![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bones |
1. Hard framework for stability 2. Act as levers to facilitate movement |
|
|
Ligaments |
Hold bones together |
|
|
Muscles |
Provide force required for movement by moving one bone in relation to another |
|
|
Tendons |
Connect muscles to bones |
|
|
Nerves |
1. Motor neurones provide stimulus for muscle movement 2. co-ordinate antagonistic muscles |
|
|
Arm: 1. Bicep 2. Tricep 3. Humerus 4. Radius/Ulna 5. Cartilage 6. Synovial fluid 7. Join capsule |
1. Flexor (bends the arm) 2. Extensor (straightens the arm) 3. Anchors muscles 4. Forearm levels (bicep/tricep) 5. Allows easy movement + absorb shock/ distribute food 6. Provide food/oxygen/lubrication to 5. 7. Seals joint space, limits range of movement, confers stability |
|
|
Compare hip and knee joints |
Similarities - synovial joints - involved in leg movement Differences - ball/socket joint vs hinge joint - between pelvis/femur vs femur/tibia |
|
|
5 feature structure of striated muscle fibres |
1. Many nuclei (many muscle cells fuse together) 2. Many mitochondria (movement = ATP) 3. Myofibrils are tubular, 2 kinds - actin/myosin 4. Sarcolemma surrounds sarcomere 5. Internal membranous network = sacroplasmic reticulum - contains high conc. of Ca2+ |
|
|
Structure of sarcomere |
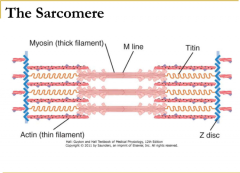
H-zone = myosin only I band = actin only A band = overlap Z line = extremities of one sarcomere |
|
|
6 Step process of muscle contraction |
1. Action potential from motor neurone = Ca2+ release into sacroplasmic reticulum 2. Ca2+ expose myosin heads by binding to blocking molecules 3. myosin heads move to form cross bridge with actin binding sites 4. ATP binds to myosin head, causes configurative change and head swivels 5. myosin head moves to form cross bridge with next actin binding site 6. Causes actin to slide over myosin, shorten the muscle |

