![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
119 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structure of human parvovirus
|
Family: Parvoviridae
No envelope ssDNA |
|
|
Strucutre of herpes simplex virus
|
Family: Herpesviridae
Symmetry: Icosahedral Enveloped dsDNA |
|
|
Structure of vaccinia virus
|
Family: Poxviridae
Symmetry: complex Enveloped dsDNA |
|
|
Structure of adenovirus
|
Family: Adenoviridae
Symmetry: Icosahedral No envelope dsDNA |
|
|
Parvovirus is a ss/ds DNA/RNA virus
|
ssDNA
|
|
|
herpes viruses, hep B, papilloma and adenovirus are ss/ds DNA/RNA viruses
|
dsDNA
|
|
|
Picorna virus, rubella virus, hepatitis C, HIV, SARS, influenza, measles and mups are ss/ds DNA/RNA viruses
|
ssRNA
|
|
|
Rotavirus is a ss/ds DNA/RNA virus
|
dsRNA
|
|
|
S. aureus
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Staphlococcus
Shape/reproduction: Clusters Respiration: Aerobic Shape: Cocci Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
S. faecalis
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Streptococcus
Shape/reproduction: Chains/pairs Respiration: anaerobic Shape: cocci Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
P. magnus
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Peptococcus
Shape/reproduction:- Respiration: Anaerobic Shape: Cocci Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
B. anthracis
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Bacillus
Shape/reproduction: Sporing Respiration: Aerobic Shape: Bacilli Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
L. monocytogenes
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Listeria
Shape/reproduction: Non-sporing Respiration: Aerobic Shape: Bacilli Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
C. tetani
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Clostridium
Shape/reproduction: Sporing Respiration: Anaerobic Shape: Bacilli Staining: Gram-positive |
|
|
P. acnes
Genus: Shape/reproduction: Respiration: Shape: Staining: |
Genus: Propionibacterium
Shape/reproduction: Non-sporing Respiration: Anaerobic Shape: Bacilli Staining: |
|
|
Example of gram-positive cocci
|
Streptococci
|
|
|
Example of gram-positive rods
|
Listeria
|
|
|
Example of gram-negative rods
|
E. coli
|
|
|
Example of gram-negative cocci
|
Neisseria
|
|
|
What causes black hairy tongue? Is it common? What's it an example of?
2009131110 |
Aspergillus. Rare UNLESS immunosuppressed
Example of overgrowth of exogenous (outside production) organism |
|
|
What is the most significant protozoal disease?
|
Malaria
|
|
|
How are protozoal diseases often acquired?
|
Via infected food, water, or by insect vectors (malaria)
|
|
|
Arthropods include:
|
Insects, ticks and mites
|
|
|
What are hydatid cysts caused by? What's a common site for them?
|
Caused by tapeworm - Echinococcus.
Lung is a common site |
|
|
Give an example of a commensal organism in man's large intestine
|
Bacteroides spp.
|
|
|
Give an example of parasitism inside man's large intestine
|
Entamoeba histolytica
|
|
|
Give an example of mutualism in the rumen of cattle
|
Bacteroides spp.
Bacteria metabolise host food to fatty acid - used as energy source |
|
|
What are the chemical and physical antimicrobial defences on man? (4)
|
Mucus, cilia lining trachea, acid in stomach, skin
|
|
|
What are the biochemical antimicrobial defences on man? (4)
|
Lysozyme (tears, nasal secretions, saliva), sebaceous gland secretions, commensal organisms in gut and vagina, spermine in semen
|
|
|
What ecological factors influence flora? (7)
|
Humidity, pH, attachment/retention, oxygen tension, host inhibitors, microbial inhibitors, nutrients
|
|
|
Give examples of commensal flora in the nose (6)
|
Gram positive cocci
Staph aureus Staph epidermidis Diphtheroids Streptococci Coryneform bacteria Maybe MRSA |
|
|
Give examples of commensal flora in the mouth (3)
|
Strep. mitis (and other streptococci)
Trichomonas tenax Candida |
|
|
Give an example of commensal flora that might be in the lung
|
?Pneumocystis jiroveci
|
|
|
Give examples of commensal flora in the urethra and vagina (4)
|
Straphlococcus epidermidis
Diptheroids Streptococci Gram-negative rods |
|
|
Give examples of commensal flora in the skin (11)
|
Mainly gram positive cocci
Staph. epidermidis Staph. aureus Diptheroids Streptococci Pseudomorias Aeruginosa Anaerobes Candida Torulopsis Pityrosporum Proprionibacterium acnes |
|
|
Give example of commensal flora in the throat (8)
|
Strep. viridans
Strep. pyogenes Strep. pneumonae Neisseria spp. Staphlococcus Epidermidis Haemophilus Influenzae |
|
|
Give examples of human commensal flora in the teeth (5)
|
Gram-negative rods
Steptococcus mutans Bacteroides Fusobacterium Streptococci Actinomyces streptococci, actinomycetes, very strict anaerobes cocci, spirochaetes, yeasts |
|
|
Example of non-invasive pathogen that produces toxin. Also causes tetanus
|
Clostridium tetani
Soil organisms which gain entry via wounds. Produce resistant endospores Strict anaerobes |
|
|
Bacilli do not produce endospores T/F
|
F
|
|
|
What is a Microaerophile bacteria?
|
Microaerophiles – ideal growth in reduced O2
|
|
|
What is a Capnophiles bacteria?
|
Capnophiles – ideal growth in increased CO2
|
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni facts (4)
|
Commonest cause of diarrhoea
Microaerophilic Tension and thermophilic – can grow at 42oC Infection is via contaminated water, milk or food – especially poultry |
|
|
Chlamydia facts. What does it cause?
|
small obligate intracellular
parasites Gram negative cell wall They have a unique developmental cycle with an infectious extracellular elementary body and a non-infectious intra Chlamydiae cause eye and cellular reticulate body genital tract infections C. trachomatis - genus of chlamydia |
|
|
Shape of Vibrio cholerae
|
Single polar flagella
Comma shaped |
|
|
What are pili? Give an example of a bacterium that has it.
|
Protein structures
that are important in enabling pathogens to attach to surfaces Escherichia Coli |
|
|
Which bacterium produce endospores?
|
Bacillus (aerobic)
and Clostridium (anaerobic) |
|
|
Bacillus are anaerobic/aerobic
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
Clostridium are aerobic/anaerobic
|
Anaerobic
|
|
|
What are spirochaetes?
|
A phylum of gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
What does Borrelia
recurrentis cause? |
Relapsing fever.
|
|
|
What are Mycoplasmas?
|
Smallest organisms capable of growth
on cell-free media Lack a rigid cell wall Typical ‘fried egg’ morphology Require sterols for growth Include four species that cause human disease: Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. genitalium M. hominis Ureaplasma urealyticum |
|
|
What are the four species of mycoplasma that cause disease?
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
M. genitalium M. hominis Ureaplasma urealyticum |
|
|
What can the fungi Cryptococcus
neoformans cause? |
Meningitis
|
|
|
Aspergillus facts
|
Mould
Pathogenic species: Aspergillus fumigatus Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus flavus produces aflatoxin - which is both a toxin and a carcinogen |
|
|
What is Alflatoxin?
|
Aspergillus flavus produces aflatoxin - which is both a toxin and a carcinogen
|
|
|
What is oral thrush caused by? What is oral thrush associated with?
|
Candida spp
Associated with antimicrobial therapy that disturbs the commensal bacterial flora and results in fungal overgrowth |
|
|
Ringworm is an example of a ____________ infection
|
Dermatophyte infection
|
|
|
What is the malaria parasite called?
|
Plasmodium
|
|
|
What is Entamoeba histolytica? What is the pathogenesis of Entamoeba histolytica?
|
Anaerobic parasitic protozoan
(histo–lytic = tissue destroying), is pathogenic; infection can lead to amoebic dysentery or amoebic liver abscess |
|
|
What are the two major floral areas of the large bowel?
|
Wall flora and lumen flora
|
|
|
The gut contains approx 1000 species and is believed to be vital for
the development of the gut and systemic immune systems. |
Colonisation after birth with bifidobacteria (occurs in breast-fed
infants) protects against diarrhoea |
|
|
Clostridium difficile facts
|
spore-forming Gram-positive bacillus
that is a strict anaerobe • It lives in the gut as a minor member of the commensal flora • The spores survive antibiotics so they can overgrow and cause a serious infection that can be fatal – pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
What is pseudomembranous colitis
|
A gut infection caused by C. Diff
Characterised by offensive-smelling diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, life-threatening complications can develop, such as toxic megacolon. |
|
|
Males/females are more likely to get a urinary tract infection
|
Females
|
|
|
Sources or urinary tract infection
|
Community acquired:
E. coli Coagulase-negative staphlocci Gram positives (Staphlococcus epidermidis, staph. aureus, Enterococcus faecalis) Nosocomically (hospital acquired): Candida Proteius mirabilis Other gram negatives (Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
|
|
Syphilis cause
|
Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Gonorrhoea cause
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
Chlamydia cause
|
Trachomatis
|
|
|
Chancroid (an STI)
|
Haemophilus ducreyi
|
|
|
Syphilis and gonorrhoea can be readily treated with...
|
..penicillin
|
|
|
Systemic gonorrhoea effects
|
Conjunctivitis of child 2-5 days after birth (opthalmia neonatorum)
Skin lesions Endocarditis ( inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium.) Female: Damage to fallopian tubes, pelvic inflammatory disease, anorectal infection Male: Occasional epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis (a curved structure at the back of the testicle in which sperm matures and is stored) - can cause redness of scrotum) Arthritis |
|
|
What is endocarditis?
|
Inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium.
|
|
|
What is Toxoplasma gondii?
|
Zoonotic protozoal infection acquired by eating cysts in undercooked meat or cat faeces
Congenital (persisting from birth) infections of foetus can lead to severe complications |
|
|
Microbes transmitted by infectious
aerosols |
Viruses
Influenza virus group Rhinovirus group Adenovirus group Mumps virus Measles virus Rubella virus Varicella zoster Epstein-Barr virus Bacteria: Bordetella pertussis Corynebacterium diphtheriae Haemophilus influenzae Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
Bacillus subtilis is a gram-positive rod affected by which antibiotic?
|
Bacitracin
|
|
|
Pacillus polymyxa is a gram positive rod affected by which antibiotic?
|
Polymyxin
|
|
|
Penicillium notatum is a fungi affected by which antibiotic?
|
Penicillin
|
|
|
Cephalosporium spp is a fungi affected by which antibiotic?
|
Cephalothin
|
|
|
Actinomycetes:
Streptomyces venezuelae: |
Streptomyces venezuelae: Chloramphenicol
|
|
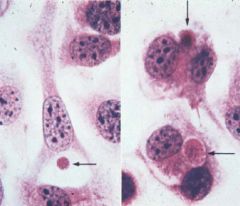
|
Photomicrograph of viral inclusion bodies (a.k.a. virus factories) due to a pox virus (vaccinia)
|
|

|
Papilloma (aka wart) virus
factory in cell nucleus |
|
|
Info on Hep B
|
DNA virus BUT unusual complex replication cycle involving an RNA intermediate.
Uses reverse transcriptase (RT) Seventh group of Baltimore classification NB HIV and hepatitis B viruses both use RT in their infectious cycle and are known collectively as reversiviruses as the infectious cycle involves a step reversing from RNA to DNA |
|
|
Example of Nucleic acid inhibitor antibiotics
|
ribavirin, zidovudine, didanosine, zalcitabine and stavudine, acyclovir, ganciclovir and foscarnet, idoxuridine and trifluridine, vidarabine, famciclovir and valaciclovir
|
|
|
Viral protease inhibitors
|
saquinavir, ritonavir (HIV)
|
|
|
What are the three groups of beta-lactams?
|
|
|
|
Which bacteria never produce beta-lactamases?
|
Gram positive rods (e.g. Listeria, Corynebacteria),
Streptococci, Neisseria meningitidis, Treponema, Most anaerobes |
|
|
Which are the bacteria that do have beta-lactamases?
|
Staphylococci (S. aureus and coagulase-negative
staphylococci) |
|
|
Ribavirin treats:
|
Influenza A, B, C, & respiratory syncytial virus)
|
|
|
Zidovudine, didanosine, zalcitabine and stavudine treat:
|
HIV
|
|
|
Acyclovir treats:
|
Systemic treatments of herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus
|
|
|
Ganciclovir and foscarnet treat
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
|
|
Idoxuridine and trifluridine treat
|
Tropical treatment of herpetic keratitis
|
|
|
Vidarabine, famciclovir and valaciclovir treat
|
Oral treatment of varicella-zoster virus infections
|
|
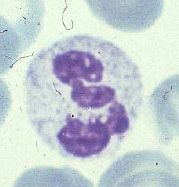
|
Neutrophil
|
|
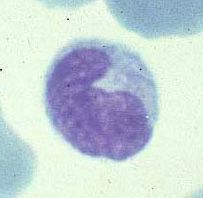
|
Monocyte/macrophage
|
|
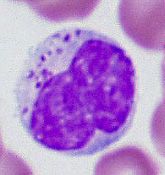
|
NK Cell
|
|
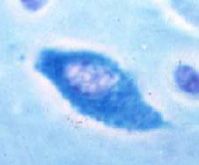
|
Mast Cell
|
|
|
What activates complement?
|
C-reactive protein (CRP) and Mannose-binding lectin (MBL/MBP)
|
|
|
What is serum amyloid P component?
|
An amyloid ( insoluble fibrous protein aggregates sharing specific structural traits) precursor
|
|
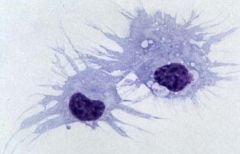
|
Dendritic Cell
|
|
|
What does Toxoplasma cause?
|
Tissue cyst
|
|
|
What kind of mosquitoes transmit malaria?
|
Anopheles mosquitos
|
|
|
Examples of protozoa
|
• Malaria
• Trichomonas vaginalis • Trypanosomiasis • Leishmaniasis • Toxoplasmosis |
|
|
Four species that cause malaria
|
– Plasmodium falciparum
– Plasmodium vivax – Plasmodium ovale – Plasmodium malariae Falciparum malaria responsible for most deaths and severe disease |
|
|
Facts about toxoplasmosis
|
Toxoplasma gondii
• Obligate intracellular parasite • Sexual cycle only occurs in cats but all vertebrates are susceptible • Non-feline hosts 2 critical phases of infection – Acute flu like disease – Establishment of chronic latent cysts • Reactivation of cysts associated with immunosuppression; HIV or transplantation • Risk of congenital transmission during pregnancy |
|
|
Three species of Trichomonas. And result of T. vaginalis
|
T. hominis
T. tenax T. vaginalis T. vaginalis results in inflammation and discharge |
|
|
What disease does Trypanosomiasis cause?
|
Chags disease
--> Cardiac failure Loss of nervous control of the gut |
|
|
Trypanosomiasis: Sub species and disease symptoms
|
Trypanosoma brucei
-sub species: T.b. gambiense, T.b. rhodesiense Fever, malaise (feeling of discomfort), anorexia, invasion of CNS --> Sleeping sickness The sub species have coats associated with avoidance of host immune response |
|
|
What diseases do Lieshmaniaisis cause?
|
Cutaneous diseases, deeper tissue may be
implicated Simple cutaneous lesion localises at site of bite resulting in a granulomatous response • Epidermis fragile and prone to further physical damage, ulceration and secondary infection |
|
|
Examples of cestodiasis (pathology due to worms in the gut)
|
Diphyllobrothium latum
Taenia saginata Taenia solium Hymenolepis nana |
|
|
Which Filariasis cause lymphatic disease?
|
Wucheria bancrofti, brugia malayi
|
|
|
Which Filariasis cause blindness?
|
Onchocerca volvulus, loa loa
|
|

|
Coenocytic hypha
|
|
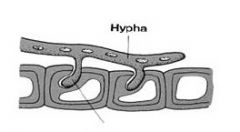
|
Haustroium
|
|
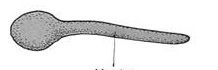
|
Hypha
|
|
|
Mycelium
|
|

|
Septate hypha
|
|

|
Spore
|
|
|
What are the three methods of fungal asexual spore formation?
|
Blastospore (blastoconidium)
Chlamydospore (chlamydoconidium) Arthrospores (arthroconidia) |

