss motivations for requesting the eng. -extent of work needed. -skills & resources needed -effect of audit comm. on scope of audit -pot'l impact on future audit assignments -pot'l benefits to org. from assignment |
|
|
Give examples of Due Prof'l Care PRINCIPLES during CONSULTING assignments.
|
-working knowledge of IIA Standards
-An understanding of org. objectives for requesting the assignment -Providing objective comments about the proposed process or activity. |
|
|
What would exemplify a LACK of DPC during CONSULTING engagements?
|
Acccepting an engagement w/o knowledge, experience or supervision in a subject area
|
|
|
Give examples of DPC PRINCIPLES
|
Includes: wkg knowledge of IIA standards,
-Understanding of "COSO"(Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) Framework of Internal Controls. -Awareness of org. objectives. -Knowledge of IAs systematic, disciplined approach to evaluating risk mgmt, control & governance processes. |
|
|
What is gained by Continuous Prof'l Development?
|
The means by which members of a profession maintain, improve and broaden the knowledge, skills & competencies required in their professional lives.
|
|
|
Describe Attribute Std 1230
|
"Continuous Prof'l Development"
-IAs s/enhance thier knowledge, skills & other competencies through continuing prof'l development. --IAs are resp. for CPD to maintain thier proficiency. -They s/keep informed about improvements & current developments in IA stds, procedures & techniques. |
|
|
Continuing Prof'l development may be accomplished via which activities?
|
-occupational assignments
-mentoring -networking -training -rsch projects -collective info. from synthesizing info. -formal education -conferences -certification & re-certification |
|
|
What continuing education opportunities are provided by the IIA?
|
-seminars
-conferences -web-based training -Vision University (designed for CAEs who want to take thier org. to a new level of excellence) |
|
|
Define "Certification"
|
The systematic measurement of characteristics, such as education & experience, that results in recognition of the individual as one who meets the suggested knowledge and other minimum requirements for a position or a profession
|
|
|
Describe Attribute Standard 1312
|
="External Assessments"
-s/b conducted once every 5 years -by a qualified independent reviewer or team. -need for more frequent reviews = discussed between CAE & the board. -s/also consider size, complexity & industry of the organization vs. experience of the reviewing teams. |
|
|
Describe Attribute Standard 1320.
|
"Reporting on the Quality Program"
-CAE s/communicate the results of external assessments to the board. |
|
|
Describe Attribute Standard 1330.
|
Use of "Conducted in Accordance with the Standards"
IAs are encouraged to report that thier activities are "conducted in accordance with the standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing" -only if the assessments of the Quality Improvement Program demonstrate that IA activity is in compliance with these standards. |
|
|
Describe Attribute Standard 1340.
|
="Disclosure of non-compliance"
-There may be situations where IA activity does NOT comply with the Standards & where auditors do NOT comply with the Code of Ethics. -In this case, disclosure s/b made to Sr. Mgmt & the board. |
|
|
Define Attribute Standard 1300 & Practice Advisory 1300-1
|
"CAE s/b responsible for establishing & maintaining QA & IP"
PA 1300-1: Quality Assurance & Improement Program states "the CAE s/b accountable for implementing processes that are designed to provide reasonable assurance to stakeholders that 1) it performs in accordance with its Charter (consistent with Standards & Code of Ethics), 2) Operates effectively & efficiently 3) Adds value & improves operations |
|
|
What are key elements of a QA&IP program?
|
QA & IP elements range from:
-policies & procedures development, -record-keeping functions -for IA activities, specifically: 1) Oversee develppment & implementation of IA policies & procedures; administer & maintain P&P manual -Assist CAE& audit mgmt w/budgeting & finc'l administration for the IA activity. 3) Maintain & update the Audit Risk Universe -oversee division of responsibilities among internal & external staff. |
|
|
...Continuation of elements of QA&IP program...
|
4) Administer of operation of process for evaluation of audit risk & long range planning.
5) Assist w/ overall scheduling process for audit & consulting engagement. 6) Assist IA mgmt w/ acquisition, maintainance & employment of audit tools & technology 7) administer external recruitment & int'l staff rotation & mgmt development 8) Oversee training & development of staff |
|
|
What are elements of a QA&IP program...continued...
|
9) oversee the system for IA statistics, metrics, & other post-audit surveys.
10) administer & monitor QA&IP program 11) oversee & administer information gathering & summary reports to Sr. mgmt & audit committee. 12) administer the f/u database for action plans 13) assist CAE, audit, mgmt, & IA staff to keep current w/Standards, best practices, other changes, etc. |
|
|
Describe the scope of Internal Assessments
|
Internal Asssessments s/include:
1) Routine & continuous supervision & testing of the performance of audit consulting work. 2) Ongoing analysis of performance metrics. 3) Validation of compliance w/laws & standards 4) Validation of compliance w/Standards & ethics. 5) Evaluate adequacy of IA activity,charter, P&Ps, goals, etc. 6) Assess contribution to an organization's governance, risk mgmt & controls. 7) Evaluate effectiveness of QA&IP. |
|
|
PA1311-1
|
Provide extensive guidance in establishing performance measures for reviews of IA activities:
-In consideration of Standards & Best Practices -No single set of Standards that is universally effective. -Qualitative & Quantitative |
|
|
What are requirements for external reviews?
|
-s/b independent of organization & IA dept.
-s/b competent in IA external assessment process. |
|
|
What types of teams are acceptable for external quality assessment reviews?
|
First is a team totally independent of the organization & available from IIIA or consulting organizations?
A second type of external assessment team is a self-assessment w/independent validation by an independent reviewer. Third type of external assessment team is a peer review team made of members of at least three different organizations. |
|
|
What skill sets should an external review team possess?
|
-IT experience
-Industry experience & knowledge -Other specialized disciplines: * Acctg * Tax * Environmental etc. |
|
|
What are critical considerations in the selection process?
|
Integrity & Objectivity
|
|
|
What does PA1312-1 recommend?
|
=External Assessments s/have a broad scope of coverage, including:
1) Compliance w/Standards & Ethics 2) Expectations of IA activity by mgmt, board, etc. 3) Integration of IA into organization governance process. 4) Tools & techniques used by IA. 5) Mix of knowledge & expertise of the staff. 6) Determination whether it adds value. |
|
|
Describe reporting requirements for both internal and external assessments
|
Internal: CAE s/share results, action plan & implementation with stakeholders such as Sr. mgmt, board, external audit, etc.
External: Preliminary results discussed with CAE during & at conclusion of process. Final results communicated in formal report to the CAE w/copis to mgmt & the board. |
|
|
What should the formal report for external assessments include?
|
-An opinion as to whether IA's stmnt is in conformity with Standards and Ethics.
-Compliance with IA's Charter & other Standards & best practices. -Provide recommendations for improvement. CAE s/communicate specifics of planned remedial action. |
|
|
What are three phrases that can be used to indicate conformity with the Standards?
|
-In Compliance
-In Conformity -In Accordance |
|
|
What requirement must be made in order to mainternal assessments.ke the assertion that Ia is in conformity with the Standards?
|
Requires an external assessment at least once every five years along with ongoing & periodic
|
|
|
What does the IIA Quality Assessment Manual provide?
|
-specific guidelines for internal assessment, reporting & f/u, including:
1) to reinforce the independence & objectivity of the assessment team -CAE team s/agree with format of reporting 2) CAE s/document an action plan & timeline 3) Final report copies s/include action plan 4) Not required, but may send copies to sr. mgmt, audit committee & the board |
|
|
According to the IIA Quality Assessment Manual, what is the most important determination of the external assessment?
|
The team's evaluation of the IA's conformity with:
-The Standards -its Charter -Extent & use of current best practices -Program of continuous improvement |
|
|
In most organizations, how does the process of the typical external assessment unfold?
|
1) External assessment results are reported to Sr. mgmt & audit committee, documented in an external QA report.
2) Lead person from external team to make presentations to mgmt & audit committee. 3) Planned actions of CAE to improve process 4) CAE reports to audit committee on implentation of process improvements. |
|
|
How does the Standards Glossary define the Code of Ethics?
|
- Principles relevant to the profession& practice of internal audit& the Rules of Conduct that describes expected behavior of IAs
-Applies to Persons & entities that provide IA services |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Code of Ethics?
|
-The purpose is to promote an ethical culture in the global profession of internal auditing
|
|
|
What are the Principles of the IIA Code of Ethics?
|
Integrity
Objectivity Confidentiality Competency |
|
|
What are the Rules of Conduct as it applies to the Integrity Section of the Code of Ethics?
|
1.1 IAs s/perform thier work with honesty, diligence & integrity
1.2 IAs s/observe the law & make disclosures expected by the law & the profession 1.3 IAs s/not knowingly be a party to illegal activity or engage in questionable acts. 1.4 IAs s/respect & contribute to the legitimate & ethical objectives of the organization. |
|
|
What are the Rules of Conduct as it applies to the Objectivity Section of the Code of Ethics?
|
2.1 IAs s/not participate in any activity or relationship that may impair thier unbiased opinion.
2.2 s/not accept anything which may impair thier professional judgement 2.3 s/disclose all material facts that, if not disclosed, may distort the reporting of activities under review. |
|
|
What are the Rules of Conduct as it applies to the Confidentiality Section of the Code of Ethics?
|
3.1 s/b prudent in the use and protection of information acquired on duty
3.2 s/not use information for personal gain or in any illegal manner or detrimental to legitimate objectives of the organization. |
|
|
What are the Rules of Conduct as it applies to Competency Section of the Code of Ethics
|
IAs:
4.1 s/engage only in those services for which they have the required knowledge, skills & experience. 4.2 Shall perform IA services in accordance with the Standards 4.3 s/continually improve thier proficiency & effectiveness & quality of thier services |
|
|
What is meant by the Proficiency Level?
|
This means that the IA is not only responsible for comprehension & recall, but also for higher level mastery including application, analysis, synthesis & evaluation
|
|
|
What are the collective defining activities of an organization that largely determines an organization's ability to succeed in the marketplace?
|
Risk
Control Governance |
|
|
How does IA help an organization manage risk?
|
1) Identify & evaluate significant exposures to risk
2) Contribute to the improvement of risk mgmt & control systems 3) Monitor & evaluate the risk mgmt system |
|
|
How does IA help maintain effective Controls?
|
-Evaluation the effectiveness & efficiency of controls
-Promoting continuous improvement of the control environment. |
|
|
How does IA help an organization address & make recommendations for improving governance?
|
-Promoting appropriate ethics & values
-Ensuring effective org. performance, mgmt & accountability -Effectively communicating risk & control information to appropriate areas of the organization. -Effectively coordinating the activities & communicating information among the board, IAs & mgmt. |
|
|
Define
Acceptable Risk |
A type of risk that revolves around the business impact that would be experienced if certain risks became realized.
|
|
|
Define
Acceptable Risk Level |
A risk level derived from an organization's legal & regulatory compliance responsibilities, its threat profile and its business drives and impacts.
|
|
|
Define
Adequate Control |
-A level of control that is present if mgmt has planned & organized in a manner that provides reasonable assurance that the org's risks have been managed effectively and that the org's goals & objectives w/be achieved efficiently & economically.
|
|
|
Define
Compliance |
Conformity & adherence to policies, plans, procedures, laws, regulations, contracts or other requirements.
|
|
|
Define
Control |
Any action taken by mgmt, the board, & other parties to manage risk & increase the likelihood that established objectives & goals w/be achieved.
|
|
|
Define
Control Deficiency |
A condition that warrants attention as a potential or real shortcoming that leaves an organization excessively at risk.
|
|
|
Define
Control Environment |
The attitude & actions of the board & mgmt regarding the significance of control within the org.
-The control environment provides the discipline & structure for the achievement of the primary objectives of the system of internal control |
|
|
The Control Environment includes what primary elements?
|
-Integrity & ethical values
-Mgmt philosophy & operating style. -Organizational Structure -Assignment of authority & responsibility -HR policies & practices -Competence of personnel |
|
|
Define
Control Processes |
The policies, procedures & activities that are part of a control framework designed to ensure that risks are contained within risk tolerances established by the risk mgmt process.
|
|
|
Define
Enterprise Risk Mgmt (ERM) |
A structured, consistent & continuous process across the whole org. for identifying, assessing, deciding on, responding to and reporting on opportunities & threats that affect the achievement of objectives.
|
|
|
Define
Event |
An incident or occurrence resulting from external or internal sources that affects the implementation of strategies or achievement of objectives.
|
|
|
Define
Impact |
The result or effect of an event
|
|
|
Define
Inherent Limitation |
Limiations of Risk Mgmt, Control & governance related to human judgement, resource limitation and the need to balance the costs pf controls vs. benefits.
-Condiders the reality of breakdowns occurring & the possibility of mgmt override & collusion |
|
|
Define
Inherent Risk (Absolute Risk) |
The risk derived from the environment without the mitigating effects of internal controls.
|
|
|
Define
Likelihood |
The probaility that a given event will occur
|
|
|
Define
Opportunity, as related to risk |
An uncertain event with a positive outcome
|
|
|
Define
Pervasive Risk |
The type of risk found throughout the environment
|
|
|
Define
Residual Risk |
The risk remaining after management takes action to reduce the impact and likelihood of an adverse event, including control activities in responding to a risk.
|
|
|
Define
Risk |
The possibility of an event occurring that will have an impact on the achievement of objectives; measured in terms of impact and likelihood.
|
|
|
Define
Risk Appetite |
The amount of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of value
|
|
|
Define
Risk Assessment (a.k.a. Risk Analysis) |
The identification and measurement of risk and the process of prioritizing risk.
|
|
|
Define
Risk Classification |
The assignment of risk into categories, such as financial risk, operational risk, strategic risk or reputational risk
|
|
|
Define
Risk Identification |
The method of recognizing possible threats and opportunities.
|
|
|
Define
Risk Mgmt (Standards Glossary) |
A process to identify, assess, manage, and control pot'l events or situations, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of the organization's objectives.
|
|
|
Define
Risk Measurement |
The evaluation of the magnitude of risk
|
|
|
Define
Risk Prioritization |
Ranking risks, formally or informally.
|
|
|
Define
Risk Response |
The actions taken to manage risks
|
|
|
Define
Risk Tolerance |
The acceptable levels of variation relative to the achievment of objectives
|
|
|
Define
Uncertainty |
A condition where the outcome can only be estimated
|
|
|
How does mgmt measure an event?
|
In terms of likelihood and impact
|
|
|
What are some common likelihood factors?
|
-Probability estimates
-Complexity of Activities -Change or stability -Control environment -Control process effectiveness |
|
|
Name some common Impact Factors
|
-Materiality
-Pot'l reputation damage -Impact on or's mission -Event duration -Recovery & costs |
|
|
What is a Risk Map?
|
Four quadrants based on likelihood (hi, lo)& impact (hi,lo)
|
|
|
What is the purpose of internal controls?
|
To mitigate risk and ensure that org's goals are carried out.
|
|
|
What are some items that internal controls can help address?
|
-achieve org's performace goals
-prevent loss of resources -support reliable finc'l reporting -support compliance w/ laws & regs. |
|
|
What items cannot be accomplished thru internal controls?
|
-Ensure org success or survival
-Ensure reliability of finc'l reporting -Ensure absolute compliance w/ laws & regs. |
|
|
What are controls designed to accomplish?
|
Help mgmt accomplish business objectives, usually by reducing risk to acceptable levels.
|
|
|
What are the types of controls?
|
-Preventive (prevent an event)
-Detective (after the fact detection) -Directive (cause an event to occur) -Mitigating (compensate for non-existant control) |
|
|
What is an Active Control?
|
A control that works by some type of concious intervention.
|
|
|
What is a Passive Control
|
Operates without human intervention
|
|
|
What is a Control Loop?
|
Functions by measuring a control ata given point and comparing it to a desired state for the system. Corrective action is then determined.
|
|
|
What are the steps involved in a Control Loop?
|
1. Determine the Objective
2. Establish acceptable Standard 3. Compare actual findings to the Standard 4. Determine corrective action |
|
|
How do IAs generally evaluate the effectiveness of a control?
|
By selecting a sample of instances when the control should have been applied, and testing to determine whether it was applied correctly in each instance.
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of effective controls?
|
1. timely identification of deviations
2. Reasonable assurance of achieving objectives with minimal cost and side effects 3. Clear accountability 4. Effective Placement (where measurement is most convenient) 5. Root cause identification 6. Alignment to business strategies |
|
|
What are limitations to Controls?
|
1. Excessive or redundant controls
2. Overreliance on controls 3. Overemphasis on controls 4. Obsolete controls 5. Resistance to controls = requires buy-in |
|
|
What does a Risk Assessment Framework provide?
|
A systematic way for the CAE and IA dept. to assess internal and external risk factors and develop an annual audit plan.
|
|
|
Define Risk-Based auditing
|
A proactive approach that focuses on anticipating future events and preventing problems from occurring.
|
|
|
What are the main steps to establishing a Risk-Based Audit Framework?
|
1. Determine the audit universe
2. Examine organizational risk factors 3. Prioritize audits |
|
|
PA 2010-2
|
="Linking the Audit Plan to Risk & Exposures"
The audit universe can include components of an org's strategic plan |
|
|
What areas do org's generally scan to understand the sources of opportunities & threats?
|
-legal
-reg -market forces -stakeholder groups -tech trends -Customers -IA capability analysis -SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) |
|
|
Describe Mgmt & Staff information gathering techniques
|
-Interviews
-Focus Groups -Questionaire & Surveys |
|
|
Describe Performance Standard 2010.
|
="Planning" States "The CAE s/establish risk-based plans to determine priorities of A activities, consistent w/ org's goals.
|
|
|
What are the mai types of org risks?
|
1. Strategic Risks
2. Specific Project, Program, Process Risks 3. Day-to-day Operational Risks |
|
|
What are the steps involved in Risk Measurement?
|
1. Probability Estimates
2. Risk Factor Measures 3. Weighed MAtrices Risk Measurement scores are then used in Risk Prioritization |
|
|
What are types of Risk Prioritization?
|
1. Absolute Ranking
2. Relative Ranking 3. Matrix Ranking |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2010.A1
|
The IA's Plan of Engagements s/b based on a Risk Assessment undertaken at least annually.
|
|
|
Implementation Standard 2010.C1
|
The CAE s/consider accepting proposed consulting engagements based on the engagement's pot'l to improve the org's operations.
|
|
|
What should engagement work schedules include?
|
-Activities to be performed
-When will they be performed -The estimated time required |
|
|
What matters s/b considered in establishing engagement work schedule priorities?
|
-Dates & results of last engagement
-Updated Risk assessments & evaluation of control effectiveness -Requests by Board & Sr. Mgmt -Current governance issues -Major changes in org's business operations -Opportunities to achieve operating benefits -Changes to & capability of IA staff |
|
|
What are the ways that risk can be managed?
|
-Acceptance
-Avoidance -Transfer -Control |
|
|
Performance Standard 2030
|
"Resource Mgmt"
The CAE s/ensure that IA resources are appropriate, sufficient and effectively deployed to schieve the approved plan. |
|
|
IF IA resources are limited, name the least desireable and most desireable course of action.
|
least = eliminate engagements
most = leverage IT and coordinating w/regulatory audits, etc. |
|
|
Performance Standard 2050
|
="Coordination"
The CAE s/share information and coordinate activities w/other internal & external providers of assurance & consulting services to ensure proper coverage and minimize duplication of efforts. |
|
|
What is the scope of Internal Auditors?
|
-Apply a systematic disciplined approach
-Concerned w/all aspects of org. -Focus on future events. -Defined in section 2100 of the Standards |
|
|
What is the scope of external auditors?
|
-To support an opinion of fairness of finc;l statements
-Historical approach -Their own prof'l standards |
|
|
What is the guidance of PA2050-1?
|
="Coordination"'
-Oversight of work of external auditors is responsibility of the board -CAE s/ensure that work of IA does not duplicate work of EAs. -Ia may perform work to assist EA, in accordance w/Standards -CAE s/regularly evaluate coordination between IA and EA. . |
|
|
What should a thorough risk assessment executed in a timely manner accomplish?
|
-Produce credible results about engagements
-Establish buy-i through its participatory process -Help mhmt and oversight body focus on top risks |
|
|
Define
Engagement |
A specific IA assignment, task, or review activity such as an IA, control self-assessment review, fraud examination or consultancy.
|
|
|
What does the planning process help ensure?
|
-that engagement has a high probability of success
-that meaningful work is performed -audit deliverables add value to the organization -audit resources are used efficiently & effectively |
|
|
Performance Standard 2200
|
"Engagement Planning"
-IAs s/develop and record a plan for each engagement, including scope, objective, timing & resource allocation. |
|
|
Performance Standard 2201
|
"Planning Considerations"
IAs s/condider: -objectives of the reviewed activity -significant risks to the activity & means by which these risks are controlled. -adequacy & effectiveness of the activity's risk mgmt & control systems compared to a benchmark -Opportunities for making significant improvements.to activity's risk mgmt & control systems. |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2201.A1
|
When planning engagements for parties outside the org:
-IAs s/establish a written understanding w/them, including: -objectives -scope -responsibilities -restrictions on distribution of results -access to engagement records -other restrictions |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2201.C1
|
IAs s/establish a written understanding w/ consulting engagement clients concerning:
-objectives -scope -responsibilities -other client expectations |
|
|
Performance Standard 2210
|
"Engagement Objectives"
Objectives s/be established for each engagement |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2210.A1
|
IAs s/establish a preliminary assessment of the risks relevant to the activity being reviewed.
-Engagement objectives s/reflect the results of the risk assessment. |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2210.A2
|
The IA s/consider the probability of significant errors, irregularities, noncompliance and other exposures when developing the engagement objectives
|
|
|
Implementation Standard 2210.C1
|
Consulting engagement objectives s/address risks, controls and governance processes to the extent agreed upon w/the client
|
|
|
Performance Standard 2220
|
"Engagement Scope"
The scope s/b sufficient to satisfy the eng. objectives |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2220.A1
|
The scope of the eng. s/include consideration of relevant systems, records, personnel, physical properties including those under control of third parties.
|
|
|
Implementation Standard 2220.A2
|
If significant consulting opportunities arise during an assurance engagement, a specific written understanding as to the scope, objectives, responsibilities, and other expectations s/b reached and the results of the consulting eng. s/b communicated in accordance w/consulting standards
|
|
|
Implementation Standard 2220.C1
|
In performing consulting engagements, IAs s/ensure that the scope of the engageemnt is sufficient to address the agreed-upon objectives.
If IAs develop reservations about the scope during the engagement, these reservations s/b discussed w/the client to determine whether to continue w/the engagement. |
|
|
Performance Standard 2230
|
"Engagement Resource Allocation"
IAs s/determine appropriate resources to achieve eng. objectives. -Staffing s/b based on an evaluation of the nature & complexity of each engagement, time constraints & available resources. |
|
|
Performance Standard 2240
|
"Engagement Work Program"
IAs s/develop work programs that achieve eng. objectives. -These work programs s/b recorded |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2240.A1
|
Work programs s/establish the procedures for identifying, analyzing, evaluation & recording information during the engagement.
-The work program s/b approved prior to its implementation and any adjustments approved promptly |
|
|
Implementation Standard 2240.C1
|
Work programs for consulting engagements may vary in form and content depending on the nature of the engagement.
|
|
|
Practice Advisory 2200-1
|
"Engagement Planning" Guidance:
-Document IAs procedures for collecting, analyzing, interpreting & documenting info. during the engagement -State eng. objectives -Set forth scope & degree of testing required to achieve eng. objectives -Identify technical aspects, activity objectives, risks, processes and transactions that s/b examoned -State nature & extent of testing required -Be prepared prior to commencement of eng. work and modify, as appropriate, during the course of the eng. |
|
|
PA 2200-1 re: communication
|
-inform pertinent mgmt about:
-Eng objectives & scope -timing of eng. -IA personnel assigned -comm. process for the eng, incl. methods, time frames, & individuals -activity being reviewed -mgmt concerns -IA concerns -describe IA reporting & f/u process |
|
|
Are unanounced visits by IA advisable?
|
No. Should be avoided whenever possible.
|
|
|
What are some important points about the first meeting re: the eng.
|
-sets the tone for the whole eng.
-an agenda s/b followed -an opptnty for IA to gain insights re: activity mgmt. -forum for other tasks , i.e., request specific assistance or inform re: IA's role in the org. |
|
|
PA2210,A1-1:
|
"Risk assessment in eng. planning"
-if appropriate,a survey s/b conducted to become familiar w/the activities, risks, controls to identify areas for eng. emphasis & to invite comments & suggestions from eng. clients. |
|
|
What are the purposes of an eng. survey?
|
-understand the activity under review
-identify areas needing special emphasis -obtain info. for use in performing the eng. -determine whether further auditing is necessary |
|
|
What are some realistic outcomes from a preliminary survey?
|
Clarification of:
-Purpose of the IA -eng objectives, scope & timing -processes to be audited -Area objectives, related risks & controls -IA resources to be used -Relevant standards |
|
|
What are some topics to be focused on during the preliminary survey?
|
-Operational objectives
-level of compliance w/ laws P&Ps -Key Processes -Org chart & structure -Info. systems -Key risks -Current controls |
|
|
What is an "Analytical Review" and what is the goal?
|
An Analytical Review examoines relationships among information.
-The goal is to identify discrepancies in information. |
|
|
Unexpected diffferences discovered in an analytic review may result from which causes?
|
-Errors or omissions
-Noncompliance -Illegal acts -Unusual events or transactions -the accounting method used |
|
|
What is a key tenet to be considered during an analytic review?
|
Reasonableness
|
|
|
What are the various types of Analytical Reviews used during Internal Audit Planning?
|
-Variance Analysis
-Trend Analysis -Ratio Analysis |
|
|
Describe Variance Analysis
|
-compare objectives of the activity vs. objectives of the org.
-Analyze factors causing difference between planned vs. actual results -Identify areas of significant change which might warrant additional inquiry. |
|
|
Describe Trend Analysis
|
-Charting historical data over time
-Identifies performance indicators, highlights significant changes, evaluates present position. -identify trends -may be long range or short range |
|
|
Describe Ratio Analysis
|
-Mathematical relationships among several numbers
-Compares relationships at a point in time -Most typical methods used by auditors are common-size statements and financial ratios - |
|
|
What is a "Common-Size Statement"?
|
-Converts all account balances to a percentage of one relative aggregate balance.
|
|
|
What are the types of financial ratios?
|
Activity (use of assets)
Liquidity (ability to pay s-t obligations) -Leverage (how much debt) Profitability (operating performance) |
|
|
Define
"Benchmarking" |
A comparison of org. performance measures vs. internal or external measures to determine areas of pot'l improvement
|
|
|
Describe
Internal Benchmarking |
Comparing similar information within & across an org.
|
|
|
List the different types of Benchmarking
|
-Internal
-Competitive -Functional -Generic |
|
|
Describe
Competitive Benchmarking |
Comparing org. measures to similar measures of direct competitors
|
|
|
Describe
Functional Benchmarking |
Comparing org. processes to other orgs w/similar processes in the same function but in a different industry
|
|
|
Describe
Generic Benchmarking |
Comparing org measures to other orgs that are best in class
|
|
|
List sources of benchmarking info.
|
-External target company
-Internal sources -Suppliers -Customers -Trade journals -Trade shows -Prof'l associations -Academia -Consultants -Public docs -Library -Internet -IIA's web site |
|
|
What are the basic considerations in selecting a benchmarking source?
|
-ease of access to info.
-Caliber of info. sought -cost of info. |
|
|
Why are interviews conducted during the eng. planning process?
|
-facilitate high-level client discussion about planned audit
-Obtain mgmt perspective -clarify info. about activity to be audited -Collect add'l info. -Provide an observation of the activities to be audited |
|
|
List Interviewing techniques
|
-Preparation
--Introductions -Opening -Rapport -Questioning -Listening / Talking -Note-taking -Nonverbal communication -Closing |
|
|
Describe
Interview Preparation |
Be prepared and organized
|
|
|
Describe
Interview Introductions |
Take time for appropriate introductions
|
|
|
Describe
Interview Opening |
Explain the purpose of the interview and timing
|
|
|
Describe
Interview Rapport |
-establish trust
-use person's name -avoid threatening statements -be cordial -communicate IA objective to help |
|
|
Describe
Interview Rapport |
-establish trust
-use person's name -avoid threatening statements -be cordial -communicate IA objective to help |
|
|
Describe Interview Questioning
|
-ask open-ended questions
-avoid leading questions (where answer is in the question) -avoid closed-end questions answerable with either yes or no -try to prevent client defensiveness |
|
|
Describe
Interview Listening / Talking |
-Listen carefully, then speak
-Don't interupt -confirm understanding by restating -provide positive reinforcement as necessary -ask for suggestions -do not make prejudiced or biased statements - |
|
|
Describe
Interview note-taking |
-try to do so unobtrusively
-minimize extensive silenses |
|
|
Describe interview nonverbal communication
|
-use nonverbal signs sparingly
-do not become distracting |
|
|
Describe
Interview Closing |
-Bring the interview to a formal close
-Thank the individual -Explain the next step |
|
|
What are some items that should be accomplished during an interview?
|
-Explain IA process
-Assure client that IA will minimize disruptions -Request client's buy-in by asking: * does this seem reasonable? *can you recommend any changes? *Do you have any concerns? |
|
|
What are the "four C's " of effective communication?
|
Clear
Concise Complete Correct |
|
|
Why is the review of prior audit documentation important?
|
-Provides familiarity with the activity to be audited
-overviews what to expect on the activity to be audited -Shows how other IAs approached the audit -Identifies specific problems found previously and areas likely to have repeat problems -reveals status of corrective action -reveals prior strengths that should have been maintained -may identify add'l activities for review |
|
|
What documents are typically appropriate for review?
|
-Org info.
-details re: recent changes -job descriptions -stmnts of auth & resp -Objectives & goals -P&Ps -project plans physical reports -performance reports -certificates of compliance -production schedules -budget info. Results of other eng. including EAs & reg reports, etc. |
|
|
What other docs are beneficial to review, especially if this is a fisrt-time audit?
|
Authoritative and technical literature appropriate to the activity.
|
|
|
What should be remembered when reviewing hard-copy files on location?
|
Never remove the files. Make copies if necessary to take with you.
|
|
|
What must an IA understand, before beginning an audit, in order to do an acurate audit?
|
A mapping and thorough understanding of related operational processes particular to the activity being audited.
|
|
|
What should IAs personally examine in each audit?
|
Every physical part of the activity being audited. A tour or walkthrough of the area to be audited reveals the physical flow of material and documents and promotes an overall understanding of the activity's processes.
|
|
|
Next to personal inspection, how is process documentation most commonly achieved?
|
Through the use of flowcharts.
|
|
|
Define: Flowchart
|
A graphical representation of the actual or ideal path followed by a service or product. It provides a visual sequence of the steps in a process., illustrates the relationship between parts, and identifies what the process does or should do.
|
|
|
Draw the symbols for:
Process, decision point, input/output,online storage, database, manual file, document (single & multi), start or end of a process, on-page & off-page connectors. |
See page 1-92 for PArt 1
|

