![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CELL BIOLOGY What does cell theory state? |
* All living things are made from cells * Cells are the smallest unite of life * All cells come from pre-existing cells |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are exceptions to cell theory? |
Skeletal muscles - made up of long muscle fibers with many nuclei Giant algae - despite being very big, are unicellular Aseptate fungi - not divided into cells, instead consist of multiple nuclei |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the requirements/functions of life for something be considered alive? |
Metabolism Reproduction Sensory/response to stimuli Homeostasis Excretion Nutrition/exchange of gas & materials Growth |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY
What are stem cells? |
Cells that can differentiate into a limited range of cells
|
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY Where are stem cells found? |
* bone marrow * skin * liver |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What is the formula to calculate magnification of a microscope image? |
Magnification = Size of image / size of organism |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What is the formula to calculate real size of organism in a microscope image? |
Size of organism = size of image/magnification |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY How much is 1 cm in μm? |
1 cm = 10,000 μm |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY How much is 1 mm in μm? |
1 mm = 1,000 μm |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the properties of a Totipotent cell? (with example) |
Can differentiate into any cell, including a placenta e.g. zygotes |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the properties of a pluripotent cell? (with example) |
can differentiate into any cell making up the body e.g. embryonic stem cells |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the properties of a multipotent cell? (with example) |
Can differentiate into a number of similar cell types e.g. adult stem cells |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the properties of a unipotent cell? (with example) |
Cant differentiate, but can replicate itself e.g. regular body cells |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the characteristics and structure of a prokaryotic cell? (at least 8) |
* no nucleus * not compartmentalized * have plasmids * (usually) unicellular * small ribosomes * circular DNA * singular chromosome * transcription and translation occur simultaneously * (usually) haploid |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the characteristics and structure of a eukaryotic cell? (at least 8) |
* nucleus * compartmentalized w/ variety of organelles * (usually) multicellular * large ribosomes * multiple chromosomes * linear DNA * DNA wrapped in histones * (usually) diploid * transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation in the cytoplasm |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What is binary fission? |
The process of which prokaryotic cells divide. |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What are the universal organelles found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? (list and briefly describe 2) |
Ribosome - site of polypeptide synthesis/translate RNA into amino-acids Plasma membrane - phospholipid bilayer to act as a semi-permeable and selective barrier |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What organelles are found only in animal cells (list and briefly describe 5) |
Nucleus - stores genetic material Endoplasmic reticulum - can be bare (smooth ER) or have ribosomes (rough ER). transports materials between organelles Golgi apparatus - sorts, stores, modifies and exports secretory products Mitochondria - the powerhouse of the cell ( ͡° ͜ʖ ͡°) Centrosome - creates spindle fibers which help cell division |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What organelles are found only in plant cells? (list and briefly describe 3) |
Chloroplast - contains stacks of thylakoids, site of photosynthesis Vacuole - fluid filled cavity, helps maintain structure Cell wall - rigid and made from cellulose |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY Describe the structure of the phospholipid bilayer |
Polar/hydrophilic heads on the outside two non-polar/hydrophobic tails on the inside |
|
|
CELL BIOLOGY What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes? |
Reduces the fluidity of the membrane and less permable
|
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Define passive transport |
natural movement of particles from high to low concentration (no energy required) |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Define facilitated difusion |
movement of particles through membrane proteins/channels |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Define active transport |
Movement of particles against its concentration gradient, required energy |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What happens when a cell is hypertonic? |
Particles/water leaves the cell causing it to shrivel |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What happens when a cell is hypotonic? |
Particles/water enter the cell causing it to swell |
|
|
CELL DIVISION Briefly describe the 4 main stages of the cell cycle? |
1. G1 - Growth and normal metabolism 2. S phase - DNA is replicated 3. G2 - Growth and preperation for division 4. Mitosis - Cell division |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What stages are part of Interphase during the cell cycle? |
G1, S phase, G2 |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What happens during interphase in mitosis? |
* DNA replicates (still uncondensed) * Organelles replicates * Cell is enlarged |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What happens during prophase in mitosis? |
* DNA supercoils into chromosomes * Chromosome clone into sister chromatids * Nucleus dissolve * Centromere move to opposite poles and form microtubule spindle fibers. |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What happens during metaphase in mitosis? |
* Microtuble spindles from the centromeres connect to the centrosome of each chromosome * Spindles contract and shorten, aligning the chromosomes along the center/equator of the cell |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What happens during anaphase in mitosis? |
* spindles contract and pull sister chromatids apart into separate poles |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What happens during telophase in mitosis? |
* two nuclei form * chromosomes decondense *cytokinesis splits the cell into two |
|
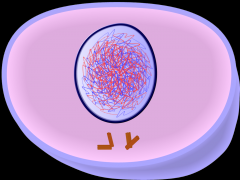
CELL DIVISION What stage of mitosis is this? |
Interphase |
|
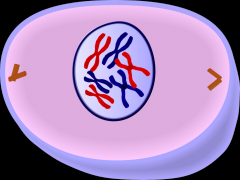
CELL DIVISION What stage of mitosis is this? |
Prophase
|
|
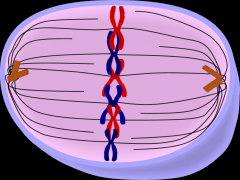
CELL DIVISION What stage of mitosis is this? |
Metaphase |
|
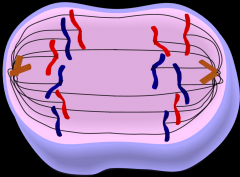
CELL DIVISION What stage of mitosis is this? |
Anaphase |
|
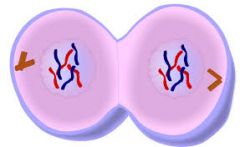
CELL DIVISION What stage of mitosis is this? |
Telophase |
|
|
CELL DIVISION What are the 5 stages of mitosis? (in order) |
1. Interphase 2. Prophase 3. Metaphase 4. Anaphase 5. Telophase |
|
|
CELL DIVISION Describe the role of cyclins in the cell cycle |
Cyclins are protein which regulate the progression of the cell cycle by forming a complex with CDK. Cyclin-CDK complex activates proteins which triggers cell cycle events. |
|
|
CANCER DEVELOPMENT Define oncogenesis |
The formation of tumor cells |
|
|
CANCER DEVELOPMENT Define oncogene |
A gene controlling the cell cycle |
|
|
CANCER DEVELOPMENT What is the difference between a primary and secondary tumor? |
Primary tumor - often harmless, don't grow as rapidly and don't spread Secondary tumor - becomes dangerous when it detaches and migrates elsewhere in the body and develop a new tumor. |
|
|
CANCER DEVELOPMENT Define metastasis |
When a tumor migrates to a new locations and starts a new tumor |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What does the theory of vitalism believe in? |
That life are dependent on a force or principle distinct from purely chemical or physical forces. That only living organisms can make organic matter |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY How was the theory of vitalism falsified? |
When Frederick Woehler artificially created urea in a lab
|
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Describe hydrolysis |
The breakdown of a polymer by breaking the oxygen bond between them and replacing it hydrogen and oxygen from water |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Describe condensation |
The creation of an oxygen bond between two monomers, making them a polymer. Water is created from this process |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What is the difference between anabolism and catabolism? |
Anabolism is the building of complex molecules from simpler monomers using energy. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler monomers, releasing energy. |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Why is water a good coolant? (e.g. in sweat) |
Water molecules evaporate when the weak hydrogen bonds between them are broken using energy from heat (for example, body heat). Therefore, evaporating water can easily dissipate heat. |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What are the benefits of using starch and glycogen to store energy? |
Both are insoluble in water, so storing large amounts of them dont cause osmotic issues in the cell.
Both are branched, making it easy to load/unload monomers from it. |
|
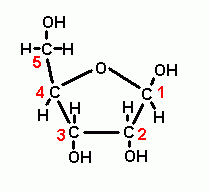
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Is this ribose or deoxoribose? |
Ribose
|
|
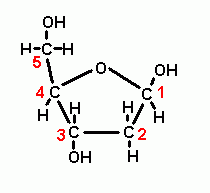
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY is this ribose or deoxoribose? |
Deoxoribose |
|
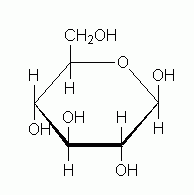
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Is this α glucose or β glucose? |
β glucose |
|
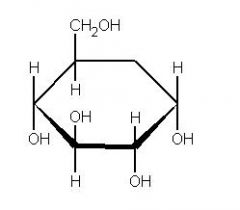
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Is this α glucose or β glucose? |
α glucose |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Whats the difference in structure and use between α glucose and β glucose? |
α glucose makes starch, form helix shaped branches and chains that are ideal for sugar storage, as sugars can easily be added and removed from the chain β glucose makes cellulose, form strongly bonded straight chains/microfibrills. used as a rigid base for plant cell structure |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What are the pros and cons of using sugar vs lipids as energy storage? |
Sugars: * release less energy * can be broken down much faster (ideal for short term storage) Lipids: * release more energy * take longer to breakdown (ideal for longterm storage) * can be used as heat insulators and shock-absorbers (protect organs) |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY What is the difference between cis unsaturated fatty-acid and trans unsaturated? |
Cis - hydrogen are bonded on the same side of the double bond, bended in shape. Trans - hydrogen are bonded on opposite sides of the double bond, straight in shape, associated with heart disease. |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Define denaturation |
the irreversible change in shape of a protein due to extreme heat/pH |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of rubisco |
An Enzyme which catalyses the photosynthesis/Calvin cycle reaction that fixes CO2 to RuBP |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of Insulin |
A Hormone that binds to insulin receptors on cells, causing them to absorb more sugar and lower overall blood pressure |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of immunoglobulin |
A antibody that binds to antigens on pathogens |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of rhodospin |
A pigment that allow the rod cells of the retina to detect and be sensitive to light |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of collagen |
Has a rope-like structure that helps maintain structure. |
|
|
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (Proteins) Describe the function of spidersilk |
Has a very strong yet flexible structure. becomes stronger when stretched |
|
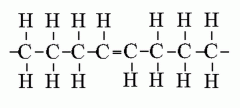
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Which fatty acid is this? |
Unsaturated trans fatty acid |
|
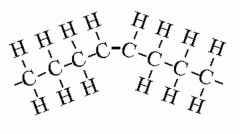
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Which fatty acid is this? |
Unsaturated cis fatty acid |
|
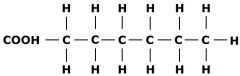
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Which fatty acid is this? |
Saturated fatty acid
|
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the difference in role between a vein and artery? |
Vein - delivers oxygenatedblood to the heart from the organs Artery - delivers oxygenated blood at high pressure from the heart to organs |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) what is the function of the aorta? |
Delivers blood from the heart to all other organs except the lungs |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the function of the pulmonary artery? |
Delivers blood from the heart to the lungs
|
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the role of the vena cava? |
Delivers deoxygenated blood from the organs to the heart |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) To which heart chamber does the vena cava first deliver blood to? |
To the right atrium |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) To which chamber does blood from the right atrium flow to? |
The right ventricle |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Through which valve does blood from the right ventricle flow into the right ventricle? |
The tricuspid valve |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Where does blood from the right ventricle flow into? |
The pulmonary artery |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Through which valve does blood from the right ventricle flow into the pulmonary artery? |
The pulmonary valve |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system)
Into which heart chamber does blood from the pulmonary veins flow into? |
The left atrium |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Where does blood from the left atrium flow into? |
The Left ventricle |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What the is term for the valves between the ventricles and arteries? |
Semilunar valves |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What the is term for the valves between the atrium and ventricle? |
Atrioventricular valves |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Define systolic presure |
The maximum blood pressure level in the arteries |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Define diastolic presure |
The minimum blood pressure level in the arteries
|
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Define vasoconstriction |
The narrowing of artery walls to increase blood presure |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Define vasoconstriction |
The expanding of artery walls to decrease blood presure |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Name 6 physical characteristics of veins |
*much larger than 10 μm *thin wall *wide lumen * consists of 3 layers * contains few elastic fibers * contains valves |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Name 5 physical characteristics of arteries |
*Larger than 10 μm * thick wall *narrow lumen * consists of 3 layers (sometimes more) * muscle and elastic fibers in cell wall |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) Name 4 physical charateristics of cappilaries |
*around 10μm * extremely thin wall * consists of one thin layer *semi-permeable cell walls |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the role of the sinoatrial node? |
To act as the pacemaker controlling the heartbeat rate |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the role of the sympathetic nerve? |
To activate noradrenaline to increase heartrate |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) What is the role of the parasympathetic nerve? |
To activate acetycholine to decrease heartrate
|
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) |
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) |
|
|
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) |
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY (Blood system) |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Define oogenesis |
The production of eggs within the ovaries |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Define spermatogenesis |
The production of sperm in the seminiferous tubules in the testes |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION In what order are these cells developed?: Spermatid, spermatagonia, spermatoza, spermatocyte |
1. Spermatagonia 2. Spermatocyte 3. Spermatid 4. Spermatoza |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION In what order are these cells developed?: Primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, oogonia |
1. Oogonia 2. Primary oocyte 3. Secondary oocyte |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Explain the function of primodial follicles in oogenesis |
Contain primary oocyte egg cells arrested in prophase I
|
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION What hormone does the corpus luteum produce? |
Progesterone |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION What is the purpose of sertoli cells? |
To provide nurishment to developing spermatoza |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION What does the hormone FSH do during the menstrual cycle? |
Triggers the continued division of a few primary oocytes |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the function and features of the zona pellucida in eggs |
* Jelly layer made from glycoprotein * Acts as a sperm barrier |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the function and features of the corona radiata in eggs |
* External layer of the egg * provides support and nourishment |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the function of the cortical granulles in eggs |
* After fertilization, releases its contents causing the cortical reaction to prevent polyspermy |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the function of the acrosome cap in sperm |
Contains enzymes needed to break past the jelly barrier/zona pellucida in eggs |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION What is external fertilization? |
The fusion of gametes outside the body of a parent, common in aquatic life |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe capacitation its purposeduring intercourse and |
* When chemicals released by the uterus dissolve the sperms cholesterol coat * Improves sperm motility * destables the acrosome cap to improve acrosome reaction |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the acrosome reaction during fertilization |
* The sperm breaks through the zona pellucida using enzymes stored in the acrosome cap * the acrosome fuses with the jelly coat and releases enzymes that soften the glycoprotein * the sperm can now reach the exposed docking protein on the eggs membrane |
|
|
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Describe the cortical reaction post fertilization |
* After fertilization, cortical granulles release enzymes into the zona pellucida to harden and thicken the glycoprotein layer, to prevent ad * this also destroys the sperm docking proteins. |

