![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What mediates a type I hypersensitivity reaction? |
1. IgE---- mast cell activation and degranulation |
|
|
What are some examples of a type I hypersensitivity reaction? |
1. Hay fever 2. Asthma 3. Anaphylaxis 4. Atopic dermatitis 5. IgE-mediated eczema |
|
|
What mediates type II hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. IgM, IgG--- cytotoxic 2. Antibodies involved that are specific for that tissue |
|
|
What are some examples of type II hypersensitivity reactions?
|
1. Autoimmune hemolytic anemias
2. ADCC 3. Goodpasture |
|
|
What mediates type III hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Antibodies formed against exogenous or endogenous antigens 2. Complement often involved--- formed in serum or EC spaces |
|
|
What are some reactions are type III hypersensitivity? |
1. SLE 2. Glomerulonephritis 3. Serum sickness |
|
|
What mediates type IV hypersensitivity? |
1. Sensitized T cells stimulate cell-mediated reactions by macrophages---- 2. Tc cells, NK cells, eosinophils, neutrophils |
|
|
What are some examples of type IV hypersensitivity? |
1. Granulomatous disease 2. Contact dermatitis 3. Graft rejection |
|
|
What is the mnemonic to help you remember the class of hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. ACID 2. Allery, Cytotoxic, Immune complex, Delayed |
|
|
How long does it take for ssx of type I hypersensitivity reactions take to present? |
1. Seconds to minutes |
|
|
What is released in type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. IgE--- basophils---- degranulation--- histamine |
|
|
What is atopy? |
1. Genetic predisposition to make IgE |
|
|
What does histamine do? |
1. Smooth muscle contraction 2. Mucus secretion 3. Increased GI fluid secretion 4. Vasodilation 5. Increased vascular permeability |
|
|
What local reactions occur in type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Skin--- urticaria, pruritis, wheal and flare, eczema 2. Nasal mucosa--- allergic rhinitis 3. Lungs-- bronchial asthma |
|
|
How do you tx full-blown type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Epinephrine |
|
|
What is the difference between anaphylactoid reactions and type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. No IgE in anaphylactoid reactions |
|
|
What are the anaphylatoxins? |
1. C5a 2. C3a 3. C4a |
|
|
What mediates anaphylactoid reactions? |
1. Anaphylatoxins 2. Calcium ionophores 3. Radiocontrast dyes 4. Opiates 5. Vancomycin |
|
|
What occurs in anaphylactoid reactions? (figure) |
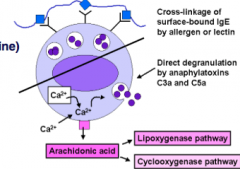
|
|
|
70% of all bronchial asthma is due to.... |
1. Type I hypersensitivity reactions |
|
|
What are the medical syndromes associated with atopy? |
1. Inhalant allergies 2. Dermatitis 3. Allergic asthma |
|
|
What is the MC atopic disease? |
1. Allergic rhinitis |
|
|
What is the presentation of type I hypersensitivity reaction eczema? |
1. Pus-filled papillose with eosinophils OR 2. Dry, crusted lesions |
|
|
How do you tx eczema induced by I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Anti-histamines 2. Topical corticosteroids |
|
|
What ar the three pathological events that lead to allergic asthma? |
1. Reversible obstruction 2. Airway hyperreactivity to physical and chemical stimuli 3. Inflammation |
|
|
What is produced in inflammation in allergic asthma? |
1. ROS 2. NOS 3. Cytokines--- IL-4, IL-5 (eosinophil maturation) |
|
|
What is the key cell involved in cytokine secretion in allergic asthma? |
1. Helper T-cell |
|
|
What causes food allergies? |
1. Mast cell degranulation in GI tract 2. Ssx--- severe stomach pain, diarrhea, emesis, dyspnea, skin hives/urticaria |
|
|
When does the recurrent anaphylaxis occur in I hypersensitivity reactions? What causes it? |
1. Hours later 2. Leukotriene and prostaglandin production
|
|
|
What are the MCC of anaphylaxis? |
1. Penicillin 2. Bee stings 3. Peanuts |
|
|
What are the stages of type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Sensitization 2. Early phase 3. Late phase |
|
|
What occurs in the sensitivity stage of type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Takes weeks 2. Initial contact with allergen 3. Th2 secretes IL-4 and ILI-13 4. B cell makes IgE 5. IgE binds FCER on mast cell |
|
|
What occurs in the early phase of type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Occurs within 20 minutes of contact 2. Allergen cross-linkes IgE 3. Mast cell degranulates 4. Histamine is released |
|
|
What occurs in the late phase of type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. 6 hours later---- 2. Newly formed mediators from arachadonic acid |
|
|
What histamine receptors are most involved in type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. H1 2. H2 |
|
|
What does the lipoxygenase give rise to? |
1. Leukotrienes |
|
|
What is the effect of LTB4? |
1. Chemotaxis 2. Hyperalgesia |
|
|
What leukotrienes are in charge of bronchoconstriction and edema in type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. C4, D4, E4 |
|
|
What is the function of PGE2? |
1. Vasodilation |
|
|
What is the function of TXA2? |
1. Platelet aggregation |
|
|
What is the function of PGI2? |
1. Inhibits platelet aggregation 2. Causes vasodilation |
|
|
What occurs in the formation of inflammatory cell infiltrate in type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. ECF, IL-8, LTB4--- recruitment of eosinophils and PMNs 2. Eosinophils degranulate when FCER is cross-linked by allergen and IgE 3. Destructive substances produced, injure epithelium |
|
|
What destructive substances are produced in the inflammatory cell infiltrate step? |
1. Major basic protein 2. Eosinophil cationic protein 3. ROS
|
|
|
What makes up SRS-A? |
1. C4, D4, E4 |
|
|
What inactivates SRS-A? When? |
1. Arylsulfatase 2. In last step of type I hypersensitivity reactions |
|
|
What deactivates histamine in the last step of type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Histaminase |
|
|
What are the outcomes of the skin prick test? |
1. Wheal and flare 5-7 mm within 15 minutes is positive 2 Late response--- 5-6 h later |
|
|
What does the RAST test measure? |
1. Allergen-specific IgE |
|
|
What does the RIST measure? |
1. Total serum IgE |
|
|
What do you look for in a nasal smear? |
1. >10% eosinophils |
|
|
How can you prevent type I hypersensitivity reactions? |
1. Prevent exposure 2. Hyposensitizaiton tx |
|
|
What occurs in hyposensitization tx? |
1. Introduce allergen 2. Isotope switch from IgE to IgG4/IgA--- mast cells don't degranulate 3. Cause shift from TH2 to TH1 |
|
|
What type of switch does sublingual administration of allergy meds cause? |
1. TH2 to T reg |
|
|
What is the function of tryptase in the early phase? |
1. Generate C3a and C5a |

