![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidemiology for Ischemic Heart Disease |
73000 deaths per year in UK 2.3 m living with it in UK More common in men 2 m affected by angina Family history |
|
|
What are causes of Ischemic Heart Disease |
Atheroma Thrombosis Spasm Emoblus Coronary arterial stenosis Coronary arteritis Obstructive coronary artery disease Smoking HBP High cholesterol No exercise Diabetes |
|
|
Investigations |
Risk assessment ECG Exercise test X-ray Echocardiogram Blood test Coronary angiography |
|
|
Signs and Symptoms of IHD |
Chest pain (angina) Heart palpitation Breathlessness Heart attack Heart failure |
|
|
Treatment for IHD |
Lifestyle changes Smoking cessation Exercise Eating healthy |
|
|
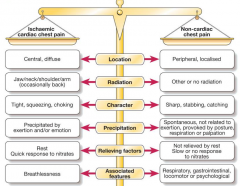
Angina: Site Onset Radiation Character Associated Features Provocation |
Site - centre of the chest Onset - Sudden, several minutes to hours Radiation - jaw, upper of lower arms (mostly left), or only at the side or back Character - dull constricting, choking, heavy; described as squeezing burning or aching, but not sharps or stabbing; breathlessness; discomfort not pain; open hand of fits to describe Associated features -sweating, vomiting, nausea; breathlessness due to pulmonary congestion form transient ischemic left ventricular dysfunction Provocation -occurs during excretion and relieved by rest, can be precipitated by emotion or after large meal or cold wind |
|
|
Non- Cardiac Chest pain (jazzys Causes) |
Musculoskeletal Psychological Mitral valve prolapse Myocarditis or pericarditis Bronchospasms Aortic Dissection Oesophegeal |
|
|
Non- Cardiac Chest pain (GP version) |
Congenital - aortic dissection, connective tissue disorder Trauma - rib fracture, intercostal muscle injury, prolapse disc Infection - Herpes Zooster, endocarditis, Bronholms disease Inflamation, myo and pericarditis, angina, aneurysm, oesophageal, bronchospasm, pulmonary infarct, tracheitis (secondary to infection), pneumothroax, massive pulmonary embolism, osteoarthritis, costochondritis, thorasic outlet syndrome. Malignancy |
|
|
Causes of central and peripheral chest pain |
Central: - cardiac - aortic - oesophageal - massive pulmonary embolus - mediastinal - anxiety or emotions Peripheral: - lung or plura |
|
|
Characteristics of Musculoskeletal chest pain |
- very common - vary in intensity and site - vary with posture and movement - local tenderness over rib and costal cartilage - can be caused by: rib fracture, arthritis, costochondritis, intercostal muscle injury, Coxsackie viral injection, minor soft tissue injury - pain is associated with specific movement - pain that occurs after rather than during exertion |
|
|
Characteristics of psychological chest pain |
emotion and stress anxiety pain not associated with exercise fear of death |
|
|
Characteristics of oesophageal chest pain |
Mimics angina Precipitated by exercise Relieved by nitrates Radiates to the back History of oesophegeal reflux |
|
|
Characteristics of aortic dissection pain |
Sharp Severe Tearing Sudden Penetrating to the back Very abrupt onset Following path of dissection Sweating, nausea and vomiting |
|
|
Asthma related chest pain |
Exertional chest tightness Relieved by rest Association with wheeze, atopy and caugh |
|
|
Myocarditis and Pericarditis chest pain |
Pain may be: Retrosternal To the L of sternum In the L or R shoulder Vary with movement and respiration Described as sharp, may catch during inspiration, coughing or lying flat History of viral illness |
|
|
Characteristics of chest pain caused by a mitral valve prolaps |
If chest pain is sharp, left sided, suggested of musculoskeletal problem |
|
|
DDX for chest pain |
|

