![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
751 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the tactical priorities in Firefighting
|
1. Life Safety
2. Incident Stabilzation 3. Property Conseration |
|
|
5 Characteristics of a Firefighter
|
1. Integrity (obedience to the unenforceable)
2.Moral Character (Truthfullness and Honesty) 3.Work Ethic (do what needs to be done without being told) 4.Pride (How you look and Behave) 5.Courage |
|
|
Organizational Principles
|
Unity Of Comand (only one supervisor)
Span of Control (number of individuals an officer can effectively manage 3-7, 5 optimal) Division Of Labor(break big job into small jobs) Discipline (setting limits and enforcing them) |
|
|
Engine Company
|
Deploys Hoseline for fire attack
|
|
|
Truck Company
|
Peforms Forcible entry, search and rescue, ventilation, salvage and overhaul, utilities control, access to upper levels of structure.
|
|
|
Rescue Squad
|
Searches for and removes victims from danger, may perform technical recue
|
|
|
HazMat Company
|
responds to and mitigates Hazardous materials incidents
|
|
|
Brush Company
|
Extinguishes wildland fires
|
|
|
Special Rescue Company
|
Responds to and performs technical rescues
|
|
|
Fire Police Personnel
|
Assist Law enforcement officers with traffic control
|
|
|
Fire Prevention Personnel
|
Fire Prevention Officer/Inspector (inspects buildings for code compliance)
Fire and Arson Investigator(Determines cause and origin of fire) Public Fire and Life Safety Educator(makes presentations) Fire Protection Engineer/Specialist(Checks building plans) |
|
|
Policy
|
Guide to Decision Making
|
|
|
Procedure
|
WRITTEN communication closely related to a policy
|
|
|
Components of ICS
|
Common Terminology
Modular Organization Integrated Communications Unified Command Structure Consolidated Action Plans Manageable Span of Control Predesignated Incident Facilities Comprehensive Resource Management |
|
|
ICS - Command Staff
Hint: SLP |
Safety Officer
Liaison Officer (Point of contact for government and nongovernment agencies in incident) Public Information Officer (Interfaces with public or media) |
|
|
ICS - General Staff
HINT: CFLOPI |
Operations Section Chief (activites that r reducing hazard)
Planning Section Chief (disseminates incident information) Logistics Section Chief (Responsible for all support requirements) Finance Information / Intelligence |
|
|
Assigned
|
Resource currently committed to an assignment
|
|
|
Available
|
Resource has checked in at incident and is available for assignment
|
|
|
Branch
|
Organization level between Divisions/Groups and the IC and Operations. (ie. Fire Branch, EMS Branch, Law enforcemnt Branch)
|
|
|
Command
|
The function of directing ordering and controlling resources by virtue of explicit legal, agency, or delegated authority.
|
|
|
Division
|
Geographical designation assigning responsibility for all operations within an area. Assigned clockwise on a wildfire and by floor on multi story fire.
|
|
|
Group
|
Functional designations (forcible entry, salvage, ventilation, etc)
|
|
|
Incident Action Plan (IAP)
|
Written or unwritten plan for managing an emergency.
|
|
|
Strike Team
|
Set number of resources of the same kind
|
|
|
Task Force
|
Any combination of resources assembled in support of a specific mission
|
|
|
Other Organizations at an Incident
|
EMS
Hospitals (MCI) Law Enforcement Utility Companies Media |
|
|
On average the number of firefighters that die in the line of duty each year
|
100
|
|
|
Fatalities by Duty (Volunteer / Paid)
|
70% - Volunteer
30% - Paid |
|
|
Causes of Firefighter Fatalities
|
54% - Stress or Overexertion
24 % - Other Causes 22% - Traffic Accidents |
|
|
Consensus Standard
|
Rules, principles or measures that are established through agreement of members of the standards-setting organization.
|
|
|
Risk Manaagement Plan
|
Written plan that identifies and analyzes the exposures to hazards and includes selection of appropriate risk management techniques to handle exposures, implementation of chosen techniques, and monitoring the result of those techniques.
|
|
|
NFPA 1500
|
Relates to Firefighter Saftey and Health
|
|
|
NFPA Topics
|
Safety and Health related policies and procedures
Training and Education Fire apparatus, Equipment, and Driver Operators PPE Emergency Operations(NIMS, Passports) Facility Safety Medical and Physical Requirements Member Assistance and Wellness Programs |
|
|
Supplied Air Respirator
|
An atmosphere providing respirator for which the source of breathing air is not designed to be carried by user
|
|
|
OSHA
|
Federal OSHA authority and regulations apply mainly to the PRIVATE SECTOR, and do not cover employees of state and local governments, including career and some volunteer programs. Does apply to federaly employed firefighters, prvate sector firefighters.
|
|
|
Industrial Fire Brigade
|
Team of employees organized within a private company who are assigned to fight fires.
|
|
|
Employee Assistance Program
|
Available to employee and their families to aid in soling work and personal problems.
|
|
|
Defusing
|
informal discussion that can happen at the scene or after units have returned to quarters.
|
|
|
Jump Clear of Apparatus
|
If in contact with energized electrical wires.
|
|
|
Student to Instructor ratio for live fire training
|
5:1
|
|
|
Size Up Critical Factors
|
Life Safety Hazard
Nature and Extent of the Emergency Building Type Arrangement and Access Resources Special Hazards |
|
|
Structure Fire Tactical Priorities
|
Firefighter Safety
Rescue Fire Control Loss Control |
|
|
Personnel Accountability Report
|
Report made to the IC signifying that companies working on incident are safe and accounted for
|
|
|
"All Clear"
|
The primary search has been completed and all salvageable occupants are out of the hazard zone.
|
|
|
"Undr Control"
|
The fire is controlled with the forward fire progress stopped, no additional units will be required, no dangers to firefighters.
|
|
|
"Loss Stoped"
|
Propert Conservation is complete
|
|
|
Rapid Intervention Crew
|
2 or more equipped and available firefighters.
|
|
|
Safety Rule
|
"Everyone Looks Out for Everyone else"
|
|
|
How many lanes next to MVA should be closed.
|
At least One
|
|
|
Personnel Accountability Systems
|
Passport System
SCBA Tag System (time of entry and expected time of exit based on scba pressure) |
|
|
IDLH
|
immediately dangerous to life and health safety
|
|
|
List three ways to preventing firefighter injuries?
|
training
maintaining company discipline/accountability following SOPs |
|
|
What are the three IFSTA principles of Risk Management?
|
Only take on significant risk if a life can be saved
No building is worh a firefighter Dont go interior if building is derilct or unoccpied |
|
|
How can you avoid slips trips and falls at fire station?
|
good housekeeping
good lighting maintain handrails |
|
|
What NFPA standard must live fire training exercises meet?
|
NFPA 1403
|
|
|
What are two basic interior operations techniques?
|
Scan the outside of bulding to locate egress routes
Wear full PPE including SCBA and use air management plan Take the appropriate tools with you Maintain team integrity Take a hoseline or tagline Pay attention to your immediate surroundings. |
|
|
Hand Tool Safety
|
Wear PPE
Remove loose clothing remove jewelry select the right tool for the job follow manufacturer's instruction |
|
|
Power Saws
|
Match the saw to the task
Wear PPE Keep saws sharp |
|
|
Mater
|
anything that occupies space and has mass
|
|
|
Exothermic heat reaction
|
chemical reaction between two or more materials that changes the materials and produces heat, flames and toxic smoke
|
|
|
Endothermic Heat Reaction
|
Chemical reaction in which a substance absorbs energy
|
|
|
combustion
|
exothermic reaction that is self sustaining process of rapid oxidation of a fuel that produces heat and light
|
|
|
fire triangle
|
Oxygen , Fuel , Heat
|
|
|
Fire Tetrahedron
|
Oxygen, Fuel, Heat, Self-Sustaining chemical reaction
|
|
|
Potential Energy
|
Stored Energy possessed by an object
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy
|
Energy possessed by a moving object
|
|
|
Energy
|
The capacity to perform work
|
|
|
Measurement For Heat Energy
|
Joule - International System of Units
BTU - Customary system (raise 1 pound of water 1 degree farenheit) |
|
|
Autoignition Temperature
|
Same as ignition temperature except that no external ignition source is required for ignition because the material itself has been heated to the ignition temperature
|
|
|
pyrolysis
|
the chemical decomposition of a solid fuel through the action of heat
|
|
|
vaporization
|
in liquid fuels is the releasing of ignitable gases or vapors
|
|
|
piloted ignition
|
when a mixture of fuel and oxygen encounter an external heat source. Autoingnition temp is always higher than piloted ignition
|
|
|
Sources of Heat Energy
|
Chemical Heat Energy
Self Heating(spontaneous) Electrical Heating Mechanical (friction) |
|
|
Spontaneous Heating Materials
|
Charcoal
Linseed Oil-Soaked Rags Hay and Manure |
|
|
mechanical heat types
|
heat of compression
heat of friction |
|
|
Three types of heat transmission
|
Conduction (direct contact)
Convection (heat from liquid or gas to a solid surface) Radiation (electromagnetic waves) |
|
|
Passive Agents
|
Materials that absorb heat but do not participate actively in the cobustion process. Fuels with high moisture content
|
|
|
Reducing Agent
|
The fuel that is being oxidized or burned during combustion.
|
|
|
Vapor Density
|
Density of gas in relation to air
Air has density of 1 Lighter than air has density < 1 |
|
|
Specific Gravity
|
ratio of mass of a given volume of a liquid compared with the mass of an equal volume of water at the same temp.
Water has SG of 1 SG < 1 Float SG > 1 Sink |
|
|
Flash Point
|
Minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapors to form an ignitable mixture with air near the liquid's surface.
|
|
|
Fire Point
|
Temperature at which a liquid fuel produces sufficient vapors to support combustion once the fuel is ignited. Usually a few degrees above the flash point.
|
|
|
Solubility
|
The extent at which a substance will mix with water
|
|
|
Liquids with low flash points
|
are easily ignited
|
|
|
Miscible
|
materials that are capable of being mixed
|
|
|
Surface-To-Mass Ratio
|
Is the primary concern for solid fuels. Fules with a higher stm ratio burn more readily. Log vs. Sawdust
|
|
|
Heat of Combustion
|
Total amount of energy releases when a specific amount of the fuel is burned
|
|
|
Heat Release Rate
|
Is the energy released per unit of time as a given fuel burns. Over TIme
|
|
|
An atmosphere that is oxygen deficient
|
Has less than 19.5% oxygen
|
|
|
Atmosphere is Oxygen enriched when
|
It has more than 23.5 % Oxygen
|
|
|
Flammable Range
|
The range between the upper flammable limit and lower flammable limit in which a substance can be ignited. Right mix of gas and O2
|
|
|
Colorless Odorless dangerous gas formed by the incomplete combustion of carbon. It combines 200 times more completely with hemoglobin
|
Carbon Monoxide
|
|
|
Colorless, odorless, heavier than air gas that nether supports combustion or burns. Used in portable extinguishers to extinguish B or C fires by smothering or displacing oxygen.
|
Carbon Dioxide
|
|
|
Colorless liquid with a pungent choking odor which is iritating to the mucous membranes.
|
Acetaldehyde
|
|
|
Reddish Brown gas
|
Nitrogen Dioxide
|
|
|
Colorless gas with a sharp pungent odor. Mixes with water to form hydrochloric acid
|
Hydrogen chloride
|
|
|
Colorless gas with a choking or suffocating odor.
|
Sulfur Dioxide
|
|
|
Colorless liquid with petroleum like odor.
|
Benzene
|
|
|
Fires that involve cooking oils
|
Class K
|
|
|
Fires that involve normal combustibles
|
Class A
|
|
|
Fires that involve flammable liquids
|
Class B
|
|
|
Saponification
|
Phenomenon that occurs when mixtures of alkaline based chemicals come into contact with cooking oils creating a soapy film
|
|
|
4 stages of fire development
|
Incipient (heat hasnt spread to other substances)
Growth Fully Developed (Flashover can occur) Decay |
|
|
Factors influencing the development of a fuel controlled fire
|
Mass and Surface Area
Chemical Content Fuel Load Fuel Moisture Orientation Continuity |
|
|
Neutral Plane
|
The interface between the hot and cooler gas layers at the opening
|
|
|
Rollover
|
Condition in which the super heated gases released in a confined space during the incipient or early steady-state accumulate at the ceiling level. These gases are pushed away from the fire area into uninvolved areas where they mix with oxygen. Then it burns and rolls over your head.
|
|
|
Flashover Indicators
|
Hot gases overhead and lowering of hot gas layer.
A strong air in smoke out phenomena. Isolated Flames traveling in the hot-gas layer. (ghosting) |
|
|
What temps do flashover commonly occur
|
900-1200 degrees
|
|
|
Backdraft
|
Instantaneous explosion or rapid burning of superheated gases that occurs when oxygen is introduced into an oxygen depleted space.
|
|
|
Visual Indicagtors of Backdraft
|
Inwardly drawn smoke
little or no visible flame puffing smoke leaving building Black smoke that becomes dense gray or yellow Pressurized smoke Smoke stained windows |
|
|
A fire in a Large Compartment
|
will develop more slowly than one in a smal compartment
|
|
|
What temp does water convert to steam and how much does it expand
|
212 degrees and 1700 X
|
|
|
Assembly
|
2 or more interconnected structural components combined to meet a specific function or design requirement.
Roof trusses, Wall frames, Doors and frames |
|
|
Balloon Frame
|
Studs extend from the basement to the roof. This allows fire ro spread undetected through holow walls
|
|
|
Bar Joist
|
Joist constructed of steel with bars in the vertical web space.Early failure when exposed to fire is likely
|
|
|
Beam
|
A horizontal structural component subjected to vertical loads.
|
|
|
Bowstring Truss
|
A roof assembly with a curved or arched top chord. Very strong unless exposed to direct flame.
|
|
|
Butterfly Roof
|
V shaped roof in which the two sides slope toward a valley in the middle.
|
|
|
Cantilever
|
A beam that is unsupported at one or both ends. Typically used to support balconies or apartments.
|
|
|
Chipboard/ Oriented Strandboard OSB
|
Wood board made by gluinf and pressing wooden strands
|
|
|
Chord
|
The main structural members of a truss as distinguished from diagnols
|
|
|
Cockloft
|
An open space between the roof and ceiling of a commercial or industrial building.
|
|
|
Attic
|
Space between roof and ceiling in a residential building
|
|
|
Column
|
A vertical supporting member. Columns may be wooden or steel posts.
|
|
|
Course
|
Horizontal lay of masonary units. (row of bricks)
|
|
|
Curtain Wall
|
Nonload bearing exterior wall used as a weather barrier but not for support. High rises have curtain wals that are sheet glass in frames
|
|
|
Curtain Board
|
Nonload bearing interior wal extending down from a roof or ceiling to limit the horizontal spread of fire and heat.
|
|
|
Eave
|
The edge of a pitched roof that overhangs an outside wall
|
|
|
Cantilever
|
A beam that is unsupported at one or both ends. Typically used to support balconies or apartments.
|
|
|
Chipboard/ Oriented Strandboard OSB
|
Wood board made by gluinf and pressing wooden strands
|
|
|
Chord
|
The main structural members of a truss as distinguished from diagnols
|
|
|
Cockloft
|
An open space between the roof and ceiling of a commercial or industrial building.
|
|
|
Attic
|
Space between roof and ceiling in a residential building
|
|
|
Column
|
A vertical supporting member. Columns may be wooden or steel posts.
|
|
|
Course
|
Horizontal lay of masonary units. (row of bricks)
|
|
|
Curtain Wall
|
Nonload bearing exterior wall used as a weather barrier but not for support. High rises have curtain wals that are sheet glass in frames
|
|
|
Curtain Board
|
Nonload bearing interior wal extending down from a roof or ceiling to limit the horizontal spread of fire and heat.
|
|
|
Eave
|
The edge of a pitched roof that overhangs an outside wall
|
|
|
Engineered I Beam
|
A woden I beam consisting of continuous wooded upper and lower chords seperated by a web of OSB or similar sheet rock
|
|
|
Fire Door
|
Solid core door, door frame, and hardware. Meant to keep fires to one section of a building
|
|
|
Fire Load
|
Total potential heat release if a building and its contents burned.
|
|
|
Fire Wall
|
A rated assembly that extends from the foundation to and through the roof of a building to limit fire spread.
|
|
|
Gable Roof
|
A pitched roof characterized by quare cut ends or sides that slope down from the ridge line to the eaves.
|
|
|
Gable Wall
|
A wall rising to meet a gable roof at the end of a building. Found at the ends of gable roofs.
|
|
|
Gambrel Roof
|
A roof characterized by a single ridge line from which roof sections on both sides of the ridge descend at different pitches. Common on barns
|
|
|
Girder
|
Horizontal structure meant to support beams or joists
|
|
|
Glue-Lam Beam
|
A wooden structural member composed of relatively short pieces of lumber glued and laminated together under pressure
|
|
|
Gusset Plate
|
Wooden or metal plate used to connect structural members that are butted together
|
|
|
Header Course
|
Course of bricks laid with the ends facing outward
|
|
|
Hip Roof
|
A pitched roof in which the ends are all beveled so that there are no gable walls.
|
|
|
Interstitial Space
|
An area between layers of building materials
|
|
|
Joists
|
Horizontal structural members used to support a ceiling or floor.
|
|
|
Lamella Arch
|
An arch constructed of short wooden members connected in a specifc geometric pattern. Found in older buildings
|
|
|
Mansard Roof
|
Steeply sloped facets surrounded by a flat or nearly flat center section.
|
|
|
mortar
|
a mixture of sand cement and water used to bond masonary unitsinto a solid mass
|
|
|
Open Web Joist
|
A joist constructed with a web composed of materials such as bars or tubes that do not fill the entire web space
|
|
|
Parallel Chord Truss
|
A truss contrsucteed with the top and bottom chords parallel the trusses are used in floor joists and in multi story buildings
|
|
|
Parapet
|
A wall at the edge of some roofs. Most parapet walls range from a few inches to a few feet in height
|
|
|
Party Wall
|
A wall shared by two adjoining buildings, usually load bearing
|
|
|
Pitch
|
ratio of rise to span of a rook assembly. The steeper the pitch the greater the trip hazard
|
|
|
Plate
|
The top or bottom horizintal member of a frame wall. Sole Plate or Top Plate
|
|
|
Platform Construction
|
Frame type construction in which each floor interrupts the exterior studs forming an effective fire stop at every floor. This is the most common type of construction
|
|
|
Plywood
|
A wooden structural panel made of glued sheets of wood
|
|
|
Rafters
|
Beams that span from a ridge board to an exterior wal plate to support roof decking
|
|
|
Rated Assembly
|
Two or more construction components combinged to form an assembly that has a specific fire resistance rating. Fire Doors, gypsum Drywall
|
|
|
Reinforced Concrete
|
Concrete that has rebar
|
|
|
Sawtooth Roof
|
A roof with a saw blade profile, These roofs are common in older industrial buildings.
|
|
|
Sheething
|
Plywood, OSB, or Wooden Planking that has been applied to a wall or roof over which a weather resistant covering is applied.
|
|
|
Shed Roof
|
Pitched roof that slopes in only one direction from the ridge.
|
|
|
Spalling
|
Degradation of concrete to prolonged exposure to high heat
|
|
|
Stud
|
A vertical structure member in a frame wall.
|
|
|
Tension
|
Force that tends to pulls the mass of a material apart.
|
|
|
Truss
|
A wooden or metal structural unit made up of one or more triangles in a flat plane.
|
|
|
Type I Construction
|
Fire Resistive
Maintains Its Integrity after a fire Made with Reinforced concrete and structural members have insulation or automatic sprinklers for protection |
|
|
Type II Construction
|
NonCombustive Construction
Same as Type I but without the insulation or other protection |
|
|
Type I Construction Strengths
|
Resists flame impingement
Confines Fire Well Little collpase potential Impervious To Water Damage |
|
|
Type I Weaknesses
|
Difficult to Breach
Difficult to Ventilate Massive debris following a collapse Floors Ceilings and Walls Retain heat |
|
|
Type II Construction Strengths
|
Almost as resistive as Type 1
Confines Fire Well Easier to vertically ventilate than Type I |
|
|
Type II Construction Weaknesses
|
Difficult to Breach
Roof systems less stable than Type I Steel components can fail |
|
|
Type III Construction
|
Ordinary Construction
Exterior walls and structural members be made of noncombustible or limited combustible material |
|
|
Type III Strengths
|
Resists fire spread from the outside
Relatively easy to vertically ventilate |
|
|
Type III Weaknesses
|
Interior structural members vulnerable to fire involvement
Fire spread potential through concealed spaces Susceptible to Water damage |
|
|
Type IV construction
|
Heavy Timber
Exterioir and Interior walls be made of noncombustible or limited combustible materials |
|
|
Type IV Strengths
|
Resists collapse
Structurally stable Relatively easy to ventilate Easy to Breach Manageable debris |
|
|
Type IV Weaknesses
|
Susceptible to fire spread from outside
Potential for flame spread to nearby structures |
|
|
Type V Construction
|
Wood Frame Construction
construction made completely or partly of wood Smaller dimansion than haevy timber construction |
|
|
Type V Strengths
|
Easy to Breach / Ventilate
Resistant to collapse from earthquakes smaller collapse debris |
|
|
Type V Weaknesses
|
Susceptible to fire spread from outside
Rapid flame spread inside Total collapse possible Water damage |
|
|
What are you looking at when doing a building size-up
|
Age of building(signs of weathering)
Construction Material (Wood, masonry, Metal, concrete) Roof Type (Arched or Lightweight) Renovations or modifications Dead Loads (HVAC, Water Units on Roof) |
|
|
Dangerous Building Conditions
|
Conditions that contribute to the spread and intensity of the fire
Conditions that make buildings susceptible to collapse |
|
|
Collapse Zone
|
The area extending horizontally from the base of the wall to one and one half times the height of the wall
|
|
|
Rain Roof
|
Second roof constructed over an old roof
|
|
|
DRD
|
Drag Rescue Device
|
|
|
Nylon and Polyester
|
Never wear these in firefighting ops, they melt. Wear cotton
|
|
|
How high should boots be
|
8 - 10 inches
|
|
|
Carbon Dioxide
|
IDLH = 40,000 ppm
Caused By Free Burning |
|
|
Carbon Monoxide
|
IDLH = 1200 ppm
CB = Incomplete Combustion |
|
|
Hydrogen Chloride
|
Colorless to slightly Yellow
IDLH = 50 ppm Burning Plastics Irritated eyes and respiratory tract |
|
|
Hydrogen Cyanide
|
Colorless, Bitter Almond Odor
IDLH = 50 ppm Burning of wool, nylon, polyurethane Chemical Asphyxiant, hampers respiration at the cellular level |
|
|
Nitrogen Dioxide
|
Irritates nose and throat
|
|
|
Phosgene
|
Colorless; Odor of musty hay
IDLH = 2 ppm Reduced when refrigerants such as freon contact flame Forms Hydrochloric Acid in the lungs |
|
|
Carboxyhemoglobin
|
Hemoglobin saturated with carbon monoxide and therefore unable to absorb needed oxygen
|
|
|
Etiological Agents
|
Living microorganisms, like germs, that can cause human disease
|
|
|
Point Of No Return
|
That time at which the remaining operation time of the scba is equal to the time necessary to return safely to a nonhazardous atmosphere.
|
|
|
Open Circuit Self Contained Breathing Apparatus
|
An CBA that allows the weares exhaled air to be discharged or vented to the atmosphere (Used IN FireFighting)
|
|
|
Harness Assembly
|
Rigid frame that holds air cylinder
|
|
|
Air Cylinder Assembly
|
Includes cylider valve, presure guage, and PASS device in some units.
Main weight of breathing apparatus |
|
|
Regulator Assembly
|
Includes High Pressure Hose with low pressure alarm, by-pass valve, and pressure redusing device
|
|
|
Facepiece assembly
|
Includes facepiece len, exhalation valve, low pressure hose.
|
|
|
Low Pressure Alarm
|
Activates when below 1/4 of air pressure
|
|
|
Open Circuit Airline Equipment
|
Airline equipment that allows exhaled air to be discharged into the open atmosphere.
Longer Duration HazMat SARs , No backpack |
|
|
Closed Circuit Breathing Apparatus
|
Exhalations are rebreathed after CO2 has been removed. Not approved for firefighting. Chemical O2 restores O2 concentrations
|
|
|
PASS
|
Personal Alert Safety System or Pull, Aim, Squeze, sweep
|
|
|
How do you check for positive presure in facemask
|
break the seal between the facepiece and cheek
|
|
|
SCBA NFPA Numbers
|
1500 & 1404
|
|
|
SCBAs
|
Clean after each use
Inspect every month Annual Maintenance |
|
|
Hydrostatic Testing
|
A testing method that uses water under pressure to check the integrity of pressure valves
|
|
|
Male Coupling
|
Side of coupling pointing to EXIT
|
|
|
Female Coupling
|
Side of coupling pointing to Fire
|
|
|
Tag Line
|
Nonload bearing rope attached to an object to help steer it in adesired direction or act as a safety line
|
|
|
Types of Fire Extinguishers
|
Smothering (Oxygen Exclusion)
Cooling (Reducing fuel below its ignition temp) Chain Breaking (Interrupting the chain reaction) Saponification (Forming an oxygen-excluding soapy foam) |
|
|
Pump-Tank Water
|
Hand Carried/Backpack
Agent=Water Class A Fires |
|
|
Stored Presure Water
|
Class A Fires
|
|
|
Dry Powder
|
Only Class D Extinguisher
Hand Carried or Wheeled |
|
|
Halon 1211 and 1301
|
Used on B & C Fires
|
|
|
Extinguishing Agent
|
Any substance used for the purpose of controlling or extinguishing a fire
|
|
|
Wet Chemical Extinguisher
|
Agent = Potassium Acetate
Class K Fires |
|
|
Carbon Dioxide Extinguishers
|
Used on B & C Fires
|
|
|
Dry Chemical Extinguishers
|
Uses a dry chemical powder as the primary extinguishing agent, often used to protect areas containing volatile flammable liquids
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of water
|
cooling
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Carbon Dioxide
|
Oxygen Depletion
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Foam
|
Oxygen Depletion
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Clean Agent
|
Chain Inhibition
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Dry Chemical
|
Chain Inhibition
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Wet Chemical
|
Oxygen Depletion
|
|
|
Extinguishing characteristics of Dry Powder
|
Oxygen Depletion
|
|
|
Alloy
|
Substance or mixture composed of 2 or more metals
|
|
|
Dry Powder
|
Extinguishing Agent suitable for use on combustible metal fires
|
|
|
Wet Chemical System
|
Extinguishing system that uses a wet-chemical solution as the primary extinguishing agent
|
|
|
Water Mist
|
atomizing water through a special applicator
|
|
|
Aqueous Flm Forming Foam
|
Synthetic foam concentrate that, when combined with water, can form a complete vapor barrier over fuel spills and fires and is highly effective extinguishing agent on hydrocarbon fuels.
|
|
|
Clean Agent Extinguishers
|
Designed to replace Halon 1211
Rapidly evaporating liquid that leaves no residue _____flurocarbons |
|
|
Carbon Dioxide Extinguishers
|
Limited reach
No freeze protection |
|
|
Wheeled extinguishers
|
Are larger
Carbon Dioxide/Dry Chemical |
|
|
Dry Chemical
|
Not the same as dry powder
Used for a,b,c fires 2 types regular b/c rated, and multipurpose a,b,c rated |
|
|
Dry Chemical Extinguishing Agents
|
Sodium Bicarb
Potassium Bi Card Potassiumj Chloride Monoammonium Phosphate |
|
|
Operating a wheeled extinguisher
|
Stretch hose out completely
|
|
|
Class A Fire Icon
|
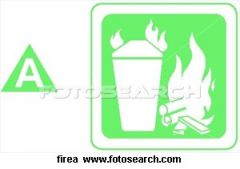
|
|
|
Class B Fire Icon
|

|
|
|
Class C Fire Icon
|
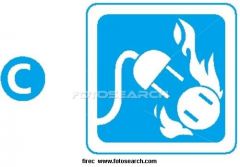
|
|
|
Class C Fire Icon
|
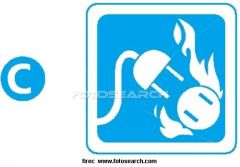
|
|
|
Class D Fire Icon
|

|
|
|
Total Flooding System
|
Fire-Suppression System designed to protect hazards within enclosed structures. Foam is released into a compartment or area and fills it completely to extinguish a fire
|
|
|
Washing Natural Fiber rope
|
Water initially strengthens then weakens it so can't use water to clean. Have to wipe of as much dirt as possible
|
|
|
Washing Synthetic Fibers
|
wash by hand
Rope washing device Front Load Washer |
|
|
Running End
|
Rope end used for hoisting, pulling, or belaying
|
|
|
Working End
|
End used in forming a not also called the bitter end or loose end.
|
|
|
Standing Part
|
Part between the working end and the running end
|
|
|
Ladder Belt
|
Belt with a hook that secures the firefighter to the ladder
|
|
|
Class I Harness
|
Goes around waist and thighs or under buttocks and is intended to be used for emergency escape.
|
|
|
Class II Harness
|
Goes around waist thighs or butocks and is intended to hold a load up to 600 lbs. Loks just lke class I harness
|
|
|
Class III Harness
|
Harness that fastnes around the waist, thighs, and over shoulders. Also known as full body harness. Up to 600 lbs.
|
|
|
Rescue
|
Saving a Life from fire or accident
|
|
|
Extrication
|
Incidents involving the removal and treatment of victims who are trapped by some type of man-made machinery
|
|
|
Fire Attack and Interior Search Operations should be started...
|
simultaneously
|
|
|
two objectives of abuilding search
|
locating victims
obtining information about the size and extent of the fire |
|
|
Primary Search Priorities
|
Most severely threatened
Largest Numbers Remainder of Hazard Zone Exposures |
|
|
Equipment used in primary search
|
radio, TIC,flashlight, forcible entry tools
|
|
|
If you cant see your feet because of smoke...
|
You shouldn't be walking upright
|
|
|
Search Line System
|
used in searching large and comlex areas filled with smoke
every 20 feet there is a ring and knot(s) after the ring 1 knot means 20 feet, 2 = 40 |
|
|
When searching a multistory building the most critical areas are the...
|
Fire flor, flor directly above the fire, and the topmost floor. These should be searched first
|
|
|
During Primary search what should be done to doors
|
they should be closed
|
|
|
Marking Systems for Search and Rescue
|
Chalk or Crayon
Duct Tape door markers latch straps |
|
|
Markings: One slash on door
|
Means room is being searched
|
|
|
Marking Systems: Two slashes
|
Means room has been searched
|
|
|
Incline Drag
|
Used by one rescuer to move a victim up or down stairs
|
|
|
Blanket Drag
|
Can be used by one rescuer and a blanket or sheet
|
|
|
Cradle In Arms Carry
|
Used to carry children or smal adults if they are conscious.
|
|
|
Seat Lift/Carry
|
Conscious or unconscious, using two recuers
|
|
|
Three -Person Lift/Carry
|
used to lift a pt who is lying down
|
|
|
Extremities Lft/Carry
|
can be used on a a conscious or unconscious victim
|
|
|
Inverter
|
step-up transformer that converts a vehicles 12 or 24 volt DC current to 110-220 volt AC current
|
|
|
Arc
|
A luminous discharge of electricity across a gap
|
|
|
Air Vacuum
|
Used with the air knife to remove soil near a trench collapse victim
|
|
|
High Pressure Bags
|
High Pressure bags made of rubber and reinforced with steel or Kevlar. Don't lift as far as medium and low pressure bags.
|
|
|
Low and Medium Pressure Bags
|
Used to stabiize and lift cars
|
|
|
How many bags should be stacked when lifting or stabilizing
|
No more than 2
|
|
|
Max contact temp allowed for air bags
|
220
|
|
|
Series of Pulleys in a wood or metal frame used to provide mechanical advantage
|
Block and Tackle
|
|
|
Turn Off Headlights
|
When they are not needed at an emergency scene to avoid blinding oncoming traffic
|
|
|
System used for sorting and classifying accident victims
|
Triage
|
|
|
Process of providing additional support to key places between an object of entrapment and the ground
|
Stabilization
|
|
|
When disabling power to vehicle by cutting cables what do you cut first
|
Black or Negative
|
|
|
SIPS
|
Side Impact Protection System
|
|
|
How long can power remain in restraint system after battery has been isolated
|
30 mins
|
|
|
Type of glass manufactured from two sheets that are bonded to a sheet of plastic between them. Used inWindshields
|
Laminated / Saftey Glass
|
|
|
Used in side windows. Designed so that glass breaks into many small pieces
|
Tempered Glass
|
|
|
Type of Construction Resistant to Earthquakes
|
Type V
|
|
|
Type Of Collapse: contains multiple voids. Simultaneous failure of exterior walls
|
Pancake Colapse
|
|
|
Type Of Collapse: Outer walls remain in tact and the upper floors and or roof sections fail. Good chance of habitable void spaces along wals
|
V shaped collapse
|
|
|
Type Of Collapse: When one outer wall fails while the other stays in tact
|
Lean-To Collapse
|
|
|
Type Of Collapse: Occurs when the floor and or roof assemblies on both sides of a center wall collapse into what might be seen as opposing lean to colapses
|
A Frame collapse
|
|
|
Collapse that happens after the initial collapse of a structure
|
Secondary Collapse
|
|
|
How far should ladders extend outside of a trench
|
3 feet
|
|
|
How far should a trench be cordoned off
|
100 feet
|
|
|
Characteristics of Confined Space
|
Large enough that an employee can bodily enter and perform assigned work
Limited or restricted means to exit and entry Not designed for continuous employee occupancy |
|
|
What must be stationed at the confined space entrance to track personnel and equipment entering and leaving the space
|
an attendant
|
|
|
In a confined space rescue where must the command post be stationed
|
out of the hotzone and not obstructing entrance/exit
|
|
|
What is the distance rescuers should stay away fom downed power lines
|
One span between poles
|
|
|
Techniques used byfire personnel to gain entry into buildings, vehicles, and aircraft when normal means of entry are locked or blocked
|
Forcible Entry
|
|
|
4 categories of forcible entry tools
|
Pushing/Pulling
Striking Prying Cutting |
|
|
Smaller versions of the pick headed and flat headed axe are used for overhoaul
|
but are ineffective for forcible entry
|
|
|
Pick Head Axe
|
6# or 8# head
Most versatile Tool |
|
|
Prying tool with a claw at one end and a spike or point at a right angle to a wedge at the other end
|
Halligan Tool
|
|
|
Rebar Cutters
|
Not meant to cut power lines
|
|
|
Oxyacetalene Torches
|
Hand carried or Wheeled
Cut through heavy metal components |
|
|
Acetylene
|
Colorless gas that has an explosive range from 2.5 to 81 percent in air. used as fuel for cutting and welding operations
|
|
|
Never exceed 15 psi operating pressure when operating
|
acetylene cutters
|
|
|
OxyGasoline cutting torches
|
Dual Hose
New to fire service fully functional undr water Fire cant go back up line because fuel is delivered in liquid form |
|
|
Burning Bars
|
Exothermic Cutting Rods
Cuts through concrete and metal very fast |
|
|
Plasma Cutters
|
Metal Cutters
Numerous gases |
|
|
Cutting Flare
|
Like a normal flare
Flames for 15 seconds to two minutes |
|
|
Rotary Saw
|
Larger than circular saw
doent need a seperate power source |
|
|
Rambar
|
Requires only one person to operate
Like Haligan witha sliding handle to open doors |
|
|
Carrying tools: Axes
|
Away from body.
Pick Headed axe: put axe head undr arm and grasp pick end |
|
|
Types Of Lifts
|
Extremities Lift/Carry (2 person
|
|
|
Fire Walls are made from
|
Masonry
|
|
|
Type III construction
|
Resists fire spread from external structures
|
|
|
Can Bowstring trusses be easily identified from street level
|
No
|
|
|
NFPA 1982 Refers To
|
Pass Devices
|
|
|
NFPA 1901 says there should be how many fire extinguishers on an apparatus
|
2
|
|
|
Wet Chemical Extinguishers are used for which type of fire
|
Class K
|
|
|
Carbon Dioxide Extinguishers work on what classes of fire
|
B and C
|
|
|
NFPA 10 recommends fire extinguishers be identified by
|
Pictographs
|
|
|
NFPA 10 refers to
|
Fire Extinguishers
|
|
|
Firefighters must continue to where their SCBA as long as carbon monoxide reading are above ____
|
50 ppm
|
|
|
3 methods of gaining access to victims in vehicles
|
Normally operating door
Through a Window By tearing off parts of a vehicles body |
|
|
3 Types of Wood Swinging Doors
|
Panel, Slab, Ledge
|
|
|
3 Types of Metal Swinging Doors
|
Hollow Metal , Tubular, and Metal Clad
|
|
|
Types of overhead doors
|
Sectional, Tilt Slab, Roll-Up, Telescoping
|
|
|
Which type of overhead door has its locking mechanism located in the center of the door
|
Sectional
|
|
|
Characteristics of Slab Doors
|
Wooden, Solid or Hollow Core, Used in Homes, Very Common, Swinging Door
|
|
|
Panel Door Characteristics
|
Wooden Swinging Door
Solid Wooden panels inset with wood or glass |
|
|
Characteristics of Ledge Doors
|
Wooden Swinging Door
Found in Warehouses, Barns and Sheds Known as Baten Doors |
|
|
Rabbeted Jamb
|
Jamb into which a shoulder has been milled to permit the door to close against the provided shoulder
|
|
|
Metal Clad Door Characteristics
|
Wetal swinging door
Wood core with metal skin |
|
|
Tubular Metal Doors
|
Metal Swining door
slot is provided for inseting glass Like doors to 101 |
|
|
Hollow Metal Doors
|
Filled with fire resistive material
|
|
|
Revolving Door Types
|
Panic Proof
Drop Arm Type Metal Braces |
|
|
Panic Proof Revolving Door Characteristics
|
1/4 " cable holding door panels. Release is triggered by force pushing in opposite direction
|
|
|
Drop Arm Revolving Door Characteristics
|
Solid arm passing through one of the panels
press pawl to disengage arm and push panel parallel to other panel then repeat |
|
|
Metal Braced Revolving Door Characteristics
|
Resembles a Gate Hook and Eye Assembly
|
|
|
Hollow Metal Doors
|
Filled with fire resistive material
|
|
|
Revolving Door Types
|
Panic Proof
Drop Arm Type Metal Braces |
|
|
Panic Proof Revolving Door Characteristics
|
1/4 " cable holding door panels. Release is triggered by force pushing in opposite direction
|
|
|
Drop Arm Revolving Door Characteristics
|
Solid arm passing through one of the panels
press pawl to disengage arm and push panel parallel to other panel then repeat |
|
|
Metal Braced Revolving Door Characteristics
|
Resembles a Gate Hook and Eye Assembly
|
|
|
Sectional Overhead Doors
|
Not too hard to force
locking mechanisms in middle Pry upward on door to force may need to remove a panel |
|
|
Tilt Slab Overhead Doors
|
Called "Awning Doors"
Can be difficult to fors May be obstructed by vehicles Very Heavy Locking mechanism located on one side or the other |
|
|
Roll Up Overhead Door
|
Called Sheet Curtain Doors
Usually have a man door next to them which would be easier to force |
|
|
Telescoping Overhead Doors
|
telescope
|
|
|
When forcing an overhead door
|
Use a rotary saw to cut an openingabout 6 feet high and nearly the full width of the door
|
|
|
Fire Door Types
|
Horizontal and Vertical Sliding
Single and Double Swinging Overhead Rolling |
|
|
Mortise Lock
|
Fits into cavity of door
consists of a latch mechanism and an opening device Has a Bolt the proturdes into a reciever mortised into the jamb |
|
|
Bored or Cylindrical Locks
|
Involves boring two holes at right angles to one another
|
|
|
Rim Lock
|
identified by a cylinder that isrecessed into the door by a bored latching mechanism
|
|
|
Whos responsibilty is it to install a lock box
|
property owners
|
|
|
wh inspects a lock boxes installation
|
fire dept
|
|
|
K Tool
|
Used to pull all types of lock cylinders
|
|
|
A tool
|
Same as K tool for most part but may cause more damage
|
|
|
J Tool
|
Made of Rigid Heavy Guage Wire
Designed to fit between double hanging doors equipped with panic hardware |
|
|
Shove Knife
|
Resembles a wide putty knife
Opens outward swinging latch-type doors |
|
|
Bam Bam Tool
|
uses a case hardened screw that is screwed into the keyway of a padlock. Pull on sliding hammer to remove tumbler
|
|
|
Tools used to break padlocks
|
Duck-Billed Lock Breaker
Hammerhead Pick Locking Pliers and Chain Hockey Puck Lock Breaker Bam Bam Tool |
|
|
Common Window Styles
|
Double Hung (Check Rail)
Hinged (Casement) Projected (Factory) Awning or Jalouise (hinge on top) |
|
|
Stitch drilling concrete
|
beforehand majes breaching easier
|
|
|
Which NFPA standard deals with ladders
|
1932
|
|
|
Characteristics of Wood Ladders
|
Highest Cost
Heaviest Retains strength when exposed to heat Very Durable Hard to Repair |
|
|
Use the 3 firefighter flat shoulder raise
|
On extension ladders up to 35 feet
|
|
|
Ladders up to 35 feet or longer should be raised by
|
3 firefighters
|
|
|
How should conscious victims be lowered down a ladder
|
Feet first facing the building
|
|
|
An unconscious victim will be lowered down a ladder
|
facing rescuer and redsting on their knee
|
|
|
When using a ladder to rescue small children
|
cradle them in your arms
|
|
|
Main structural component of a ladder supporting the rungs or rung blocks
|
Beam
|
|
|
Lowest and widest section of an extension ladder
|
Bed Section
|
|
|
Bottom end of ladder
|
Butt
|
|
|
Metal plates or spikes, cleats attached to the butt of a ground ladder
|
Butt Spurs
|
|
|
Upper section of an extension ladder
|
Dogs/Pawls
|
|
|
Swivel plates attached to the but of the ladder, usually have rubber or neoprene bottom surfaces
|
Footpads
|
|
|
Wood or metal strips, sometimes in the form of slots or channelson an extension ladder that guide the fly while being raised
|
Guides
|
|
|
Rope or cable used for hoisting and lowering fly sections of an extension ladder
|
Halyard
|
|
|
Label affixed to the inside of each beam of each ladder section
|
Heat sensor label
|
|
|
Curved metal devices installed near the top end of roof ladders to secure the ladder to the highest point on apeaked roof
|
Hooks
|
|
|
Another name for the bed of a ladder
|
Base or main section
|
|
|
Devices attached to the inside of the beams on fly sectionsused to hold the fly section in place after it has been extended
|
Pawls / Locks / Dogs
|
|
|
Strips of metal attached to ladders at chafing points, such as the tips, ar at areas where they com into contact with the apparatus mounting brackets
|
Protection Plates
|
|
|
Small grooved wheel through which the halyard is drawn on an extension ladder
|
Pulley
|
|
|
Two lengthwise members of a trussed ladder beam that are seperated by truss or seperation blocks
|
Rails
|
|
|
Cross members that provide the foothold for climbing
|
rungs
|
|
|
Another name for footpads on a ladder
|
Shoes
|
|
|
Metal rods extending from one beam to another
|
Tie Rods
|
|
|
Extreme top of ladder
|
Tip
|
|
|
Spacers set between the rails of a trussed ladder; sometimes used to support rungs
|
Truss Block
|
|
|
scaling ladder with a single beam and a large curved hook that can be put over windowsills for climbing
|
Pompier ladder
|
|
|
Types of Single Ladders
|
Roof (folding hooks)
Attic Ladders (folding ladders) |
|
|
Length of Roof Ladders
|
12 - 24 feet
|
|
|
Lngth of Folding Ladders
|
8 - 16 feet (10 feet most common)
|
|
|
Types of Extension Ladders
|
Extension
Pole (Bangor) |
|
|
Large extension ladder that requires tormentor poles to steady and the ladder as it is raised
|
Pole Ladder
|
|
|
Length of Extension Ladders
|
12-39 feet
|
|
|
Ladders longer than ____ must me equipped with stay poles
|
40 feet
|
|
|
Most modern pole ladders do not exceed ______
|
5o feet
|
|
|
Keeping equipment or apparatus in a ready state
|
Maintenance
|
|
|
To restore or put together that which has becomeinoperable or out of place
|
Repair
|
|
|
Ladders designed so that they may be self supporting step ladders (A frame)
|
Combination Ladder
|
|
|
Length of combination ladders
|
10-16 feet
|
|
|
Used to climb from floor to floor via exterior windows
|
Scaling or Pompier Ladders
|
|
|
Characteristics of a Metal ladder
|
Good conductor of heat
Easy to repair Can fail when subjected to heat Widest Range of Sizes |
|
|
Characteristics of Wood Ladders
|
Highest cost of Ladders
Heaviest per unit of length Retains strength when exposed to heat or flame Very Durable |
|
|
Characteristics of Fiberglass Ladders
|
Poor conductor of electricity
Can suddenly crack or fail when overloaded Can burn when exposed to flame |
|
|
NFPA 1931
|
Referes to certification of ladders, states ladder meets the standard
|
|
|
NFPA 1932
|
Standard on Use, Maintenance, and service testing of ladders
|
|
|
Most effective way to clean a ladder
|
Soft bristle brush and running water
|
|
|
Do not place ladders
|
Near exhaust pipes
|
|
|
Inspect ladders when
|
On a monthly basis and after each use
|
|
|
What to look for when inspecing wooden ladders
|
Areas where finidh has been scraped or chafed
Darkening of the varnish Dark streaks in wood Marred, worn, cracked or splintered parts Rounded or smooth edges Water Damage |
|
|
Inspecting Roof ladders
|
Make sure hook assemblies operate with ease, no rust or deformities
|
|
|
NFPA 1901
|
Standard for automotive apparatus
sets minimum lengths and types of ladders to be carried on all pumpers |
|
|
What ladders should be carried on all pumpers
|
Straight ladder with roof hooks
Extension Ladder Attic Ladder |
|
|
Aerial Apparatus must have the following ladders
|
1 10 foot or longer attic ladder
2 roof ladders equipped with hooks 1 combination ladder 1 24 foot or longer extension ladder 1 35 foot extension ladder |
|
|
Do not raise ladders within ____ of electical lines
|
10 feet
|
|
|
On a ladder firefighters must be placed no closer than
|
10 feet
|
|
|
Use a leg lock or ladder belt to
|
tye into ladder
|
|
|
Rules of thumb for ladder length
|
Extend the ladder 3-5 rungs above the roof edge
Place the tip of the ladder even with the top of the window and to the upwind side for ventilation place the tip of the ladder just below the window sill for rescue from a window |
|
|
On extension ladders the measured length may be as much as ____ inches less than the designated length
|
6
|
|
|
Who gives command to lift ladder
|
firefighter at the butt
|
|
|
Who determines exact placement of ladder
|
firefighter at the butt
|
|
|
Carry the forward end of the ladder slightly ____ to provide better balance
|
lower
|
|
|
Types of Ladder Carries
|
One Firefighter Low Shoulder (single or roof ladders)
2 Firefighter Low Shoulder (single, roof, extension laddrs up to 35 feet) 3 firefighter flat shoulder (extension ladders up to 35 feet) 4 firefighter flat shoulder carry (same as 3 ff ) 2 Firefighter arms length on edge (light ladders on bed section side) |
|
|
Carry a roof ladder
|
use low shoulder with tips forward
When tips are opened carry them away from firefighter |
|
|
Gasoline or hydraulically driven blower device used primarily to expel smoke from burning buildings. Sometimes used to blow fresh air into a building to assist in purging smoke or other contaminents
|
Smoke Ejector
|
|
|
When using a ladder to hold a smoke ejector place it
|
directly in front of window with tip on wall above window
|
|
|
In general all metal or fiberglass ladders are designed to be placed ___
|
Fly Out
|
|
|
Secure the halyard with a
|
Clove hitch and saftey knot
|
|
|
Wooden Ladders are typically placed
|
Fly In
|
|
|
Lowering an unconscious victim
|
Can be done with victim facing in or out resting on rescuers knee, keep legs outside of beams to avoid entanglement.
Or place one arm under victims arm and another under vistims leg |
|
|
The systematic removal of heated air, smoke, and fire gases from a burning building and replacing them with cooler air
|
Ventillation
|
|
|
4 types of fire service ventillation
|
Natural
Vertical Horizontal Mechanical |
|
|
Why should you never direct a hose stream into a ventillation opening before the fire has been controlled
|
Doing so may compromise ventillation and put fire crews in danger
|
|
|
Ceiling Jets and Mushrooming
|
Ceiling jets are a more tchnical term for mushrooming
|
|
|
Considerations affecting the need to ventillate
|
Is there a need to ventilate at his time (based on moke, heat)
Where is ventillation needed? What type of ventillation should be used? Do fire and structural condiions allow for safe roof openings? Are your personnel trained enough to do the ventillaion? |
|
|
Phenomenon oa a strong air draft moving from ground level to the roof level of abuilding. Affected by building height, configuration, and temperature differences between inside and outside air
|
Stack Effect
|
|
|
How is the personnel involved in in firefighting operations different between low-rise and high rise buildings?
|
You typically need 4 to 6 times the amount of personnel
|
|
|
Ususally only the _____ penetrates the roof in high rise buildings
|
Stair Well
|
|
|
Engineered trusses in roofs
|
can fail without warning
|
|

|
Mansard
|
|

|
Gambrel
|
|

|
Hip
|
|
|
Single cut made the width of a saw blade made in a roof to check for fire extension
|
Kerf Cut
|
|
|
Rectangular exit opening cut in a roof, allowing a section of roof deck to be tilted thus creating an opening similar to a louver
|
Louver or vent cut
|
|
|
Horizontal member between trusses that supports the roof
|
Purlin
|
|
|
Defensive tactic that involves cuttin an exit opening in the roof of a burning building , extending from one outside wall to the other, to create an opening which a spreading fire may be cut off
|
Trench Ventillation
|
|
|
Technique used to develop artificial circulation and to pull smoke out of a structure.
|
Negative -Pressure Ventillation
|
|
|
Smoke churns when a smoke ejector is not properly sealed witha asalvage cover in the window
|
Churning
|
|
|
In PPV how far should blower be placed from doorway?
|
4 - 10 feet
|
|
|
Method of ventillating a fire building by directing a fog stream of water out a window to increase air and smoke movement
|
Hydraulic Ventilation
|
|
|
Flat Roof are found on
|
Commercial, Industrial, Appartment Buildings and some single family residences
|
|
|
Advantages of forced ventilation
|
supplements and enhances natural ventillation
Ensures more positive control of air flow Speeds the removal of contaminents Reduces smoke damage promotes public relations |
|
|
Firefighters need to know the following in regards to pressure in a water supply system
|
Static Pressure
Flow Presure Residual Pressure |
|
|
4 Components of a Water Supply System
|
Sources of Water Supply
Means of Moving Water Water Treatment Facilities Water Storage and Distribution Systems |
|
|
Three methods of moving water in a water supply system
|
Direct Pumping
Gravity Systems Combination Systems |
|
|
Water supply system supplied by a series of pumps rather than elevated storage tanks
|
Direct Pumping System
|
|
|
How much higher must the water source of a gravity fed water system be than the highest point of water in the system to be considered effective
|
100 feet
|
|
|
Fire hydrant that receives water from two or more directions
|
Circulating Feed
|
|
|
Water main arranged in a complete circuit so that water will be supplied to a given point from more than one direction. Also called circle system, circulating system, or belt system.
|
Loop System
|
|
|
Wate system's network of underground pipes
|
Mains
|
|
|
Fire hydrant that receives water from only one direction
|
Dead End Hydrant
|
|
|
A distribution system that provides circulating feed from all directions is called a
|
Grid System
|
|
|
Large Mains, with widespread spacing, that convey large quantities of water to various points in the system for distribution to secondaryfeeders and smaller mains
|
Primary Feeder
|
|
|
Network of intermediate-sized mains that subdivide the grid within various loops of primary feeders and supply the distributors
|
Secondary Feeders
|
|
|
Grid arrangement of smaller mains serving individual fire hydrants or blocks of consumers
|
Distributors
|
|
|
Recommended size for fire hydrant mains in residential Areas
|
6 inches (should be cross connected with 8 inch mains not more than 600 feet apart)
|
|
|
Recommended size for fire hydrant mains in commercial Areas
|
8 inches
|
|
|
Recommended size for fire hydrant mains in principal streets and in long mains not cross-connected at frequent intervals
|
12 inches
|
|
|
A type of control valve for sprinkler systems in which the position of the center screw indicates whether the valve is open or closed
|
OS&Y valve (Outside stem and yoke)
|
|
|
A type of valve used to control underground water mains that provides a visual means for indicating "open" or "shut" position. Found n the supply main of installed fire protection systems
|
Post Indicator Valve
|
|
|
Control valve with a solid plate operated by a handle and screw mechanism.
|
Gate Valve
|
|
|
Type of control valve that uses a flat circular plate in the pipe which rotates ninety degrees across the cross section of the pipe to control flow
|
Butterfly Valve
|
|
|
Three pressures that are of concern in a water distribution system
|
Static Pressure
Flow Pressure Residual Pressure |
|
|
Potential energy that is available to force water through pipes. Pressure at a point in a water system when no water is flowing
|
Static Pressure
|
|
|
Pressure at the test hydrant while water is flowing from another nearby hydrant
|
Residual Pressure
|
|
|
Pressure created by the rate of flow or velocity of water coming from a discharge opening
|
Static Pressure
|
|
|
In general all fire bonnets, barrels, and foot pieces are made of
|
Cast Iron
|
|
|
Internal parts of hydrants are made of
|
bronze
|
|
|
These type of hydrants are avilable whenever there are prolonged periods of subfreezing temps
|
Dry Barrel
|
|
|
Who oversees the installation of fire hydrants
|
Water Dept Personnel
|
|
|
Where should fire hydrants be placed/spaced
|
300 feet in high value districts
at every other intersection |
|
|
Light Blue Hydrant Specs
|
Class AA
1500 gpm or greater |
|
|
Green Hydrants
|
Class A
1000 - 1499 gpm |
|
|
Orange Hydrants
|
Class B
500 - 999 |
|
|
Red Hydrants
|
Class C
< 500 gpm |
|
|
Fire Hydrant Testing
|
Remove all caps except 1 2/12 cap
|
|
|
Instrument that is inserted into a flowing fluid to measure the velocity pressure of the stream
|
pitot tube
|
|
|
Standard on water supplies for suburban and rural firefighting
|
NFPA 1142
|
|
|
Water shuttles are recommended for distances of over
|
1/2 mile
|
|
|
Portable water tanks should hold
|
1,000 gallons plus
|
|
|
Point at which a fire dept can connect into a standpipe or sprinkler to boost the waterflow into the system.
|
Fire Dept Connection (FDC)
|
|
|
Flexible tube used by firefighters to carry water or other extinguishing agents under pressure from a source of supply to a point of application
|
Fire Hose
|
|
|
Most Common Types of Fire Hose
|
Single Jacket
Double Jacket Rubber Single Jacket Hard Rubber/Plastic non collapsible |
|
|
Type of hose that is
Rubber Covered Rubber Lined Fabric Reinforced |
Booster 3/4 - 1 "
|
|
|
Type of hose that is
One or Two Woven Jackets Rubber Lined |
Woven Jacket Hose
|
|
|
Type of hose that is
Polymer Covered Polymer Lined |
Impregnated Single Jacket
|
|
|
The size of a fire hose refers to its
|
Inside Diameter
|
|
|
Common Sizes of Fire Hose
|
50" or 100"
|
|
|
Pieces of fire hose are referred to as
|
Lengths or Sections
|
|
|
Large diameter collapsible fire hose used to connect a pumper to a pressurized water source
|
Soft Intake Hose
|
|
|
Flexible rubber hose reinforced with a steel core to prevent collapse from atmospheric pressure
|
Hard Intake Hose
|
|
|
NFPA standard for fire hose
|
1961
|
|
|
NFPA standard for fire hose connection
|
1963
|
|
|
NFPA standard states that a pumper must carry how much hose
|
15' large soft intake or 20' hard intake
800' of 21/2" hose 400 ' of 11/2 ,13/4 or 2" |
|
|
What do you do to keep hose liner from drying out
|
roll hose in a straight roll
|
|
|
Woven jacketed hose is subject to dangers from mold and mildew
|
true dat
|
|
|
How to clean hose exposed to chemicals
|
scrub with baking soda and water
remove from apparatus peiodically and wash and dry it |
|
|
Wash hose with rubber hose and hard intake hose wih
|
water only
|
|
|
If hose has been exposed to oil
|
wash with mild soap and water, rinse thoroughly with water
|
|
|
Male Side of Coupling
|
Has rocker lugs on shank
No lugs on female shank |
|
|
Part of coupling that serves as a point of attachment to the hose
|
Shank (Tailpiece, Bowl, Shell)
|
|
|
Three types of lugs
|
Pin (not common)
Rocker Recessed (booster) |
|
|
Special cut at the beginning of the thread on a hose coupling that provides positive identification of the first thread to eliminate cross-threading
|
Higbee Cut (On threads)
|
|
|
Notches or grooves cut into coupling lugs to identify by touch or sight the exact location of the higbee cut
|
Higbee Indicators (On Lugs)
|
|
|
Storz Couplings Unlock with
|
A 1/4 turn
|
|
|
Used to make connection water tight between female and male threaded connections
|
Swivel Gasket
|
|
|
Used at the end of the hose where the hose is expanded into the shank of the coupling
|
Expansion Ring Gasket
|
|
|
Any piece of hardware used in conjunction with fire hose for the purpose of delivering water
|
Hose Appliance (water flows through appliances not tools)
|
|
|
Used in pumper discharges and gated wyes.
|
Ball valves
|
|
|
Used to control water flow from a hydrant. Has a baffle that is moved by handle and screw arrangement
|
gate Valves
|
|
|
Used on large pump intakes and incorporate a flat baffle that turns 90 degrees . 1/4 turn
|
Butterfly Valve
|
|
|
Used in siamese appliances
|
clapper valves
|
|
|
Hose appliance with one female inlet and two or more male outlets
|
Wye
Gated Wye is valve controlled |
|
|
Combines 2 or more hoselines into one
|
siamese
|
|
|
Any of a variety of hose appliances with one female inlet for 2 1/2 inch or larger hose and with three gated outlets
|
Water Thief (T in wildland connections)
|
|
|
Another name for Large Diameter Hose Appliances
|
Portable Hydrants
Phantom Pumpers |
|
|
Allows additional pumpers to connect to a hydrant without losin pressure
|
Hydrant Valves
|
|
|
Fitting for connecting hoses with dissimilar threads
|
adapter
|
|
|
device that facilitates the connection of hoselines of different sizes to provide an uninterrupted flow of extinguishing agent
|
Fitting
|
|
|
Adapter used to attach a smaller hose to a larger hose
|
adapter
|
|
|
provide support for intake or discharge hose at a pumper
|
elbow adapters
|
|
|
Protect threads on male discharge outlets
|
hose caps
|
|
|
Female inlets areHO capped with
|
Hose Plugs
|
|
|
Can be applied to a hose to temporarily repair a rupture or leak in a hose
|
Hose Jacket
|
|
|
Prevent mechanical damage to hoselines that cross windowsills or wall parapets
|
Hose Rollers
|
|
|
Hose Tools (water doesn't flow through these)
|
Hose Roller
Hose Jacket Hose Clamp Spanner Wrench Hose Bridge |
|
|
When do you use a straight roll
|
When loaded back on apparatus at fire scene
When returned to quarters for washing Storage |
|
|
Can be used to reduce stress on the nozzle operator and improve the mobility of a charged hoseline
|
Hose Straps
|
|
|
Use this roll where fire hose is likely to be deployed for use directly from a roll
|
Donut Roll
|
|
|
This roll can be slung together with webbing and can be used in high rise applications
|
Twin Donut Roll
|
|
|
Arrangement of hose usually placed on top of a hose load and conected to the end of the load
|
Finish
|
|
|
3 common loads for supply hoselines
|
Accordian
Flat Horsehoe |
|
|
2 purposes of a dutchman
|
Changes direction of coupling
changes the location of a coupling |
|
|
Arrangement of fire hose in a hose bed in which the hose lies on edge with the flods adjacent to one another
|
Accordian Load
(ease of loading and shoulder carry) |
|
|
Arrangement of fire hose in a hose bed or compartment in which the hose lies on edhe in the form of a horshoe
|
Horshoe Load
|
|
|
Hose Load Finishes 2 Categories
|
Those for forward lays (Straight Finish)
Reverse Lays (reverse horseshoe, skid load) |
|
|
This load is adaptable for varying widths of hose beds and is often used in transverse beds
|
Preconnected flat load
|
|
|
This load has hose folded in three layers. Pulled by one person
|
Triple Layer Load
|
|
|
This type of load can be carried and advanced by one person. Carried on the shoulder
|
Minuteman Load
|
|
|
Hose lay deployed by two pumpers, one doing a forward lay the second doing a reverse lay
|
Split Lay
|
|
|
One of the quickest and easiest ways to move hose at ground level
|
The working line drag
|
|
|
Preservice tests on fire apparatus or equipment performed at the factory or after delivery to ensure the purchaser that the apparatus or equipment meets bid specifications
|
Acceptance Testing
|
|
|
Series of tests performed on equipment to ensure their readiness
|
Service Test
|
|
|
How many components make up threaded couplings
|
2 male and female
|
|
|
What is the easiest supply hose load to load
|
Flat Load
|
|
|
When replacing a burst section of hose how many additional sections should be used to replace one burst section
|
2
|
|
|
Test for fire hose that should not be attempted by fire dept personnel and exerts pressures much higher than those in the field
|
Acceptance Testing
|
|
|
Extinguishing qualities of water
|
cooling
dilluting or excluding oxygen absorbs heat by converting to water vapor or steam |
|
|
Visible form of steam
|
condensed steam
|
|
|
Quantity of heat absorbed by a substance at the point at which it changes from a liquid to a vapor
|
Latent heat of vaporization
|
|
|
Hose stream that stays together as a solid mass as opposed to a fog or spray stream. Produced by a solid bore nozzle.
|
Solid Stream (not to be confused with a straight stream)
|
|
|
Water stream of finely divided particles used for fire control
|
Fog Stream
|
|
|
Stream of water that has been broken into coarsely divided drops
|
Broken Stream
|
|
|
That part or total pressure that is lost while forcing water through pipes, fittings,fire hose, and adapters
|
Friction Loss
|
|
|
Discharges less than 40 gpm including those fed by booseter lines. Typically supplied by 3/4 inch, 1 inch, 1 1/2" hoseline
|
Low-Volume Stream
|
|
|
Supplied by 1 1/2" - 3" hose, with flows from 40 - 350 gpm.
|
Handline stream (flows greater than 350 gpm not recommended)
|
|
|
Discharges greater than 350 gpm and is fed by 2 1/2 or 3" hoselines or LDH
|
Master Stream
|
|
|
Fire Streams
|
Low Volume (40 gpm or less)
Handline (40 - 350 gpm) Master (350+ gpm) |
|
|
Fire Stream Patterns
|
Solid
Fog Broken |
|
|
A stream that does not lose its continuity until it reaches the point where it loses forward velocity
|
BreakOver
|
|
|
These streams operate at lower pressures
|
Solid Stream
|
|
|
When spraying enegized electrical equipment
|
Dont use solid streams. Use fog streams with at least 100 psi
|
|
|
Types of streams created with fog nozzles
|
Straight Stream
Narrow Fog Wide Fog |
|
|
The designed operating pressure of most combination nozzles
|
100 psi
|
|
|
Cellar nozzle is an example of a
|
broken stream nozzle
|
|
|
Valve control that seats a movable cylinder against a shaped cone to turn off the flow of water.
|
Slide Valve
|
|
|
Consists of an exterior barrel guided by a screw that moves it forward or backward, rotating around an interior barrel.
|
Rotary Control Valve
|
|
|
Act of creating a barrier between the fuel and the fire
|
Seperating
|
|
|
Reduction of heat by the quenching action or heat absorption of the extinguishing agent
|
Cooling
|
|
|
Act of excluding oxygen from a fuel
|
Smothering
|
|
|
Flammable liquids that have an attraction for water, much like positive magnetic pole attracts a negative pole
|
Polar Solvents
|
|
|
Lowers the surface tension of water and allows it to penetrate deep seated fires
|
Foam
|
|
|
Raw foam liquid before the introduction of water and air
|
Foam concentrate
|
|
|
Device that introduces foam concentrate into the water stream to make the foam solution
|
Foam Proportioner
|
|
|
Mixture of foam concentrate and water before the introduction of air
|
Foam Solution
|
|
|
Completed product after air is introduced into the foam solution
|
Foam
|
|
|
mixed with water
|
proportioned
|
|
|
mixed with air
|
aerated
|
|
|
Foam concentrate that combines the qualitites of fluoroprotein foam with those of aqueous film forming foam
|
Film Forming Fluroprotein Foam FFFP
|
|
|
Process used to mix foam concentrate with water in a nozzle proportioner. Water is drawn into the water stream via the venturi method
|
Eduction (part of induction)
|
|
|
Method of proportioning foam that uses an external pump or head pressure to force foam concentrate into the fire stream at the correct ratio for the flow desired
|
Injection
|
|
|
Mechanocal blower generator that is similar in appearance to a smoke ejector
|
Mechanical Blower Generator
|
|
|
Eductor that is placed along the length of a hoseline
|
In-Line Eductor
|
|
|
Foam Application Techniques
|
Roll-On (spray in front and foam rolls onto fuel)
Bank-Down (spray object near fuel, foam banks down object onto fire) Rain Down (used on large fires or spills) |
|
|
Which type of foam is commonly used at the rate of 20:1 or 200:1 through hydralically operated nozzle delivery systems
|
Medium Expansion
|
|
|
What is the best appliance for the generation of low expansion foam
|
Air aspirating foam nozzle
|
|
|
Class B foams are best used on what two types of flammable liquids
|
polar solvents
hydrocarbons |
|
|
Solid bore nozzles and foam
|
can only deliver certain types of class A foam
|
|
|
These nozzles can be used to produce a short acting low expansion foam
|
fog nozzles
|
|
|
20:1 - 200:1
|
Medium Expansion Foam
|
|
|
200:1 - 1000:1
|
High expansion foam
|
|
|
Start fire attack here
|
unburned side
|
|
|
For interior firefighting what is the smallest handline to be used
|
1 1/2"
|
|
|
A fire that you cannot see from the doowrway because objects are shielding it
|
Shielded Fire
|
|
|
reducing the hazard presented by the hot gas layer
|
gas cooling
|
|
|
When gas cooling what do you set the fog nozzle at
|
40 - 60 degree fog pattern
|
|
|
Technique for gas cooling
|
1 to 2 second bursts
stop spraying smoke when water droplets begin to fall overhead |
|
|
Attack method that involves discharge of water or a foam stream directly onto burning fuel
|
Direct attack
|
|
|
Applying short burts of water directly onto the fire in a direct attack until the fire "darkens down" is known as
|
Penciling
|
|
|
TEchnique used to cool hot surfaces to slow or stop the pyrolysis process by gently applying water and allowing it to run over the hot material
|
Painting
|
|
|
Directing fire streams toward a ceiling of a room or building in order to generate a large amount of steam.
|
Indirect Attack
|
|
|
Battling a fire using an indirect and direct attack
|
Combination Attack
|
|
|
Biggest difference between direct and indirect attack
|
Direct is started inside compartment wheile indirest is started outside compartment
|
|
|
When to use master streams
|
Direct Fire Attack
Backup handlines Exposure Protection |
|
|
Master streams should enter structure so they bounce of ceilings
|
werd
|
|
|
What are the smallest hoselines used to supply a master stream
|
2 1/2"
|
|
|
a Maximum of _____ feet should be used to supply a master stream.
|
100
|
|
|
Most common aerial devices
|
Quints
Aerial Ladders Aerial Platforms Water Towers |
|
|
Pumper with a hydraulically operated extension ladder with a pump
|
Quint
|
|
|
Pumper with a hydraulically operated extension ladder
|
Aerial Ladder (50-135 feet)
|
|
|
A power operated aerial device that combines an aerial ladder with a personnel carrying platform supported at the end of a ladder
|
Aerial Ladder Platform
|
|
|
Aerial device in which the structural member support is hinged and operates in a folding manner
|
Articulating Aerial Platform
|
|
|
Pumpers equipped with hydraulically operated booms
|
Water Towers (50 - 130 feet)
|
|
|
Liquids that have flash points of less than 100 degrees farenheit
|
Flammable Liquids
(Gasoline and Acetone) |
|
|
Flammable liquids with flash points higher than 100 degrees farenheit
|
Combustible Liquids
(Kerosene and Vegetable oIL) |
|
|
Rapid vaporization of a liquid stored under pressure upon release to the atmosphere following major failure of its containing vessel.
|
Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion (BLEVE)
|
|
|
Method most often used to control flammable liquid fires
|
Applying Foam
|
|
|
Using water to Control Class B Fires
|
Cooling Agent
Mechanical Tool (sweeping back and forth to move fuel) Crew Protection (shutting off control valves) |
|
|
What happens to natural gas that leaks underground in wet soil
|
Can lose its odorant
|
|
|
Natural gas in its pure form is called
|
Methane
non toxic and lighter than air |
|
|
odor added to methane
|
mercaptan
|
|
|
Natural gas is explosive in concentrations between
|
5 and 15 percent
|
|
|
Another name for liquefied Petroleum Gas
|
bottled gas
|
|
|
Two main types of LPG
|
butane
propane |
|
|
LPG charactersitcs
|
Heavier than air
|
|
|
If gas is burning from a broken gas pipe what do you do
|
Protect exposures dont put out fire
|
|
|
Cutoff valve found at gas meter
|
petcock
|
|
|
When it is necessary to turn off electricity to a structure the main power switch should be
|
Locked and Tagged
|
|
|
Toxic compound found in some older oil-filled electrical transormers
|
Polychlorinated Biphenyl (PCB)
|
|
|
USe this type of extinguisher to extinguish fires in transformers at ground level
|
dry chemical or carbon dioxide
|
|
|
Allow pole top transformers to be put out by utility personnel
|
kj
|
|
|
Entrants should search high voltage areas with a _____
|
clenched fist to avoid grabbing wires
|
|
|
You do not need to turn off power to the whole building if fire is only located in part of i
|
you can use electricity for lighting etc...
|
|
|
Do not pull the electrical meter
|
IFSTA says so
|
|
|
Produced by an electrical current passing from a downed power line through the ground along the path of least resistance
|
Ground Gradient
|
|
|
Size Up Questions
|
Are there occupants in need of immediate rescue?
Are only contents involved or is it a structure fire Are exposures threatened by fire? Are there enough resources? |
|
|
Second Due Engine Co Responsibilities
|
Ensure adequate water supply
Backup Initial Atack Line Protect secondary means of egress Prevent Fire Extension Protect the most threatened exposure Assist in extinguishment Assist with fireground support company operations |
|
|
First Due Engine companies priorities
|
Intervene between trapped occupants and the fire
Protect rescuers Protect primary means of egress Protect interior exposures Protect exterior exposures Initiate extinguishment from the unburned side Operate master streams |
|
|
To aggressively attack a fire from the exterior with a large diameter fire stream
|
Blitz Attack
|
|
|
Support companies are typically
|
ladder trucks, quints, rescue units
|
|
|
Staging on a muti story building is locate where
|
2 floor below the fire floor
|
|
|
On a multistory fire where is the fire attack initiated
|
On the floor below the fire
|
|
|
Fire Orders
|
Keep informed on weather conditions
Know what the fire is doing at all times Base al actions on current and expected behavior of the fire Identify escape routes and safety zones Post lookouts Be alert keep calm think clearly, act decisively Maintain communications with your forces Give clear instructions make sure they are understood Maintain control of your forces at all times Fight fire aggressively providing for safety first |
|
|
3 main uses for a master stream
|
Back up handlines that are already atacking fire from the exterior
Direct Fire Attack Exposure Protectionq |
|
|
System of water pipes, discharge nozzles, and control valves designed to activate during fires by automatically discharging water
|
Automatic sprinkler System
|
|
|
Sprinkler, standpipe, carbon dioxide, and halogenated systems, as well as their fire pumps, dry chemical agents and their systems, foam extinguishers, and combustible metal agents that sense heat, smoke, or gas and activate automatically
|
Automatic Suppression Systems
|
|
|
Alarm that detects fire and alerts those only on the immediate premises. They do not notify fire dept
|
Protected premises alarm system
|
|
|
Types of Heat Detectors
|
Fixed Temperature (activate when a certain temp is reached)
Rate of Rise Detectors (when temp rises more than 12 degrees in 1 minute) |
|
|
Fixed Temp Devices
|
Fusible Link (expansion of heated materials)
Fusible Bulb Continous Line |
|
|
Small glass vial fitted into the discharge orifice of a fire sprinkler
|
Frangible Bulb
|
|
|
Conecting link device that fuses or melts when exposed to heat
|
Fusible Device
|
|
|
Can detect heat over a linear surface as opposed to others that can only detect in the spot where they are located
|
Continuous Line Detector
|
|
|
Stip or Disk composed of two different materials thate are bonded together
|
Bimetallic
|
|
|
3 basic types of flame detectors
|
Those that detect ultraviolet light
Infrared Both IR and UV |
|
|
These are released from all fires
|
Water vapor
Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide |
|
|
Detection Device Responses
|
Smoke Detector Fastest
Fire Gas Detector Heat Detector |
|
|
3 types of auxillary systems
|
Local Energy System
Shunt System Parallel Telephone System |
|
|
An auxillary alarm system that is within an occupancy that is attached directly to a hard wired or radio type municipal fire alarm box
|
Local Energy System
|
|
|
system that connects the protected property with the fire dept alarm communications center by a municipal master fire alarm box or over a dedicated phone line
|
Auxillary Alarm Syatem
|
|
|
Alarm actuated by heat smoke or gas. Or alarm boxes that automatically transmit a coded signal to the fire station to give the location of the alarm box
|
Automatic Alarm
|
|
|
NFPA standard for installation of Sprinkler systems
|
13
|
|
|
How much clearance should be between sprinklers and stored materials
|
18"
|
|
|
Vertical water pipe used to carry water for fire protection systems such
|
riser
|
|
|
Types of sprinklers
|
Pendant (points downward, storage areas or industrial occupancies)
Upright(Sits upright and sprays against a deflector) Sidewall (sits on wal of room) Special Purpose |
|
|
Sprinkler cabinets store a minimum of ___ sprinklers
|
6
|
|
|
Yoke on the outside with a threaded stem
|
OS & Y
|
|
|
Hollow metal post that houses valve stem. Attached to the valve is a movable plate reading "open" "Closed"
|
PIV
|
|
|
Similar to a PIV except that it extends horizontally through the wall with the target and valve operating nut on the outside of the building
|
WPIV (Wall Post Indicator Valve)
|
|
|
Does not use plate like PIV but instead uses a circular disc
|
Post Indicator Valve Assembly
|
|
|
A minimum water supply has to deliver the required volume of water to the highest sprinkler with a residual pressure of ____
|
15 psi
|
|
|
Whsn supplying to an FDC
|
Pumper should have a 1,000 gpm pump
minimum of 2 x 2 1/2 " Operate from hydrants other than the main supplying the sprinkler system |
|
|
Types of Sprinkler systems
|
Wet Pipe (temp > 40)
Dry Pipe (temp < 40) Preaction (like dry pipe with 2 detection systems) Deluge (like dry, spinklers have no fusible link and do not detect heat) Residential |
|
|
Who connects to the FDC
|
First arriving company
|
|
|
Turn off control valves to
|
Replace sprinklers
Interrupt Operation Perform Maintenance |
|
|
Which type rate - of - rise detectors of detector is designed for use in areas that are normally subject to regular temperature changes that are slower than those in fire conditions
|
Rate compensated detector
|
|
|
Quality of an organization's relationship with individuals, both internal and external who have contact wih the organization
|
Customer Service
|
|
|
The practice of minimizing damage and providing customer service through effective mitigation and recovery efforts, before, during, and after an incident
|
Loss Control
|
|
|
The process in which specific potential risks are identified and evaluated
|
loss control risk analysis
|
|
|
Methods and operating procedures associated with fire fighting by which firefighters attempt to save property and reduce further damage from water, smoke, heat and exposure during or immediately after a fire by removingproperty from a fire area, by covering it, or by other means.
|
Salvage
|
|
|
Operations conducted once the main body of the fire has been extinguished and consists of searching for and extinguishing remaining fire, placing building and contents in safe condition, determining cause of fire, recognizing and preserving evidence of arson
|
Overhaul
|
|
|
Salvage cover arrangement that channels excess water from a building.
|
Chute
|
|
|
Waterproof cover made of cotton duck, plastic, or other material used by fire dept to protect unaffected furniture and building areas from heat, smoke, and water damage
|
Salvage Cover
|
|
|
Used to carry debris, catch falling debris, and provide a water basin for immersing small objects
|
Carryalls (Debris Bags / Buckets)
|
|
|
Used to remove water from basements, elevator shafts, and sumps
|
Deatering devices
|
|
|
Used to hang salvage covers from walls or vertical openings
|
J Hooks
|
|
|
Used to hang salvage covers from rails or furniture
|
S Hooks
|
|
|
This type of throw is the most common for 2 firefighter to deploy a large salvage cover
|
Balloon Throw
|
|
|
When can salvage operations Begin
|
At the same time as fire attack
|
|
|
Where does overhaul typically begin
|
In the area of most severe fire involvement
|
|
|
A fire deliberately set
|
Incediary or Arson Fire
|
|
|
In an arson fire the prosecution must prove the perpetrator acted _____ and _____
|
willfully and maliciously
|
|
|
Three factors relating to cause of a fire
|
Fuel that ignited
Form and Source of Heat Ignition Act or omission that helped to bring these two factors together |
|
|
Continuous changes of possession of physical evidence that must be established in court to admint such material into evidence
|
Chain of Custody
|
|
|
In most jurisdictions the ____ has the legal rsponsibility for determining the cause and origin of he fire
|
Fire Chief
|
|
|
First arriving fire fighters should make note of
|
Vehicles and people present
Status of doors and windows Evidence of forced entry Contents of rooms Indications of unusual firebehavior |
|
|
Observation en route to a fire
|
Time of Day
Weather and Natural Hazards Barriers People leaving the scene |
|
|
Observations made upon arrival at a fire
|
Time of arrival and extent of fire
Wind direction and velocity Doors or windows locked or unlocked Location of Fire Containers or Cans Burglary Tools Familiar Faces |
|
|
Combustible material, such as rolled rags, blankets, newspapers, or flammable liquid,often used in intentionally set fires
|
Trailer
|
|
|
Observations during firefighting Ops
|
Unusual Odors
Abnormal behavior of fire when water is applied Obstacles hindring fire fighting Incendiary Devices Trailers Structural Alterations |
|
|
Should owners be allowed to speak freely about the fire if they are inclined to do so
|
Yes
|
|
|
Firefighters should not interrogate a potential arson subject unless they are trained and authorized to do so
|
jkjh
|
|
|
What should be your reply to questions about the fire?
|
The fire is under investigation
|
|
|
Evidence presented by a witness who did not see or hear the incident in question but heard about it from someone else
|
Hearsay
|
|
|
Does the fire dept have the authority to deny access to any building during fire fighting operations
|
Yes
|
|
|
Once firefighters clear a fire scene they may be required to get ____ to renter
|
Search Warrant
|
|
|
The fire scene emains in control of the ______ until the investigation is complete
|
Fire Dept
|
|
|
Time accepted to be standard to dispatch call
|
1 minute
|
|
|
Any location or facility at which 911 calls are answered either by direct calling rerouting or diverting
|
Public Safety Answering Point
(PSAP) |
|
|
NFPA standard that refers to the qualifications for a pubplic safety telecommunicator
|
1061
|
|
|
The ____ is the most widely used device for communicating fire alams.
|
Public Telephone
|
|
|
feature that allows telecomunicators to maintain access to a caller's phone line as long as the telecommunicator does not hang up
|
called party hold
|
|
|
The reverse of called party hold, when a telecommunicator hangs up the person calling can keep the line open if they lose consciousness this feature disconnects them
|
forced disconect
|
|
|
Enhanced 911 feature that displays the address of the party calling 911 on a screen for use by the public safety telecommunicator
|
Automatic Location Identification
|
|
|
Feature that allows the telecommunicator to call back a caller's phone after he or she has hung up
|
Ringback
|
|
|
Low powered radio transceiver that operates on frequencies authorized by the federal communications commision for public use with no lcense requirement
|
Citizens Band (CB) Radio
|
|
|
What is the role of a public safety answering point
|
Forward calls to the station
|
|
|
What is the first step a telecommunicator should do when receiving an emergency call
|
Identify the agency
|
|
|
What is not used to alert personnel of an unstaffed station
|
House Light
|
|
|
Hazard that arises as a result of the processes or operations that are characteristic of an idividual occupancy
|
Special Fire Hazard
|
|
|
Building in which there is a greater than normal likelihood of loss of life or properyt due to fire.
|
Target Hazard
|
|
|
Where are carbon monoxide detectors usually installed
|
In the same locations as smoke detectors
|
|
|
Where should smoke detectors be installed
|
In every bedroom and at every level of occupancy
|
|
|
According to title 29 code of the federal regualtion what must be made available free of charge by employers
|
Hep B Vaccine
|
|
|
In which stage of stress does your body's functions return to normal having adapted to the stimulus
|
Second Stage (Resistance)
|
|
|
During chest compressions the amount of time you spend compressing should be _____ the time for the release
|
The same as
|

