![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bus topology |
Computer network in which a "bus" connects ask devices together through a common cable |
Cable: copper wire (usually coaxial and twisted pair) and fibre (fibre optic cable made from glass). Cables allow for the connection of computers over a network. |
|
|
Check digit |
Extra digit added to numerical data that is used to check data integrity after input, transmission, storage and processing |
|
|
|
Data integrity |
The accuracy of data after input, transmission, storage or processing. |
|
|
|
Check sum |
Error-detecting procedur that generates a sum from the digits of a number |
|
|
|
Data packet |
Portion of a message that is transmitted through a network. |
Contains data such as check digits and designation address. |
|
|
Gateway |
Link that resides between computer networks and is responsible for converting data passing through into the appropriate format so it can be understood by the recieving network. |
|
|
|
Handshaking |
Exchange of predetermined signals to signify that a connection has been established between 2 systems |
|
|
|
Hub |
Network connection point for devices (using an ethernet cables attached to a port; there can be multiple). Data arriving at a hub is copied and sent to all the devices on the network. The device waiting to receive it accepts it while the rest ignore it. This is inefficient, slow and causes lots of traffic over the network. |
|
|
|
ISDN |
International communications standard that allows for the transmission of audio/video and other data over digital telephone lines. |
Integrated Services Digital Network |
|
|
LAN |
Computer network where all the connected computer are within a limited geographical area (E.g. a home or school). Connections between computers may be through cables and/or microwave transmissions. |
Local Area Network |
|
|
Modulator/demodulator/modem |
Electronic equipment that converts computer digital signals into audio signals and back. |
The audio signals are transmitted over telephone lines, which allows for distant communication. |
|
|
Network |
Computer systems that are interconnected and can share resources and data. |
|
|
|
Packet |
Group of bits. May include control signals, error control bits, coded information, as well as destination for the data. |
|
|
|
Packet switching |
Network communication method that creates and transmits small units of data, called packets, through a network, independently of the overall message. |
|
|
|
Networking |
Making use of a network |
|
|
|
Parity bit |
Error-detecting procedur that appends a binary digit to a group of binary digits. The sum of all the digits, including the appended binary digit, establishes the accuracy of the data after input, transmission, storage or precessing. |
|
|
|
Protocol |
International rules that ensure the transfer of data between systems. |
A protocol that is recognised as the standard for a specific type of transfer is call standard protocol. (E.g. TCP/IP) |
|
|
TCP/IP |
Communications protocol used to connect hosts on the internet. |
Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol |
|
|
WAN |
computer network where all the connected computers are in a larger geographic area than that served by a LAN or a MAN (metropolitan area network) |
Wide Area Network |
|
|
Server |
Can be either a computer system or software application that provides a service to the other computer systems connected to the same network. E.g. a server can provide the ability to the rest of the computers on the network to store and share files, taking the role of a file server. |
|
|
|
Client |
Can either be a computer system or a software application that requests a service from a server connected to the same network. E.g. an email client software application can request from an email server software application to fetch any new emails that may have been received. |
Requests content from server while not sharing any of its resources. |
|
|
Way in which one can connect 2 or more computer systems to make a network. |
• Hub • Switch • Router |
|
|
|
Switch |
Similar to a hub however, it can identify which network device is connected to which port. When a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the switch which then sends the data to the appropriate receiver. |
Much faster than a hub |
|
|
Router |
It's use is to join multiple networks and to serve as an intermediary between them so that data can be exchanged effectively. E.g. can be used to connect a home network to the internet. A hub/switch and a router are usually integrated into a single box, allowing the creation of a wired and wireless network, as well as connection of that network to other networks such as the internet. |
It is a more sophisticated device than both a hub and switch. |
|
|
Types of networks |
• Local Area Network (LAN) • Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) • Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) • Wide Area Network (WAN) • Storage Area Network (SAN) • Extranet • Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Personal Area Network (PAN) • Peer-To-Peer (P2P) |
|
|
|
Benefits of LAN |
• Allows sharing of peripheral devices between the connected computer network. This eliminates the need to buy certain peripheral devices for every computer (E.g. printers).
• Data can be shared. Allows clients to exchange data without using physics means such as USB sticks. This increases flexibility and reduces wasted time.
(Most common technology used to build wired LAN is a hub or switch using ethernet cabling.
|
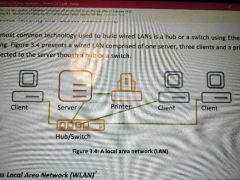
|
|
|
WLAN |
Similar to LAN but uses wireless connection methods instead. This allows the user to have mobile devices and laptops connected to the network and be able to move around. WLANs have all the benefits of LANs but they can be less secure that wired LANs because they can be assessed by anyone who can find access to the wireless signal. Most common technology used to make WLANs is WiFi which allows the exchange of data between computer systems using radio waves. |
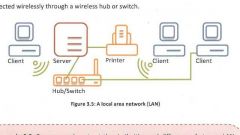
|
|
|
Similarities and differences between LAN and WLAN |
Similarities: both act on a local level - both allow communication - both are used to connect devices - both allow sharing of resources. Differences: they use different transmission mediums - LAN is safer - LAN is faster - WLAN offers greater flexibility. |
|
|
|
VLAN |
A network of computers that behave as if they're connected to the same topoly but are physically located in different segments of a LAN. VLAN configurations are generally compromised and maintened via software rather than hardware. This makes the network really flexible as it allows computers to be removed from the VLAN and located elsewhere without having to physically rewire the whole system to fit the new configuration. |
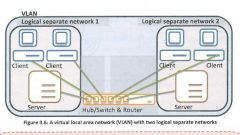
Virtual Local Area Network |
|
|
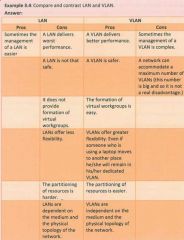
Similarities and differences between LAN and VLAN |
Similarities: both act on a local level - both have the same attributes - both allow communication - both allow sharing of resources
Differences: the formation of virtual work groups is easier - VLANs offer great flexibility. Even if someone who is using a laptop moves they will remain to their dedicated VLAN. - VLANs Are independent on the medium and the physical topology of the network. - the management/administration of a VLAN is more complex. |
|
|
|
WAN |
Connects computer systems that are within large geographical areas. The internet is an example of a WAN. It typically consists of LANs connected over a broad geographical area. Often one node on a LAN is set up at a gateway to handle all communication going through that LAN and other networks. |

Wide Area Network |
|
|
SAN |
It's a network that was created so that large storage devices can be accessible from servers in a convenient way. It is needed because there needs to be enough storage for certain tasks to be completed. |
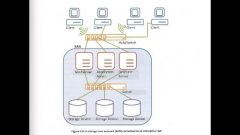
Storage Area Network |
|
|
Intranet |
Botas term for a collection of private computer networks within a company, school or organisation for example which utilizes protocols like TCP/IP. |
|

