![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common structural cause of hydrocephalus? |
An obstruction of normal CSF flow.
|
|
|
What are the effects of hydrocephalus on the brain? |
Stretches periventricular white matter; Reduces blood flow; Build up of toxins; Subcortical disconnection syndrome |
|
|
What are the 4 common types of congenital hydrocephalus? |
Spina bifida Myeomeningocele. Aqueductal Stenosis Dandy-Walker Syndrome Prematurity IVH |
|
|
Compare internal vs. external hydrocephalus. |
Internal Hydrocephalus: obstructive hydrocephalus (usually foramen of Monro or Aqueductal Stenosis)
External Hydrocephalus: absorption hydrocephalus (usually caused by meningitis) that affects the subarachnoid spaces. |
|
|
What are the medical findings in Internal (Obstructive) Hydrocephalus? |
Increased ICP; Ventricular Dilation; Compression of the brain |
|
|
How is communicating hydrocephalus different from non-communicating hydrocephalus. |
Communicating hydrocephalus is NOT an obstructive process, but and ABSORPTION problem (i.e., external hydrocephalus). May or may not result in increased ICP.
Non-communicating hydrocephalus is due to an obstruction (also known as ex vacuo, arrested, or compensated hydrocephalus). |
|
|
What conditions can result in communicating hydrocephalus? |
Alzheimer disease;
Loss of brain tissue;
Meningitis |
|
|
Is communicating or non-communicating hydrocephalus typically associated with congenital hydrocdphalus? |
Non-communicating (However, non-communicating hydrocephalus can also be developed by other obstructions, like cysts, tumors, etc.). |
|
|
What is the most common type of hydrocephalus in adults? |
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
|
|
|
What are the classic clinical symptoms of normal pressure hydrocephalus? |
Patients are wet, whacky, and wobbly. [Urinary incontinence, confusion, gait (often magnetic) abnormalities]. |
|
|
What type of hydrocephalus is posttraumatic hydrocephalus normally classified as? |
Non-communicating (also acquired). |
|
|
What are the three types of congenital hydrocephalus associated with disorders of embryogenesis? |
Dandy-Walker Syndrome; Spina Bifida Myeomeningocele; Aqueductal stenosis |
|
|
What is a common acquired cause of congenital hydrocephalus? (remember, congenital simply means early rather than genetic, per se). |
Premature IVH. |
|
|
What hydrocephalus classifications are associated with congenital hydrocephalus? |
Internal, obstructive, and non-communicating (these three classifications tend to go together). |
|
|
What is the most common cause of congenital hydrocephalus? |
Spina bifida Myeomeningocele; Accounts for 70% of all congenital hydrocephalus |
|
|
How does Spina Bifida Myeomeningocele lead to hydrocephalus?
|
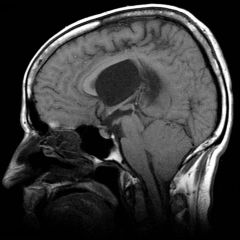
Chiari II malformation where the posterior fossa is too small, allowing the malformed cerebellum to compress the 4th ventricle. |
|
|
What is the neuropathology of Aqueductal Stenosis? |
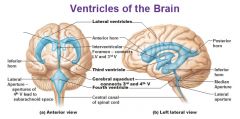
Narrowing of the aqueduct of Sylvius between the 3rd and 4th ventricles. |
|
|
How does Dandy-Walker Syndrome cause hydrocephalus? |
Cystic fourth ventricle. Also, the cerebellar vermis is not developed (complicating the interpretation of motor deficits).
Also, it has the opposite problem of Spina Bifida Myelomeningocele in that the posterior fossa is enlarged. |
|
|
How does premature IVH cause hydrocephalus? |
Bleeding from the germinal matrix obstructs blood flow. |
|
|
Does IVH related hydrocephalus progress? |
No. It is arrested. |
|
|
How are premature IVH graded? |
Grade 1- Bleeding from the Germinal Matrix,but not into the ventricles.
Grade 2- Bleeding from the Germinal Matrix, and into the ventricles.
Grade 3- Bleeding with enlarged ventricles (i.e., hydrocephalus)
Grade 4- Bleeding into periventricular tissue, and ventricular enlargement (i.e., hydrocephalus).
HYDROCEPHALUS IS ONLY ASSOCIATED WITH GRADE 3&4. |
|
|
What age increases risk of NPH? |
65 or older. |
|
|
What differences in the skull have implications for NPH vs. congenital hydrocephalus? |

In NPH, the skull is formed and there is nowhere for brain to go. In congenital hydrocephalus, the skull is not formed. In fact, Dandy-Walker Syndrome and Aqueductal Stenosis are often notable because the infant's head is "like an orange on a toothpick" |
|
|
What is the most common shunt placement site in the brain? |
Right posterior ventricle that then drains into the peritoneal cavity. |
|
|
What is a third ventriculostomy? |
When a perforation is placed in the floor of the third ventricle in order to drain CSF into a subcistern.
(NOTE: Often used when shunts cannot; and primarily to treat Aqueductal stenosis). |
|
|
What are common cognitive symptoms of congenital Hydrocephalus? |
FINE MOTOR SKILL IMPAIRMENTS;
Posterior inattention
Timing;
Hypersocial |
|
|
What symptoms or associated features of NPH are associated with poorer cognitive outcomes following shunting? |
Severe gait difficulties are negatively associated with outcomes.
NPH related to dementia or stroke is also indicative of poor outcomes. |
|
|
What type of academic problems is most negatively affected by hydrocephalus? |
Math Followed by reading comprehension and writing. |
|
|
What academic abilities are intact in hydrocephalus? |
Word reading and spelling. |
|
|
How will a patient with hydrocephalus tend to preform on the WAIS-IV? |
Better VCI than PRI.
Slowed motor and processing speed affecting tests with those components (e.g., Block Design)
|
|
|
What are the primary attention problems in congenital hydrocephalus? How do they differ from ADHD? |
Problems with the posterior attention system (i.e., orienting and engaging), but stable engagement once oriented and engaged.
Differs from ADHD in that, ADHD patients have more problems with the anterior attention system (i.e., self-regulation, maintaining stable engagement). |
|
|
How is processing speed in hydrocephalus? |
Terrible. |
|
|
Describe language functioning in hydrocephalus. |
Problems with "higher" language functions of comprehension, prosodics, and pragmatics
BUT
Intact raw functions of vocabularly, grammar, and expressive language. |
|
|
Visuospatial functioning in hydrocephalus is... |
impaired for complex configurational skills, but categorical perception is intact. |
|
|
Describe executive functioning in hydrocephalus |
Primarily due to attention and motor problems. Performance on executive functioning tests is characterized by improvements across trials. |
|
|
What are typical motor problems in hydrocephalus? |
Upper extremity motor deficits. Gait problems in NPH. |
|
|
Describe the emotional/relational considerations in hydrocephalus |
Hypersocial; Overly talkative at times; Intrusive with poor perception of social cues.
BUT
Can have strong interpersonal skills. |
|
|
Do stimulants work for attention problems in hydrocephalus? |
Not really...at least, not beyond the benefits any of us enjoy on stimulants. This is because it is a posterior attention problem. |
|
|
How do children with congenital hydrocephalus tend to perform on verbal compared to non-verbal memory measures?
|
Comparatively poor on nonverbal
|
|
|
In which direction does hydrocephalus progress in terms of thinning the ventricles? |
Posterior to anterior Helps explain the PRI being worse that the VCI, too. |

