![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coronal Sections
|
Periventricular Zone
Medial Zone Lateral Zone |
|
|
Midsagittal Sections
|
Anterior
Middle Posterior |
|
|
Anterior Region
|
Preoptic nucleus (GnRH)
Paraventricular Nucleus and supraoptic (TRH/CRH, oxytocin) Suprachiasmatic (master clock) (temp. sleep/wake) |
|
|
Middle Region
|
Arcuate (GHRH)
Dorsomedial (HR, BP, GI, feeding, drinking) Ventromedial (satiety, fear, libido) |
|
|
Posterior Region
|
Posterior Hypothalamic (ADH)
Mammillary body (memory) |
|
|
Hypothalamic Nuclei Main Functions
|
ANS center
Emotion/biorhythm Sex drive Temperature regulation Food intake Water balance Sleep/Wake center Neuroendocrine |
|
|
posterior pituitary stores:
|
ADH and oxytocin
|
|
|
Hypothalamus special functions
|
-Crucial for harmonious growth of the body
-Differentiation of sexual characteristics -Sexual and reproductive activities -Often included in the limbic system- actions involves the emotional response to situation (cognitive) |
|
|
Hypothalamus exerts effects via:
|
-Its neuroendocrine role (regulatory effect on pituitary gland via releasing/inhibiting hormones, and production of ADH & oxytocin )
-Its influence on the autonomic nervous system (regulate body temperature, the cardiovascular system, and food and water intake) --An integral component of the limbic system (behavioral response). |
|
|
Input (Afferents)
Recieved from: |
1. Various parts of the forebrain - septal nuclei, orbital cortex (a.k.a. orbitofrontal cortex – prefrontal area involved in decision making), retina, limbic structures (e.g. amygdala)
Convey information relevant to the role of hypothalamus in mediating visceral and somatic responses of affective state 2. Brainstem and spinal cord Convey visceral and somatic sensory information HT also contain intrinsic sensory neurons (temp, blood osmolarity, glucose conc, certain hormones) |
|
|
Fiber Tracts Carrying Input
|
FOREBRAIN--Medial forebrain bundle (from septal nuclei, orbital cortex and other cortical area to lateral hypothalamus to midbrain tegmentum - stimulation produces intense pleasure)
Stria terminalis (connects amygdala with medial hypothalamus) Fornix (from hippocampus to mammillary body -major output from hippocampus) BRAINSTEM AND SPINAL CORD Dorsal longitudinal fasiculus DLF (connects hypothalamus with brainstem (central gray area of midbrain) Mammillo-tegmental tract connects spinal cord to mamillary nuclei |
|
|
Outputs of the hypothalamus
|
Most are reciprocal (bidirectional), except mamillothalamic tract, which is efferent only (mammillary body anterior nucleus of the thalamus – alertness, learning, memory; and hippocampus to mammillary body)
Medial forebrain bundle (links the cortex, hypothalamus, and brainstem) Stria terminalis (connects amygdala and medial hypothalamus) Dorsal longitudinal fasiculus - connects hypothalamus with brainstem (midbrain) central gray Dorsal longitudinal fasiculus – connects paraventricular, supraoptic and periventricular nuclei to preganglionic autonomic nervous system neurons (both SNS & PNS) Hypothalamohypophyseal pathways |
|
|
Major Afferent Pathways
|
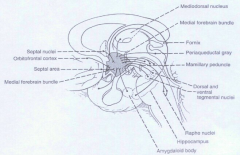
|
|
|
Major Efferent Pathways
|
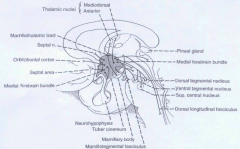
|
|
|
Neurosecretory Output
|
Posterior Lobe Hormones
(vasopressin and oxytocin) Releasing and Inhibiting Hormones (secreted into pituitary portal vessels) |
|
|
Posterior pituitary
Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal Pathways |
Evagination of the HT (embryology)
Neurosecretory cell axons of HT Neurohypophysis Stores and releases ADH, oxytocin |
|
|
Anterior Pituitary
Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal Pathways |
Pure gland (neurosecretory)
Adenohypophysis From Rathke’s pouch (mouth roof evagination - embyrology) Release of many hormones is controlled by hypothalamic hormones (releasing and inhibiting) |
|
|
tropic hormones
|
pituitary hormones that trigger the release of other hormones from other endocrine glands
-Gonadotropins -adrenocorticotropin -thyrotropin |
|
|
gonadotropins
|
stimulate hormone production by gonads (FSH, LH)
|
|
|
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)
|
stimulates hormone production by adrenal cortex
|
|
|
Thyrotropin (TSH)
|
stimulates hormone production by thyroid
|
|
|
Nontropic Pituitary Hormones
|
Prolactin
During pregnancy it helps in the preparation of the breasts for future milk production. After birth, prolactin promotes the synthesis of milk. secretion is -stimulated by TRH -repressed by estrogens and dopamine. Growth Hormone (a.k.a.somatotropin) is a protein of 191 amino acids. The GH-secreting cells are stimulated to synthesize and release GH by the intermittent arrival of growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) from the hypothalamus |
|
|
Targets of these Homrones:
Growth Hormone Prolactin FSH and LH TSH ACTH MSH Endorphins |
Bones
Mammary Glands Ovaries or Testes Thyroid Adrenal Cortex Melanocytes Pain receptors in brain |
|
|
Hypersecretion of GH
|
Gigantism (childhood onset)
Acromegaly (adult onset) |
|
|
Hyposecretion of GH
|
pituitary dwarfism
|
|
|
Neurohypophyseal Hormones
|
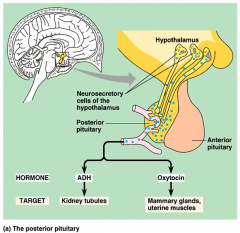
ADH and Oxytocin
Kidneys and mammary glands and uterine muscles |
|
|
Hypothalamic Syndromes
|
Diabetes insipidus
Characterized by increase urine production (polyuria) Lesion of supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei, or the supraopticohypophyseal tract Interfere with formation of ADH (which causes water retention in body) Psychosomatic disorders Environmental stress emotional arousal and endocrine changes pathological changes (cardiovascular, eating disorder etc) |
|
|
Hypothalamic Syndromes
|
-HT functions related to organized patterns of autonomic events, closely related to endocrine functions
-Disturbances in feeding behavior Lesion the ventromedial nucleus - obesity Lesion the lateral nucleus - starvation -Disturbances in Temperature regulation Lesion anterior nucleus (heat loss center) hyperthermia Lesion posterior nucleus hypothermia |

