![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
253 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
trt:capnocytophaga
|
amp+sulbactam, amox+clav, alt: clinda,ctx,mero
|
|
|
|
asplenics and immunosuppressed have sepsis with DIC
|
capnocytophaga
|
|
|
|
what immunosupp is contraindicated with vori
|
sirolimus. use taco at 1/3 dose. increases cyclosporine levels:sz,azotemia
|
|
|
|
2 genes for macrolide resistance
|
erm(B) altered binding (europe)mef(a) efflux pump (US)"
|
|
|
|
bartonella eye lesions
|
star/stellate lesions.
|
|
|
|
trt listeria when pen allergic
|
bacrtrim
|
|
|
|
anthrax trt+ in pregnancy
|
cipro or doxy + clinda. if preg,amox +- rif.
|
|
|
|
trt tularemia, preg, post exp.
|
gent or strep. pep with doxy or cipro. if preg use gent or cipro for trt, cipro for propylaxis.
|
|
|
|
trt vivax and ovale in preg and non, chloro sens or not.
|
primaquine + a quinine (chloro or hydroxychloro) if chloral sensitive. Have to add primaquiine for read of hypnozoites.
if chloro resist: meflo,or malarone+primaquine, or quinine + doxy or tetra + primaquine. if preg: chloro or hydrocychloro if chloro sens if chloro resistant - mefloq. |
|
|
|
trt babesia
|
clinda+quinine. atov+azithro if not sick.
|
|
|
|
which antimalarial to avoid for conduction abnormalities
|
mefloquine
|
|
|
|
malarial prophyl non preg cholorq resistant:
|
malarone, doxy, mefloquin
|
|
|
|
chloroquine reisistant vivax trt: normal and preg
|
Quinine, doxycycline, and primaquine orAtovaquone-proguanil and primaquine or Mefloquine and primaquine All three choices are recommended equally Quinine alone is recommended for the treatment of pregnant women"
that is, malarone or quinine+doxy or mefloqune , each w. primaquine, or quinine alone for preg. |
|
|
|
vivax prophylaxis
|
primaquine
|
|
|
|
malaria prophyl if preg. chloroquine resistant and not
|
meflo-CAN, quinine if not resistant. don't use primaquine because your PRIMATE baby can get g6PD.
|
|
|
|
trt Chloroquine-resistant P falciparum
|
Atovaquone-proguanil (malaraone) x 3d or Artemether-lumefantrine or Quinine and either doxycycline or clindamycin (doxycycline preferred)All three choices are recommended equally Fourth choice is mefloquine
for preg: .Quinine and clindamycin are recommended for treatment in pregnant women" |
|
|
|
which antimalarial can cause hemol anemia in g6pd deficient
|
prima-quine. PRIME problem of hemolysis
quinidine. |
|
|
|
which ARV has mito toxicity with ribavarin
|
DDI
|
|
|
|
which ARV can give cpk elevation and weakness
|
AZT. this is a myopathy.
|
|
|
|
which ARV assoc w ICH
|
tripinavir
|
|
|
|
which ARV do you not start on someone with cd4>250
|
nevirapine. hepatotox
|
|
|
|
which ARV do you avoid in 1st trimester
|
EFV
|
|
|
|
which ARVs are assoc w lactic acidosis during preg
|
DDI/D4T
|
|
|
|
during TB therapy, which ARV is preferred for minimizing rifampin interaction?
what antifungal is that arv contraindicated w? |
efv. Avoid PIs and most NNRTIs.
note efv contraindicated w vori |
|
|
|
st johns wort interacts with which arv
|
All PIs, DLV, NVP, ETR, MVC, and RAL.
|
|
|
|
start antililpid tx when? given 0 -1 risk factors? and >2 factors
|
190, 130 or 160
|
|
|
|
which abx to avoid in preg.
|
SAFE Moms Take Really Good Care Sulfonamides, Aminoglycosides, Fluoroquinolones, Erythromycin, Metronidazole, Tetracyclines, Ribavirin, Griseofulvin, Chloramphenicol"
also cannot give azoles (fluc itra etc) |
|
|
|
T/F does bartonella helms cause bony lesions?
|
T
|
|
|
|
which org has coke bottle like appearance on slide
|
mallasezia
|
|
|
|
sizes of micro,crypto,cycle,isospora
|
microspor 1-2,Cryptosporidium is 4-8u Cyclospora is 10-20u Isospora is 20-30 u
|
|
|
|
where is HHV6 seen on MRI
|
mesial lobes.
|
|
|
|
what does hhv8 cause
|
kaposis
|
|
|
|
which arv requires hlab57 testing? what reaction is seen
|
abc. hypersensitivity rxn, skin desq.
|
|
|
|
what abd imaging finding do you see with bartonella helms in HIV patients
|
pelosis and splenitis. liver filled with blood pockets.
|
|
|
|
whixh virus is implicated in hairy leukoplakia
|
ebv
|
|
|
|
treatment of chancroid
|
Azithromycin 1 g PO as a single dose.
Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM as a single dose. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg PO twice daily x 3d. Erythromycin base 500 mg PO four times a day x 7d. Regimens in pregnancy Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM x 1. Erythromycin base 500 mg PO four times a day x 7d. Azithromycin: 1 g PO as a single dose. |
|
|
|
peripheral outher retinal necrosis vs retinal necrosis: caused by which 2 viruses, how are they different immunologically as far as risk factors? which one assoc w pain
|
porn(no pain): VZV 2^ hsv RN (pain): vzv,hsv porn:cd4 < 50 RN: cd4>100
|
|
|
|
which enterics cause fever and don't
|
invasive(cause fever):e.invasive e coli,c jejuni,yersinia,salmonella typh,shigella
no fever: etec cholera ehec salmon enter" |
|
|
|
alternative prophylaxis for t.gondii in HIV
|
dapsone+leucovirin+pyremethamine
a DaLP of proylaxis for toxo |
|
|
|
pcp prophylax for pregnants?
|
1st trimester aerosolized pentamidine then bactrim is ok for 2 and 3.
|
|
|
|
what do you prophylax for histo with ?
|
itra. if living in endemic region. and cd4 < 100
|
|
|
|
suspect epiglottitis treat with:
|
cefotax or ctx (taxa down the throat). Hflu, strep primary bugs
|
|
|
|
what cx grows all enterics except 1
what is the culture medium for lepto? |
macconkey agar, except pleisomonas
fletcher medium for lepto. |
|
|
|
which cephalosporin is assoc with flushing and headach
|
cefotetan.
|
|
|
|
which rickettsia has rash that starts periph and does not spare palms soles face
|
rickettsia ricketsia (RMSF). deer tick.
|
|
|
|
which rickets is rickstsial pox
|
akari. playing atari with his friend the mouse(mites on mouse).
|
|
|
|
which 2 rickettsia have rashes that spare the palms soles face. which one is less severe?
|
prowazeski(epidemic) and typhi (less severe). by rat flea
|
|
|
|
treatment of choice for tularemia
|
aminoglyclosides (gent or streptomycin)
|
|
|
|
ticks/vectors and diseases
|
Hard ticks: anaplasmosis, babesiosis, ehrlichiosis, Rickettsia conorii and africae, Colorado tick fever, Lyme, Rocky mountain spotted fever, • Soft ticks: Endemic relapsing fever
Flies: African trypanosomiasis, Onchocerciasis, Loa loa Sand flies: leishmaniasis Mites: rickettsialpox, scrub typhus Fleas: Rickettsia felis, Ricketsia typhi (murine typhus), plague, cat scratch disease Lice: Epidemic relapsing fever, Epidemic typhus (R. prowazekii) Mosquitos: too many infections to name!" |
|
|
|
choice diagnostic test for ricketsial diseases
|
indirect imunoflour. (IFA)
|
|
|
|
which 2 ticks are assoc w tick paralysis in the US?
|
d.Andersoni and d.variabilis (Mr.anderson is paralyzed to program variables.)
|
|
|
|
trt cutaneous and visceral leismania
|
stibogluconate x 20d. for cutaneous. ampho b for visceral x 38 days
|
|
|
|
parasites with resp sx.
|
Entamoeba histolytica--- Acquired by consumption of contaminated food or water; occurs worldwide especially where there is poor sanitation. Suspect in person with hepatic amebiasis with an elevated right hemidiaphragm and "anchovy paste" expectorate due to hepatobronchial fistula. Pleural effusion is a common finding with hepatic abscess and may be sterile (inflammatory reaction) or represent an empyema
.Ascaris lumbricoides --- Acquired by consumption of contaminated food or water; occurs worldwide especially where there is poor sanitation. Suspect with fever, cough, expectoration, eosinophilia, patchy alveolar exudates on CXR or chest CT that clear within 10 days; confirmed larvae in sputum +/- eggs in stool. Strongyloides stercoralis --- Can be seen in an immunocompetent person as well as immunocompromised (more severe illness). Suspect with suspect exposure and fever, eosinophilia (may be absent in immunocompromised person), bronchospasm or bronchitis, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Ill-defined, patchy, migratory airspace consolidation that resolves in 7-10 days. Definitive diagnosis by finding larvae in sputum. Hyperinfection can lead to overwhelming diseases with ARDS. Echinococcus granulosus --- Occurs wherever there are canines. Long incubation period; may be asymptomatic for years. Hydatid cysts found in liver>lung>other organs. Lung disease causes cough, hemoptysis, pneumothorax, lung abscess, bilioptysis, parasite pulmonary embolism. Definitive diagnosis is made by histopathology. Pre-surgical ELISA and abdominal ultrasound are useful. Consult with infectious disease expert and surgeon strongly advised. E. multilocularis --- Exposure history to canines in Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, Turkey, China, South America, Australia, New Zealand, Russia, Japan, Canada, Alaska. Very long incubation of 5-15 years. Liver commonly involved. Lung ds. causes cough, fatigue, weight loss, hemoptysis, tumor-like invasion of chest wall, ""metastases."" Dx by histopathology or serology (available from CDC) plus characteristic appearance on imaging. Consult with infectious disease expert and surgeon strongly advised. Paragonimus westermani --- Exposure in Southeast Asia, Asia, Latin America (primarily Peru), Africa (primarily Nigeria). Lung is the target of this fluke. Fever, chest pain, chronic cough, hemoptysis with eggs found in the sputum, feces and pleural fluid. Often mistaken for TB on CXR. Alert laboratory as acid fast staining for TB will destroy eggs in sputum or pleural fluid." |
|
|
|
what treats c.glabrata
|
any echinocandin. ampho.
|
|
|
|
STD with painless nodes, with painful nodes
|
chancroid: painful(h.ducrey). trt: ctx, azithro
LGV: chlamyd. trach. painful. (ulcer gone while nodes enlarge-not so w chancroid), trt:doxy x 21d Klebsiella granulomatis- granuloma inguinalis.- kleb gran. - painless. Nodules grow for 10 days. then burst., trt doxy for 3 wks min, or bactrim or cipro |
|
|
|
prevention of CMV in double negative transplants would require:
|
leukoreduced transfusions
|
|
|
|
which anaerobe is implicated in traumatic eye injury
|
b. cereus
|
|
|
|
varicella preexposure post exposure prophylaxis for HIV pts
|
cd4 <200 nothing, >200 give vaccine . post exposure cd4>200 vaccine,<200 acyclovir.
|
|
|
|
trichosporin is resistant to ?
|
echinocandins
|
|
|
|
can use echinocandins for aspergillosis?
|
salvage only
|
|
|
|
azoles inhibit synth of?
|
sterols
|
|
|
|
what is only agent for mucor treatment?
|
ampho
|
|
|
|
what predisposes to mucor
|
deferox.deferasirox is protective
|
|
|
|
how long does posaconazole take to build to therapeutic doses
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
|
which azole is concerning for sun exposure
|
voriconazole
|
|
|
|
which azole contraindicated in heart failure
|
itraconazole
|
|
|
|
flucytosine in azotemic patients causes
|
leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. (marrow suppression)
|
|
|
|
compared to ppd quanti is spec/sens
|
more specific less sensitive
|
|
|
|
which influenza type does not have HN types
amat/rimant can only treat 1 type of flu- which one? |
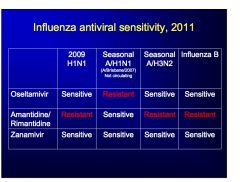
flu B
amant/rimant only for seasonal A/h1n1 |
|
|
|
which influenza is avian influenza.which one is next possible pandemic
|
h5n1, next one possibly h2n2
|
|
|
|
t/f do you need n95 mask for influenza at hospitals
|
no
|
|
|
|
3 diseases that require N95
|
TB chickenpox measles
|
|
|
|
rapid nonTB mycobacteria
|
AFChI, abs,fort,chel,immunogenum
|
|
|
|
treatment for pulmonary mac
|
c/e/r+a/s clari,etham,rif + amik or streptomycin (18-24 months)
|
|
|
|
primary toxicity of ethambutol and clari
|
ocular, clari->GI upset
|
|
|
|
which ARV not to use absolutely with rifabutin
|
saquanivir
|
|
|
|
when do you prophlax for MAC in hiv pts (cd4 count)
|
<50, azithro 1200qw. can stop if cd4 > 100 for 3 months.
|
|
|
|
treatment of kansasii
|
RIE. pza not useful for NTM. treat for 12months after cx negative.
|
|
|
|
trt leprosy
|
Dr.Clofaz. Leper (leperot) (can really see the leper - heavy skin involvement with heavy bacillary load)
Dr.T(tubercu) dapsone,rif,clofaz |
|
|
|
which viral pna assoc with hemmorragic cystitis, conjunct,pharyngitis, hepatic involvement.
|
adeno 14. outbreak in portland. assoc w ICU admssion, severe disease in young patients. conjunct not seen in adeno14.
|
|
|
|
which viral pna is assoc with asthma,chf,copd exacerbations and late fall spring most common.
|
RSV
|
|
|
|
hantavirus from where has been transmitted person to person
|
s.america/andes.
|
|
|
|
does hantavirus have a cardiopulm phase
|
yes. leakage of fluid into lung, cardiac suppression. give only modest fluid resusc.. thrombocytopenia in 93% and atypical lymphs. + abnormal LFTs. white out on X-ray.
|
|
|
|
which one is agitated+rigid, somnolent+rigid (NMS, malig hyperthermia). time course to sx?
|
NMS - agitated. in days not hours. anti emetics/metaclopromide.
MHypertherm- halothane, somnolent. usually < 1 hour after trigger. CV instability (HTN) |
|
|
|
3 causes of draining lesion through layers
|
actino (see sulphur granules) , tb , staph(sick).
|
|
|
|
buzzword for r.equi
|
salmon pink. weakl acid fast. non branching (unlike nocardia)
|
|
|
|
burh mallei classic lesion
|
ulcerative tracheobronchitis
|
|
|
|
post exposure for hep A. At what age and above must Ig be given.
|
vaccine, over 40 or immunosupressed then Ig is preferred.
|
|
|
|
liver enzymes in lepto
|
high high bili , modest elevated transaminases.
|
|
|
|
T/F toxo assoc w splenomegaly
|
F
|
|
|
|
b-glucan test is negative for which fungus
|
mucor
|
|
|
|
false positive galactomannan is seen with ??
|
amox/clav, pip-tazo.
|
|
|
|
beta glucan false positive caused by?
|
ivig
|
|
|
|
brain abscess with dark color (melanin) on growth. is hyphae septate or not? treat?
|
phaeohyphomyosis . septate hyyphae
treat with non fluc azole (partic vori), ampho,(preferred) |
|
|
|
which fungus requires olive oil for growth
|
mallasezia. seen with TPN. needs lipids.
|
|
|
|
diagnosis of peniciliosis
|
silver stain best (shows binary fission yeast), blood cx. see fever weight loss, anemia, generalized LAD, hepatosplenomegaly. painless skin lesions with central dimpling.
|
|
|
|
.treatment of penicilium
|
ampho then itra
|
|
|
|
painful skin nodules in immunocompromised .cx grown mold
does it have hyoahe? how do you treat it? |
fusarium. important that it has hyphe. trt w vori.
|
|
|
|
mucicarmine stains only one fungus
|
cryptococcus.,
|
|
|
|
hcv + skin rash
|
porph cut tarda.
|
|
|
|
what is a major side effect of ribavarin?
|
hemolytic anemia (?with PI), gout, teratogenic
|
|
|
|
interaction between ribavarin and ARV
|
DDI fatal pancreatitis.
AZT makes anemia worse. |
|
|
|
are hiv-2 patients resistant to certain arvs
|
nnrti and t-20
|
|
|
|
HTLV-1 assoc with what type of bone lesion
|
lytic. not infarction.
|
|
|
|
which arv assoc w kidney stones
|
indinavir/atazanavir
|
|
|
|
which arv assoc w fanconi
|
TDF
|
|
|
|
what is the preferred PI in pregnants
|
boosted LPV
|
|
|
|
which PI most assoc with lipidemia
|
RTV. also GI SEffects.
|
|
|
|
what VL above which is not a blip
|
500
|
|
|
|
5 pathogens that are bad for splenectomy
|
hflu,meningococc,pneumoco,capnocytophag,babesia,
|
|
|
|
which statins ok to use w ARV
|
ATORVA,RESUVA,PRAVA. DON'T USE SIMVA (CONTRAINDICATED)
|
|
|
|
where do you see foamy macrophage ?
|
whipples
|
|
|
|
lipoid granuloma in liver
|
q fever
|
|
|
|
how do you trt whipples endocarditis?
|
surge + ctx (pcn/gent) followed by cotrimazole for 1-3 years.
|
|
|
|
trt q fever endocarditis. I got q fever in Dc (the chlorine pool)
|
doxy + chloroquine
|
|
|
|
which arv assoc w kidney stone
|
atazanavir.
|
|
|
|
trt hpylori reimen
|
CAP,CMP (m=metro,a=amox).
2nd line Bis+PMT (t=tetracycline) BP MT |
|
|
|
do you see pulm sx with rmsf?
|
NO
|
|
|
|
is g6pd def make RMSF worse
|
yes
|
|
|
|
tick assoc diasease from missouri. what does the rash look like?
|
STARI. see bullseye here too, so don't think lyme is only one with bullseye.!
|
|
|
|
which ricketsial disease assoc with multilple black eschars?
|
R.Parkeri;single eschar more likely akari
|
|
|
|
how many months out of hospital do u need to be to have comm acq cdiff
|
3 months.
|
|
|
|
groups at risk for community cdiff
|
peripartum, IBD, children
|
|
|
|
which abx most assoc w cdiff
|
2/3 cephalos
quinolones clinda amp/sulb |
|
|
|
what does fever w c.diff mean?
|
clue to a bad infection as usually fever is absent.
|
|
|
|
c.diff toxins
|
toxin b > toxin A ie B is BAD is worse.
|
|
|
|
T/F abx resistance is important in cdiff
|
F
|
|
|
|
how do you treat recurrent cdiff
|
first recurrence , reconfirm and retreat. don't use flagyl past first recurrence. third time, taper and pulse vanco.
|
|
|
|
in primary syphilis can rpr or fta be neg?
|
yes both. in secondary treponemals always positive. non-trep can revert.
|
|
|
|
t/f can neuro-syph occur at any stage?
|
yes
|
|
|
|
what is typical syphilis assoc CVA
|
MCA stroke
|
|
|
|
how does csf look like with opthalmic syphilis, how is it treated
|
trt like neurosyh. 50% have normal csf.
|
|
|
|
most common cause of false positive trepomenes
|
lyme, non-oathogenic gingival treponemes.
|
|
|
|
what is prozone pheomen
|
rpr initially negative. falsely, because of high ab titers. need to dilute sample.
|
|
|
|
csf vdrl sens or specific
|
very specific, 50% sensitive.
|
|
|
|
can you use azthri for syph
|
no. resistance
|
|
|
|
doxy dose for syph
|
prim. 14d, 2ndary
|
|
|
|
can u use ctx in pregnants for neurosyph?
|
no! pcn only, ctx can be used for non preg patients.
|
|
|
|
when do you do c-section for preg+hsv
|
only if active lesions are present
|
|
|
|
parvo-b19- arthritic presentation. unilateral vs bilteral. fever (yes/no)
|
bilateral. mimics arthritis. swelling of joints w fever.
|
|
|
|
what is histologically indistinguishable from crohns
|
LGV. rectal pain, proctitis. chlamyd. trach
|
|
|
|
LGV sx
|
painless ulcer. painful nodes. rectal pain, tenesmus, proctitis.
|
|
|
|
diagnostic test of choice for chancroid.
treatment? do you treat partner? |
cx. trt. azithro or ctx x 1. trt all partners inlast 60days.
|
|
|
|
trt granuloma inguinale
|
doxy bid or azithro 1g qwk. 3 wks.
pregnants: use erythro wright stain tissue. azithro/ctx for chancroid. remainder is doxy/azithro. |
|
|
|
screening for chlamyd trach
|
all sexually active females <25.yearly. for D-K. rescreen 3months after treatment for test of cure.
|
|
|
|
ghonnorhea trt
|
CTx 2nd line cefixime. fkouroquinolones OUT,
|
|
|
|
trt of choice for mycoplasma genitalium
|
azithro. doxy 50% success rate.
|
|
|
|
trt of trich vag
|
flagyl x 1, sex partners 60d. no need to screen preg. unless BV also, then need to treat for 1wk.
|
|
|
|
what are BV assoc with pregnancy
|
preterm, PROM, post partum endometritis. treat if symptomatic during preg, or is high risk for early delivery (current or previous).
|
|
|
|
trt PID
|
ctx x 1 + doxy bid x 14 days. treat sex partners. add flagyl if BV is there. no options for pcn allergic patients. admit if no improvment in 3 days.
|
|
|
|
TF get echo on anyone with MRSA bacteremia
|
T. and check f/u blood cx after starting therapy.
|
|
|
|
is dapto ok for L sided MRSA endoc
|
no. not FDA approved.
|
|
|
|
how long to trt IVDU tricusp
|
naf +- gent 14d, vanco +- 4wks , dapto 2-4wks.
|
|
|
|
know compl vs uncompl bacteremia
|
neg cx, dferv 72h,no hardware,no metasttic foci
|
|
|
|
how does VRSA wirk
|
vanA from VRE. remodeled cell wall, vRsa Remodeled
|
|
|
|
which anaerobes are vanc sens
|
archae. lacto,erypselothrix is vanc resistance.
|
|
|
|
what pulm sx assoc w dapto
|
eosinoph pna
|
|
|
|
mixed pyogenes MRSA skin infec
|
use clinda or bactrim + beta lactam.
|
|
|
|
T/F SOTransp vaccinate for pneumococc
|
T. both before and after xplant
|
|
|
|
T/F nocardia is neurotropic
|
T. must image brain to look for brain abscess in transplant/IC patients.
|
|
|
|
features of CMV syndrome
|
fatigue,leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated of hepatic enz.
hepatitis,pneumonitis,colitis. |
|
|
|
CMV prophylaxis in SOT
|
gan/valgan. IV or PO.. can also monitior weekly CMV PCR. in R+ use preemptive or universal. for D+/R- or ALA use universal proph.
|
|
|
|
when do you stop treating CMV
|
until viremia clears. If no reduction after 14d tx, then think about resisitance.
|
|
|
|
CMV resistance genes
|
UL97- ganc resistance
ul54 - cross resistance ot all (gan,fos,cidof) |
|
|
|
trt resistant cmv
|
cidof +- Ig.
|
|
|
|
trt PTLD
|
from EBV. antivirals not useful
anticd20 (ritux) reduce immunosuppress (first choice) |
|
|
|
trt BK virus nephropathy
|
reduce suppression. gold standard is renal bx. option blood PCR
|
|
|
|
number one fungal infection in SOT
|
candida all organs except. aspergillus/moulds more common in lung xplants.
|
|
|
|
trt TB in SOT
|
avid rif based regimen.
|
|
|
|
3 vaccines reccomended post SOT
|
pneum,tDAP, inact flu. live vaccines not used.
|
|
|
|
do you prphylax for CMV for neutropenic pts?
|
No. not common in neutropenics.
|
|
|
|
do you prophylax for candida in neutropenics
|
yes
|
|
|
|
neutropenic with bactermia and ARDS- what bacteria should you consider?
|
viridans. endicarditis rare.
|
|
|
|
hepatosplenic candida trt
|
ampho+followed by fluc.
|
|
|
|
review human MNV
|
review it.
|
|
|
|
TF CMV retinitis is very rare in BMT patients
|
T.retinitis is very uncommon. pneumonitis and hepatitis more common.
|
|
|
|
how is tumbu fly sx different than botfly sx?
|
tumbi- multiple lesions. usually around waste and under arms. larvae sit on clothes. botfly - 1 lesion
|
|
|
|
trt creeping eruption(hookworm)
|
ivermectin
|
|
|
|
what causes swimmers itch
|
avian shisto. great lakes, south africa.
|
|
|
|
sea lice clue to symptoms
|
distribution is areas covered by swimsuit. gulf of mexico common
|
|
|
|
trt brucellosis
|
7d gent, 6wks doxy
gently cylcle the cows nipples. |
|
|
|
when not to give abx for diarrh
|
when suspect HUS: those with NO FEVER, bloody diarr, abd pain.
|
|
|
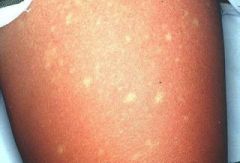
where do you see white islands on red sea rash
|
dengue
|
|
|
|
classic dengue sx
|
arthralgia,rash, fever, epistaxis, generalized LAD.lumbosacral pain. no GI sx. see mild fluid around GB or ascites w/US.
|
|
|
|
severe dengue sx
|
after defever -> severe hemorr, end organ damage (CNS,hep,renal), pleural effusions,ascites
|
|
|
|
dengue vector
|
aedes mosquito
|
|
|
|
torniquet test
|
in severe dengue (as well as others) . BP cuff .5 sys/dias. count petechia, >20=+
|
|
|
|
triad of yellow fever
|
hemmor fever,jaundice(hepatic necrosis),renal(protenuria). only other is rif valley fever w these 3 systems.
|
|
|
|
risk factor for adverse outcome in yellow fever vaccine
|
contraindi: thymus dysf., ie myasthenia, xplant, immunosupress.
|
|
|
|
important points re arenavirus (lassa)
vector? onset gradual vs sudden? other sx? |
deafness,trt w ribavarin, gradual onset, all rodent transmitted, sorre throat, cough.
lassa hearing. |
|
|
|
which viruses tropicla can u use ribavarin?
|
lassa,rift valley,crimean-congo HF
|
|
|
|
dengue ncubation time
|
max 7 days. diagnose day 2 with pcr
|
|
|
|
chronic anemia seen in which parasite
|
hookworm
|
|
|
|
tracking on plate - which parasite?
|
strongyloides.
|
|
|
|
chronic anemia seen in which parasite
|
hookworm
|
|
|
|
tracking on plate - which parasite?
|
strongyloides.
|
|
|
|
afternoon vs midnight blood film
|
afternoon for onchocer (afternoon river trip), midnight wuscheria . See bancroft at night..
|
|
|
|
calabar swelling
|
loa loa
|
|
|
|
salmonella UTI suspect?
|
shistosomiasis
|
|
|
|
hypnoziote forms
|
ovale,vivax ->ov medsakoon
|
|
|
|
what antimalarial agent assoc w hypoglycemia
|
quinine. if worry, use artesunate based agent.
|
|
|
|
distribution and special fever cycle of knowlsii
|
asia, q24h. pan sens. very high parasitemia.
|
|
|
|
which antimalarial prophylactic only needs seven days post return
|
atovaq/proguanil (malarone). rest for 4 wks post return. all 7 days pre.
|
|
|
|
org for buruli ulcer
|
m.ulcerans
|
|
|
|
cause of mucocutan leishmania
|
l.braziliensis,
|
|
|
|
3 pathogens causing visc leishmania
|
donavan infant chagasi, donovan the infant - visceral rap session. visceral rappin at donovani my infant has chagasi.
|
|
|
|
sx+labs with visc leish
|
hypergamma, lymphocytosis leukopenia, hypoalb.fever+ MASSIVE hepato spenomegaly
|
|
|
|
african trypanosome chancre painful? rash?
|
painful+diffuse rash.non tender LAD (generalized+ post cerv).must do LP.
|
|
|
|
triad of hantavirus
|
-left shift with granulocytes
->10% bands -thrombocytopenia incubation (think 3 wks) |
|
|
|
is thrombocytopenia seen with lepto?
|
no. but is seen with dengue.
|
|
|
|
prarie dog assoc with?
|
tularemia. trt w aminogly: strep or gent
|
|
|
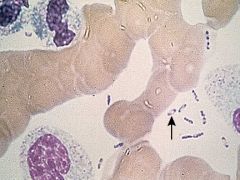
organism?
treatment? post exp prophylaxis? |
safety pin. y.pestes.trt:strep/gent post exp:doxy or bactrim for preg . isolate for 48hours of treatment.
|
|
|
|
HCV genotypes and response to treatment
|
1 50%
2,3- 80% |
|
|
|
rose spots on trunk. last/oxidase neg. abd pain. fever.
treatment? |
s.typh ->typhoid fever. trt:cipro or bactrim
|
|
|
|
vector for loa loa
|
chyrops fly. found only in western africa. calabar swelling more common in visitors than endemics.
|
|
|
|
Ehrlichia chaff infects which cells? vector? how about Analplasmosis? rash more common in ?
|
monocycle cheufer with a rash. lone star (HME). anaplasmosis infects granulocytes (HGE) ixodes ->coinfection with lyme seen.
riding the moncycle on a lonely star. |
|
|
|
what are path and clinical findings in sweets
|
neutrophlic cuffing without vasculitis. painful lesions. acute fever,injected watery eyes, arthralgia/myalgias. assoc w hematopoetic malign. or viral,strep infections.
|
|
|
|
treatment of smallpox
|
cidof.
|
|
|
|
antimalarial contraindicated in preg
|
mefloquine
|
|
|
|
which is more toxic cidofovir or foscarnet?
|
cidofovir.
|
|
|
|
what is cyclospora associated with as far as exposure
|
raspberries (from guatemala), snow peas
|
|
|
|
treatment of diphtheria and prophylaxis for contacts
|
trt: erythro or pcn, contacts single dose PCN IM
|
|
|
|
trt babesia
|
atovaquone+azithro, alt:clinda+quinine.
|
|
|
|
cigar shaped yeast
|
sporothrix
|
|
|
|
lactose fermenting g neg bacill
|
VEK. the fermenter--
vibrio, e.coli,enterobacter,kleb. |
|
|
|
chediak higashi features
inheritance infecting pathogens (fungal yes/no) trt with? |
-AR
-no fungal infections, mostly resp infection with staph/strep dx:large granules in neuts impaired chemotax.defect in lyst gene. trt:gcsf/ifn |
|
|
|
CVID features:
fungal infection seen? dx? trt? |
low Ig levels
recurrent enteric and pulm infections. fungal inf not seen dx: check Ig levels +- immunization trt: give Ige |
|
|
|
neutrophil elastase deficiency features
|
low normal neutrophil counts.
|
|
|
|
chron. gran disease features
inheritance bugs ifected with dx treatment |
x linked, AR
catalase positive infections(nocardia, burkhold,staph, serrat). aspergillus. dense absecess in liver wound dehisc. dx:nitro-blue test trt:ifn,bactrim,itracon |
|
|
|
leukocyte adhesion defic-
inheritance fungal infection seen? typical bugs typical sx dx/trt |
AR
gingivitis no neutrophils at site of infection no fungal infections seen staph,strep,g neg enterics necrotizing skin infections non healing skin ulcers from trauma dx: check cd18 levels by flow tx: treat infections, but |
|
|
|
jobs features:
fungals? pcp? candida? |
hyper IGe
exzema, cysts in lungs, mucocut candida, frequent boils. staph, strep, aspergillus, PCP,MAC scoliosis, fractures.eosinophilia retained baby teeth. trt: infections |
|
|
|
IFG receptor defic
|
disseminated NTMyc infections
cocci,hsv,vzv auto dom- good surv, AR- most die dx:flow for IFNg rec trt: antibacterials. BMT for AR form |
recessives worse off than AD.
what does IFN remind you of systemically? |
|
|
CSF profile with west nile- neut vs lymph
what is the duration of rash, and incubation period of WNV? |
neutrophilic. also maculopap rash that is diffuse , usually 7days duration.
incubation up to 14d. |
|
|
|
which pathogen looks like seagulls ?
|
shigella (seagella)
|
|
|
|
antimalarials contraindicated in preg
|
quinine. primaquine.coartem,
use q caution: malarone. mefloquine (not assoc w g6pd). |
|
|
|
trt lepto
|
pcn or ctx. doxy for mild disease
|
|
|
|
trt pasturella
|
amox/clav. or doxy or quinolone
|
|
|
|
trt bartonella
|
erythro,doxy,
|
|
|
|
which NTM need lower temp
|
MUH. haem(also needs iron), ulcerans, marinum.
|
|
|
|
which encaphalitis has unique feature of dysuria
|
st.louis
|
|
|
|
antivirals with HBV activity
|
entecovir
lamivudine(3tc) ftc(emtricit) TDF adefovir |
|
|
|
which pcp meds have g6pd def warning?
|
dapsone
and primaquine if treating pcp. not pentamidine, prime number of diapers at the G6 summit. where no one showed up/ |
|
|
|
what precautions with dapsone
|
g6pd also sulpha
|
|
|
|
precautions with pentamidine
renal or hepatic tox? cardiac? GI? sulpha pr g6pd? |
prolongs qt
torsades hypoglycemia renal tox leukopenia no hepatotox rate related hypotension pancreatitis remember it is being infused so more consistent in a mnemonic way with renal tox. |
|
|
|
precautions with atovaquone
yes/no g6pd duration till works renal/hepatic tox? side effects |
G6pd not an interaction
need fat for absorb diarrr hepatotox takes days to work no renal tox |
|
|
|
treatment of active TB for pregnants?
|
no PZA. RIE for 2 months, then RI for 7 months (9 months total). avoid pza
|
|
|
|
treatment of latent TB for pregnants?
|
inh x 9 months, or 6 months
2md choice - rif for 4 months |
|
|
|
CA-MRSA vs HA-MRSA:
usa xxx? mec # PVL pres/abs |
HA: usa100, mec 2,PVL abse
CA:usa300, mec 4, PVL pres. |
|
|
|
treatment of PCP other than bactrim
|
Pentamidine Nephrotoxicity, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia, hypotension, pancreatitis, dysrhythmias, transaminase elevation
Atovaquone Rash, fever, transaminase elevation TMP plus dapsone Trimethoprim: Rash, gastrointestinal distress, transaminase elevation, neutropenia Dapsone: Rash, fever, gastrointestinal upset, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia, (check for G6PD deficiency) Primaquine plus clindamycin -Primaquine: Rash, fever, methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia (check for G6PD deficiency) -Clindamycin: Rash, diarrhea, Clostridium difficile colitis, abdominal pain. PA TD PC! |
|
|
|
distinguishing features of hyperemesis, HELLP and AFLP
|
• HSV
– 50% mucocutaneous lesions – Fulminant/fatal/treatable • Hyperemesisgravidarum(trimester one) • HELLP (normal PT and PTT – HTN, increased fibrinogen vs. sepsis and AFLP) • AFLP(third trimester,lowglucose,incPT) |
|
|
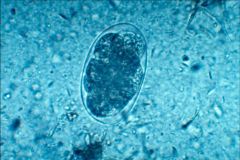
|
hookworm
|
|
|
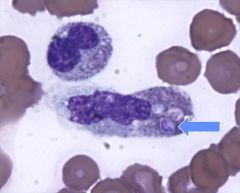
what causes these lesions?
|
histo. intracellular yeasts. crypto not seen on periph smear.
|
|
|
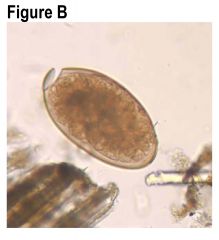
name the parasite
how was it aquired? |
fasciola hepatica. from aquatic plants
|
|

