![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
429 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Difference between training and education |
Training teaches a specific skill, education is general and touches many topics |
|
|
Explicit knowledge |
Knowledge that can be formalized, codified, and communicated. IE manuals, formulas |
|
|
Tacit knowledge |
Personal knowledge based on individual experience and is much more difficult to explain. IE group norms and cultural values |
|
|
Top Five skills for new employees to be successful |
Professionalism, teamwork, oral communicating, ethics and social responsibility, reading comprehension. |
|
|
Functionally illiterate |
Those who can't read or write well enough to function in society |
|
|
Prose literacy |
Ability to search and use information from continuous texts such as news articles |
|
|
Document literacy |
Ability to search and use information from maps, train schedule, application etc |
|
|
Quantitative literacy |
Ability to perform computations with numbers such as balancing a checkbook |
|
|
Benefits of training |
Improved production, reduced learning time to reach performance standards, more favorable attitudes and loyalty, Dartford satisfies hr planning requirements, reduces accidents, helps employees develop and advance, and helps organizations respond to market changes |
|
|
Systems approach to training |
An analysis of training and how it interacts with other organizational activities |
|
|
Interaction between training and development and other hr functions chart |

|
|
|
What to consider when developing a training program |
Why should you have one, what types should you have, who will be trained, who will supply it, how will it be evaluated, what incentives will motivate the trainee to learn |
|
|
Three ways of funding trading |
Allocated yearly budget, Rayner's operate under budgets of the programs, treat the training as a profit center and sell it's services |
|
|
Training costs include what elements |
Staff training development hours, cost of materials, training time, cost of production losses while employees are trained |
|
|
What benefits of the training should be evaluated? |
Increased productivity, reduced errors, improved safety, reduced operating costs |
|
|
Cost per trainee = |
Total training costs divided by number of trainees |
|
|
How to decide if a particular training program is worth attending |
Talk to someone who has attended it, investigate the trainers, look for evaluation evidence such as studies |
|
|
Benefits of doing an ROI study on your training |
Justifies it to management and shows you where you can change or improve |
|
|
Contents of an ROI training analysis |
The major issues addressed with the training, the training functions goals and objectives and indicators used to measure success or failure, realistic assessment of the budget, conclusions drawn from the last year's performance and improvements for next year |
|
|
Methods of continuing to give trainings during rough times |
Increase class sizes, reuse materials, provide in house trainings, train only those who truly need it, eliminate travel costs by videoconferencing, combine trainings with meetings, eliminate refreshments, develop a wiki database, put training online, tell employees about free online training |
|
|
Systems model for taining chart |
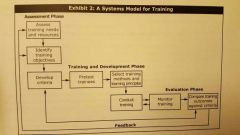
|
|
|
Assessment phase of training development |
Need for training is examined as well as resources available, who should be trained, objectives of training |
|
|
Training and development stage of the training development |
Training is designed and developed |
|
|
Evaluation phase of training development |
After training is given evaluate and get feedback |
|
|
ADDIE model of training |

|
|
|
A good training assessment includes |
How well the org is achieving goals, skills needed by emps to accomplish these goals, strengths and weaknesses of the current emps |
|
|
Organizational analysis |
Examines the kinds of problem areas an org is experiencing and where they're located, specifically org effectiveness indicies, hr succession planning and org climate |
|
|
Training needs analysis chart |
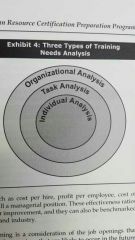
|
|
|
Org effectiveness indicies |
Measures such as labor costs, production efficiency, quality, machine maintenance, accidents, turnover and absenteeism |
|
|
Task analysis |
Lists the different tasks an emp performs and identifies the kinds of skills and behaviors required to perform them. |
|
|
A good task analysis identifies |
Tasks to be performed, conditions under which they're performed, description of when and how, quantity and quality required, skills and knowledge required, where the skill and knowledge is best acquired |
|
|
Individual analysis aka personnel analysis |
Examines how well an individual emp is performing their job. Aka training should be for those who need it so this IDs who needs it. |
|
|
Ways to find out what trainings are needed |
Questionnaires, surveys, interviews performance data, observations, audits, tests, assessment centers, focus groups, group discussion, document review, advisory committees, and competency modeling |
|
|
The major learning theories |
Classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social cognitive theory and andagogy |
|
|
Classical conditioning |
Connecting or pairing a neutral stimulus with a reflexive response. Ex stress causes blood pressure to rise, Pavlov trained dogs to salivate when they hear a bell |
|
|
Classical conditioning chart |
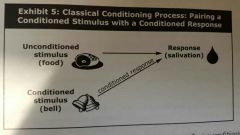
|
|
|
Classical conditioning aka |
Responsive conditioning or reflexive conditioning |
|
|
Operant conditioning |
Learning voluntary behaviorsnl that are under the control of the muscle system of the body. Theory by BF Skinner. Ex behavior modification |
|
|
Behavior modification |
Identifying the desired response and selectively reinforcing it |
|
|
S-R bond |
When an organism already knows the response, but needs to be trained when to have the response, you create a stimulus environment. |
|
|
S-R bond diagram |

|
|
|
Chaining and shaping |
When an organism doesn't know how to make the response do you have to teach how and when |
|
|
Chaining |
Combining a series of simple responses into a complex response pattern. Break task down into smaller steps and reinforce each small step, but as they get better you stop reinforcing each step and only reinforce the final result. |
|
|
Chaining diagram |

|
|
|
Shaping aka method of successive approximations |
The process of acquiring a unique response by reinforcing closer and closer approximations of it. Ex 'good job close enough, but next time...' So as training progresses you only reinforce the end result closest to what you wanted achieved |
|
|
Reinforcement contingencies |
They explain the relationship between behavior and consequences |
|
|
5 reinforcement contigencies |
Positive reinforcement, punishment, avoidance(person tried to avoid a consequence), escape(person experiencing an unpleasant consequence makes a response to escape it), extinction (no reward if they eliminate the response) |
|
|
Different classifications of reinforcers |
Positive vs negative reinforcers, primary(food water rest) vs secondary(social approval money) rewards, intrinsic(feeling of pride) vs extrinsic(praise from others, gifts) |
|
|
Reward schedules |
The timing of the reinforcement and how often the correct response is reinforced |
|
|
Three major reinforcement schedule types |
Continuous, intermittent aka ratio(ex only every third response is rewarded), interval(ex receives reward after five minutes) |
|
|
Ups and downs of reinforcement schedules |
Continuous yields results only when a reward is present so response stops as soon as you stop rewarding. Variable ratio and interval actually provide high yield rate and reliable responses |
|
|
Social cognitive theory aka social learning theory |
Developed by Albert bandura. Behavior is influenced by the consequences of the behavior. Individual is influenced by environmental reinforcers but they have the ability to change their environment and self regulate |
|
|
Reciprocal determinism |
Environment, behavior, and personal factors interact to influence each other |
|
|
Reciprocal determinism chart |
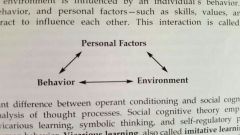
|
|
|
Vicarious learning aka imitative learning |
The process of learning by observing others. Important to social cognitive theory. |
|
|
Symbolic learning |
The use of symbols such as words or pictures greatly facilitates learning. Important to social cognitive theory. |
|
|
Self regulatory capacities of humans |
Important to social cognitive theory. People are able to effectively control their own behavior by arranging environmental rewards, by generating cognitive supports, and by producing consequences for their own actions. |
|
|
Behavioral modeling |
Involves extensive participant involvement by providing the participants with opportunities to observe the performance of new skills, to practice, and to get feedback. Important in social cognitive theory. Say out loud cognitive thought processes for participants to learn from. |
|
|
Self efficacy |
A belief in ones iwn capability to perform a specific task. Similar to self esteem. Important to social cognitive theory. Predicts performance. |
|
|
Three dimensions of self efficacy |
Magnitude(level of task difficulty you believe you can achieve), strength(amount of confidence that you can do task) and generality(degree to which your expectations are spread across situations or restricted). |
|
|
Self efficacy is a learned characteristic that is acquired by what four kinds of info cues |
Enactive mystery(confidence that comes with practicing the task), vicarious experience (observing others), verbal persuasion, perceptions of ones physiological state |
|
|
Is efficacy self reinforcing? |
Yes. If you think you'll suck you'll suck, if you think you'll succeed most likely you will. |
|
|
Andragogy |
Adult learning theory that believes learning is experience based, problem centered, enhanced by active participation, collaborative, and involvement. |
|
|
Is andragogy truly unique only to adults tho? |
No, some elements of teaching children is the same, except for the experience piece because adults have lived through more. |
|
|
Does andragogy work for learning a technical skill? |
No because learning a technical skill is too rigid |
|
|
Action learning |
Brings SETS(groups of 5-8) of people together to find solutions to real problems and they have discussions |
|
|
Key findings of studying the brain |
Can learn at any age, to retain info brain must move info from working memory to the basal ganglia which happens during sleep, thoughts take literal energy/blood glucose, during REM the brain stores info in hippocampus then basal ganglia, can retain info better by reviewing just before bed, positive things release serotonin which increases retention, unfairness releases cortisol which inhibits retention, moderate levels of arousal improve learning, stress and high arousal cause the brain to shut down, expectations impact learning |
|
|
What principles are important in designing training programs |
Stimulus, response, motivation, feedback, transfer, learning curves, and forgetting. |
|
|
Stimulus in learning |
Must be easily perceived and well organized(the next concept builds on the one you just learned) |
|
|
Response in learning |
Practice and repetition. The response should be practiced accompanied by intermittent reinforcement. But social cognitive theory claims you don't always need to practice, only when developing new skills. |
|
|
Massed vs distributed practice |
Massed-doing a training in 12 hrs in 1 day or distributed 12 hrs over 12 days. Distributed is better. |
|
|
When is distributed practice needed most |
When material is complicated or when the trainees are inexperienced |
|
|
Open learning |
Individual learn atbtheir own pace by studying materials that's are presented to them, ex online |
|
|
Whole training, pure part training, and progressive part training chart |

|
|
|
Two deciding factors when determining whole task or part task training |
Task complexity(difficulty of each of the subtasks) and task organization (degree of integration among set of sub tasks) |
|
|
What training method is more effective for highly organized tasks or those that build on each other/are dependent on each other? |
Whole task |
|
|
Examples of training motivators |
Financial incentives, recognition, intergroup competition, or threat of termination |
|
|
Is feedback important for improvement? |
Yes. Trainees should be told if theyre right or wrong and why and how to avoid mistakes in the future. |
|
|
Transfer of training |
When trainees can apply knowledge learned in their training to their job. |
|
|
The three transfer of training possibilities |
Positive transfer of training, negative transfer of trainings (training actually inhibited performance), no observable effect of training |
|
|
Predicting transfer of training chart |

|
|
|
Factors that influence transfer of training |
Design and presentation of training, if the training is important to the trainees, if the work environment is conducive to changed behaviors |
|
|
3 factors that are the most serious impediments to effective training transfer |
Lack of on the job reinforcement, interference from the immediate environment, and nonsupportive org climate |
|
|
How to combat these interferences |
Have trainees develop an action plan at the training to implement in their work |
|
|
Learning curves |
Graphs that show the number or percentage of correct responses during successive learning periods |
|
|
Learning curve chart |

|
|
|
Negatively accelerating learning curve aka decreasing returns |
Learn the most at the beginning. Most frequently occurring type of learning curve |
|
|
Positively accelerating learning curve aka increasing returns |
Most common for difficult or complex material, when trainee lacks background, when motivation is low but increases |
|
|
Three explanations for plateaus |
Hierarchy or habits (a series of habits must be learned before moving on), motivation decline, unlearning incorrect responses |
|
|
Theories that explains forgetting |
Passive decay through disuse, retroactive inhibition (new learning interferes with recall of old learning), proactive inhibition (old learning interferes with retention of new learning), motivated forgetting (they want to forget the info). |
|
|
Repression |
A person wants to unlearn info because it's threatening to their self esteem or damages their ego |
|
|
Zeigarnik effect |
Forget info after you don't need it anymore, ex server takes drink orders delivers drinks then forgets what you ordered because she already delivered it so the info isn't needed anymore |
|
|
3 learning styles chart |

|
|
|
Illustration of level of learning chart |

|
|
|
Levels of learning |
Knowledge-recalls facts, comprehension- can explain facts, application-can apply info to other problems, analysis- can understand why phenomena exists, synthesis- can draw from related sources to reach broad understanding and come to conclusions, evaluation- can make judgements of value and worth |
|
|
Learning strategies chart |
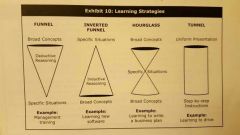
|
|
|
Four kinds of major learning |
Motor response, rote, idea and value internalization |
|
|
Motor response learning |
Physical acts, you have to actually ride a bike to learn to ride a bike |
|
|
Rote learning |
Memorizing arbitrary associations between words symbols objects or events. Ex memorizing a poem |
|
|
Learning ideas |
Confronted with complex stimulus environment and expected to make response and thinking process or intermediary response or mediating response occurs in the middle |
|
|
Value internalization |
The process of acquiring personal values. Moral behaviors. Cognitive info about proper standards of conduct become internalized a a personal moral value. |
|
|
3 levels of Kohlberg's cognitive development stage theory |
Pre-conventional(kids, egotistic right and wrong defined by authority figures and rules followed to avoid punishment ), conventional(adults conform with social norms of a few highly respected people) and post conventional/principled level(rare right and wrong based on universal moral principles people follow them based on sense of moral duty). Each level then has two stages for a total of six stages. |
|
|
Behavioral objectives |
What the objectives of the training are |
|
|
Examples of poor behavioral objectives |
At the end of this training trainees will: think like a manager, sharpen communication skills, learn the art of making sound decisions, discover proven methods for planning and organizing |
|
|
3 basic attributes of good beh training |
Objective is described using verb, specifies a standard of performance expressed in number degree or accuracy, and specifies the relevant constraints or time limitations for performing beh. |
|
|
Ex of good behavioral objectives |

|
|
|
Guidelines for writing behavioral objectives chart |

|
|
|
Method for teaching motor responses |
Familiarize trainee with equipment materials and surroundings, demonstrate the activity, let then trainee practice, provide guidance and feedback |
|
|
Three phase process of skill acquisition |
Declarative knowledge(acquires basic knowledge of the task), knowledge compilation(practices), procedural knowledge(overlearns the skill so is now quick and accurate) |
|
|
Rote learning methods |
Familiarize trainee with material, identify patterns that might help trainee remember info, let trainee practice repeating the material through slient study and oral repetition over a long distributed period of time if possible, provide immediate feedback, require repetitive practice so overlearning occurs |
|
|
Idea learning methods |
Divide ideas into sequential pattern of concepts and subconcepts, master one concept before moving on to the next, trainee should practice each response and demonstrate mastery, reinforce the trainee, review material frequently to avoid forgetting |
|
|
Most important techniques for developing value internalization |
Induction and modeling |
|
|
Induction |
All forms of verbal explanation suchbas reasoning teaching and oreaching., reinforcing appropriate behaviors |
|
|
Modeling |
The example that individuals will observe in others behavior ex what they see their manager do they're more likely to do |
|
|
***on the job training methods |
Focus on increasing immediate productivity. Job instruction training, apprenticeships, internships/assistantships, job rotation and cross training, action learning: project assignments and committee assignments, coaching and counseling |
|
|
Job instruction training |
Most popular training method. Begins with explanation of job and then step by step demonstration of the job operations and explanation of why it's being done, then the trainee if given the chance to do the task themselves and gets feedback from instructor and then periodic checks after training to make sure they're still doing it right. |
|
|
Apprenticeship |
Having a new worker work along side and under the direction of a skilled technician. Ex plumbing: 4000 hrs continuous work plus 144hrs/yr classroom instruction. After this they become a journeyman. |
|
|
Internships and assistantships |
Similar to apprenticeships but are for higher level education type positions. Some college internships are part of cooperative education-work at a company under experienced employee and reports to experienced faculty member from school. |
|
|
Job rotation and cross training |
Typically reserved for managerial and technical occupations. Idea is to expose individuals to multiple org challenges by rotating them through key departments. They take on responsibilities in these departments and also get supportive guidance from a supervisor. Job swapping is when two employees switch positions. Usually the jobs require similar knowledge and skills. Employees who are cross trainer are typically compensated for their higher skills. Good for prepping for absences or executive advancement. Advantage increases productivity. Disadvantage makes employee feel temporary and some time loss orienting the employee to the job. |
|
|
Action learning |
Assigning trainees to projects or assignments and having then learn while doing. |
|
|
Coaching and counseling |
Feedback on job performance that's encouraging and patient. Trainer must have a good relationship with the trainee and allow trainee time to learn. An effective coach is a good model, sets specific goals, provides timely feedback, provides proper reinforcement. |
|
|
***off the job training methods |
Independent study, corporate universities vestibule training, lecture, case studies, conferences and discussions, role playing, simulations and business games, programmed group exercises, television and films, asynchronous learning networks, computer based training, teletraining and e-learning, mobile learning and social media |
|
|
Independent study |
70% of learning happens informally on the job this way. Books magazines courses massive open online courses (free university course unless you want to pay for the credit) etc. When taking online course consider reputation of school, presentation of material, evaluation method, cost, time required, and your level of self discipline. Tuition reimbursement progams are good to have: improve job performance and retention and skills |
|
|
Corporate universities |
An organization's own school. Instructors are company trainers, subject matter experts, consultants, professors etc. They reduce cost of training, make learning convenient, provide encouraging learning environment etc. Includes everything from orientation to executive training. |
|
|
Vestibule training |
Tailored towards teaching specific job skills for production. Small training area equipped like the production area. High training transfer since the environment is the same and provides immediate feedback and opportunity for practice. Can be expensive to maintain. |
|
|
Lecture |
Down side doesn't allow for trainee participation or pratice or feedback which inhibits transfer of learning |
|
|
Case studies |
Popular in business classes. Analyze a problem and come up with a solution. Success of training depends on skill of the leader, need to know when to allow discussion and when to jump in and guide it. |
|
|
Conferences and discussions |
Forums where people learn from each other. Studies show people are more involved to change their minds because of influence of group discussion. |
|
|
Role playing |
Participants assume specific characterizations and act out a scenario then attempt to solve the problem through acting it out. Typically high participation, great for facilitating attitude change when playing a role opposite of your own feeling of a situation or when doing a role reversal. Effectiveness cab be increased by videotaping and freeze framing and then critiquing (great for managerial skills) |
|
|
Simulations and business games |
Creating an artificial learning environment that approximates the actual job conditions as much as possible. In basket simulation-trainee plays new manager, has to work through problems in a limited amount of time, then it's evaluated. Business management lab- game where participants assume management of small manufacturing company where they make decisions which are then analyzed by an algorithm that approximates real life and they get reports as feedback. |
|
|
Programmed group exercises aka experiential group exercises |
Trainees work together in a discussion group to solve a specific problem then analyze the process and outcome. Useful in identifying potential managers. Outdoor experiential training-improve effectiveness of managers through outdoor challenges-studies sore they improve functioning of work groups. |
|
|
Television and films |
Can watch a video tape of something being done and critique it. Advantage is you can edit and show only the content you want to show and can share with groups despite location. Best use of videotapes is to illustrate correct behavior patterns for imitative learning (watch someone doing it right). |
|
|
Asynchronous learning network |
Networks of people designed for anytime anywhere learning. Self study with interactivity with others involved in the learning process. Ex webinar that makes you participate. |
|
|
Programmed instruction |
An application of the principles of operant conditioning in which learners are presented with a series of concepts and after learning each concept they are required to demonstrate their understanding by answering multiple choice questions. |
|
|
Computer based learning |
Any form of interactive learning between a computer and a learner in which the computer provides the majority of the stimulus and the learner has to make a response during the learning. Advantage: learner must respond to all questions without fear of embarrassment of wrong answer. Takes 120-300 hrs to make1 hout of content though and it's costly. American society for taining and development good resource. |
|
|
Linear sequencing |
Logical sequence where an earlier concept serves as a building block for more complex learning |
|
|
Branching sequencing format |
Subsequent information is determined by the learner's response |
|
|
Teletraining and e-learning |
Teleconference or webinar. Train many learners in different locations without cost of bringing them together. Requires high skill trainers because they can't see their audience to see how well their ideas are being received |
|
|
Mobile learning and social media |
Aka on demand learning or disconnected learning. Advantage- flexible and convenient. Disadvantage- requires concentration |
|
|
Advantages to on the job techniques |
No special space or equipment needed, practical side employees learn while they work, provides immediate transfer of training, allows employees to practice, allows trainees to associate with future co-workers and observe their behaviors |
|
|
Off the job training disadvantage |
Doesn't provide immediate transfer of training |
|
|
Advantages of off the job techniques |
Doesn't tie up expensive equipment, promotes an environment conducive to learning new ideas, allows employees to get away from job pressures, provides resources, challenges executives to grow and improve |
|
|
Facilities planning considerations |
On site vs off site, space requirements, seating arrangements, environmental considerations, ADA accessibility |
|
|
On-site work training advantages and disadvantages |
Work location is best when teaching a specific task especially when equipment is needed, maximizes transfer of training. Distracting though due to job pressures and happenings and can usually only train one person at a time. |
|
|
Conference room on site advantages and disadvantages |
Don't have to travel but away from desk distractions, but can still be distracted by work pressures. Good for knowledge that is brief and uncomplicated. |
|
|
Off site training advantages |
Leave work situations so leave distractions. Good for complex learning. New environments can foster creative thinking. |
|
|
Space requirement considerations |
Do they need to write or manipulate objects or move around? If writing should be three to four feet apart. If moving, may need up to 100 sq ft per person. |
|
|
Seating arrangements chart |
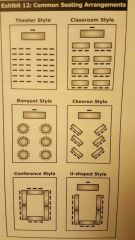
|
|
|
Theater style seating |
Ideal for lectures films and video |
|
|
Classroom style seating |
Good for listening to presentations and taking notes |
|
|
Banquet style |
Good for small group discussions and interaction |
|
|
Chevron style seating |
Good for trainees to interact with each other and the oresenter |
|
|
Conference style seating |
Group discussions for people of equal status |
|
|
U shaped style seating |
Good for case discussions where everyone can see each other and the trainer. |
|
|
Environmental considerations |
Temperature, lighting, ventilation, sound, comfortable chairs(padded or contoured) |
|
|
Training materials |
Manuals, handouts, leader guides, audio-visual |
|
|
Training manuals |
Contain schedule, outline, articles, and reports and copies of ppts. |
|
|
Handouts |
Serve a variety of purposes: presentation outline, supplemental info, presentation highlights. |
|
|
Leader guides |
For when training is presented by someone other than the person who designed it. Usually contain suggestions for how to present material and discussion points and sometimes a test |
|
|
Audio visual materials |
Should supplement the training not replace it. |
|
|
Copyright statutes |
The exclusive right or privilege of authors out proprietors to print or otherwise multiply distribute or sell copies of their literary artistic or intellectual creations when the copyright is obtained in compliance with the copyright statute. Must obtain permission or pay fee if copyrighted and the trainer is using more than 250 words from a book length work or 5% from article or one line from poetry or song. |
|
|
Cautions regarding copyright infringement |
Copyright applied to all types of material, original tangible expressions are copyrighted the moment they're created even if not registered yet, paraphrasing or changing a few words is still copyright infringement, must obtain permission to use movie clips or videos for audience, copyright remains with the author unless they give it away, can get permission through iCopyright.com or the copyright clearing center or broadcast music Inc or American society of composers and performers or getty images or corbis |
|
|
Two issues to address when evaluating training |
What criteria should be used and when and from whom should the data be collected |
|
|
The criteria for evaluating a training should be determined by |
The training objectives |
|
|
For proposed criteria for evaluating training |
Reactions. Learning, behavior and results. |
|
|
Extent to which training techniques utilize the five principles of learning |

|
|
|
How to test participants reactions to the training |
Hand them a questionnaire to fill out at the end |
|
|
How to test how much the trainee learned |
Tests |
|
|
How to test if trainee behavior changed |
Self report or by observation |
|
|
How to test measurable results such as reduced turnover or costs |
Conduct a utility analysis- how much did the training cost and what are the financial returns, ex decreased accidents so decreased ins costs. |
|
|
Sources of data |
Archive data, questionnaires and surveys, performance tests, interviews, simulations, ratings/checklists, critical incidents, observations, performance appraisals |
|
|
Unobtrusive measures |
Archive data in the personnel file: doesn't influence employees behavior obtaining it because it's just access to their file. |
|
|
Questionnaire advantages and disadvantages |
Easy to administer but time consuming to develop and they can only address limited topics. |
|
|
Performance tests |
Relevant for jobs that produce a physical product. |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of interviews |
Rich source of info, time consuming and only a limited number of people can be reached. |
|
|
Simulations |
Provide an opportunity for trainees to practice what they've learned where performance can be observed and thus training can be evaluated for effectiveness |
|
|
Ratings/checklists |
Trainees rated on each of the important behaviors they are expected to learn as a result of training. |
|
|
Critical incidents |
Essay descriptions of when a trainee does something really good or really bad. Ex write up |
|
|
Hawthorne effect |
Most employees behave differently when observed. Downside of observations to determine training effectiveness |
|
|
Research design chart- first two are bad |

|
|
|
Essential element in evaluating a training program |
Having a standard for comparing results |
|
|
History in training evaluation |
Refers to the historical events that transpire between the pretest and post test |
|
|
Maturation in training evaluation |
The development and growth that occurs within the trainees independent of the training program |
|
|
Sensitizing the effects of the pretest |
The effects that pretesting might have on the trainee |
|
|
Instrument decay |
Lack of consistency or accuracy in the measuring instrument. |
|
|
Three kinds of instrument decay |
Alpha, beta. Gamma |
|
|
Alpha change |
Occurs when the observed differences between the pretest and post test measures represent true change in the person providing the data as a result of the training |
|
|
Beta change |
Occurs when the instrument being used is recalibrated, such as when the person providing the data adopts a different reference group and evaluates everything more leniently or harshly than before |
|
|
Gamma change |
Occurs when the construct being evaluated is redefined such as a sales training program that redefines the meaning of quality customer service |
|
|
Internal referencing strategy |
Imporves the usefulness of the pre post test comparison design by detecting the presence of competing explanations by using a combination of relevant and irrelevant questions to evaluate how well training increased learning. Only useful for evaluating the criteria of learning. Trainees should be able to answer the relevant questions and the irrelevant questions provide an internal reference for assessing the benefit of the training-if there are changes to the irrelevant questions then changes to relevant questions might be due to a cause other than the training. |
|
|
When is post test only control group design test ideal |
When the training and post test can be administered to employees as a single natural package or where a pretest could be offered. |
|
|
Most highly recommended design for evaluating training programs |
Solomon four group design because it successfully eliminates alternative explanations for why the post test scores of different experimental groups might be considerably higher than their pretest scores |
|
|
Quasi experimental designs |
Experiments that occur in a natural setting where researchers don't have complete control on experimental setting. Recommended to use when other designs aren't feasible such as when you can't randomly choose a design group. Not as conclusive as other designs but can still tell if a training program has a significant impact. |
|
|
What two designs are considered quasi experimental designs |
Time series design and separate sample pretest post test control group |
|
|
Multiple baseline design aka time series design |
Measuring something periodically and introducing an excitement change at some point. Disadvantage is there is no control group so can't tell if change is due to a factor other than training |
|
|
When would you use the separate sample pretest post test control group design |
When you can't randomly test, because employees work in a group setting. |
|
|
Talent management |
All the activities associated with ensuring that a company has a competent workforce that is capable of performing the necessary activities. Recruiting selecting motivating training promoting and retaining people. |
|
|
What's the heart of an effective talent management plan |
Active management succession plan |
|
|
What's the goal of a good talent management program |
To increase workplace productivity by developing improved processes for attracting, c developing, retaining and utilizing people with the required skills and aptitude to meet current and future basic needs |
|
|
Most popular developmental activities for talent management |
Executive education seminars, university courses, job rotations, new assignments, action learning projects and expatriate assignments |
|
|
Socialization |
The process of molding attitudes and behaviors to socially acceptable standards |
|
|
Three most prominent work socialization processes |
New employee orientations, training and development, and performances appraisals |
|
|
Organizational integration |
When an individual's interests and goals are consistent with the mission of the organization |
|
|
Balance in socialization chart |

|
|
|
Rite of passage |
Process of advancing from one stage to another |
|
|
Three phases of rite of passage |
Separation of the person from the former role, initiation into new role, and assimilation into new environment. |
|
|
Two psychological processes that occur between stages of the role transition process |
Anticipatory socialization(adopt new attitudes attributes and self perceptions) and reality shock (difference between new and old work environment) |
|
|
Role transition process chart |

|
|
|
Realistic job previews |
Help reduce shock and exaggerated recruiting. Gives both favorable and unfavorable aspects of job and company |
|
|
Purpose of orientation training |
To disseminate info, to provide direction and new knowledge |
|
|
Effects of a good orientation |
Reduced turnover, alleviates anxiety, creates positive work values, reduces start up costs |
|
|
What info should an orientation contain |
Basic survival knowledge, working hours, break rules, facility locations, special terms used by the group, paydays and method of pay, health and safety considerations, info on who to contact in case of problems, info on parking, info on use of communication devices |
|
|
How are expectations of success created in the minds of trainees |
Kind of info and ideas given to them, output expected from them, type of feedback they receive, encouragement and reinforcement they're given |
|
|
Tips for successful orienting |
Don't introduce to everyone all at once, assign a mentor, reduce anxiety by reassuring, provide written instructions and stretch the training out over a couple days |
|
|
Guidelines for creating an effective training program |
Begin with most relevant information, provide sponsors/mentors, introduce to group gradually, space out the orientation training, provide oral generic info and written detailed information |
|
|
Employee development methods |
Literacy training, competency training, mentoring, attitude change, personality adjustments |
|
|
Purpose of a mentor |
Teach valuable job skills, help develop a network of contacts, provide emotional support. Improves retention rates and salary increases and promotions |
|
|
Downside of mentorship |
Will fail if protégé becomes overly dependent, mentor resists freeing the protégé, or jealousy/romantic relationship occur |
|
|
Attitude change trainings |
Usually lectures, videos, printed material. Ex used to prevent sexual harassment or discrimination, diversity training. Attitude change won't occur just by info alone, other reinforcers must be present. |
|
|
Personality adjustments |
Ex hypnosis. These trainings seek to alter people and their corporations by unleashing energies that purportedly remain unused in most people. Often occurs in unusual places. Often continuous long and intense. Shouldn't require participation in radical trainings. |
|
|
Personal branding |
Managing ones own career. Employees should create their own personal brand. |
|
|
Career |
The sequence of work related experiences individuals acquire during the span of their work lives |
|
|
Career ladders |
Well defined career path that moves systemical from one thing to the next higher. Ex junior partner to senior partner. |
|
|
Career lattice |
Advancing to higher levels in an organization but with occasional lateral moves. |
|
|
Career development |
Helping individuals plan their future careers within the organization. |
|
|
Career plateau |
When the probability of a person moving up the organizational ladder is low. |
|
|
Three kinds of plateaus |
Structural (no where else to move to to), content (person has mastered job and is bored), life (person lacks meaning and purpose in life) |
|
|
Hoarding problem |
When managers won't let good employees move up. Good employee gets frustrated. |
|
|
Employability training |
Making oneself employable in the future with multiple friend in spite of dynamic economic forces and evolving job demands. |
|
|
Three strategies to enhance ones employability |
Managing one's identity(be positive confident), self training and networking, voluntary and marginally paid work. |
|
|
Stages of career development- Erikson's life stages model |
Individuals must pass through eight stages to reach complete maturity: oral, anal, genital, latency, adolescence, young adulthood, adulthood, maturity |
|
|
Last four stages chart |

|
|
|
At what stage does Erikson say people usually fail |
Don't get past six. Go on with a mix of partial successes and failures. |
|
|
Four stages of working career model stages of career development |
Exploration, establishment, maintenance, decline |
|
|
Exploration stage |
Agreed 15-25. Completing school, solidifying career choices and seeking employment. Main concern is finding and securing a job. |
|
|
Establishment stage |
Ages 25-44. Strive to create permanent position in company. Success is greatly influenced by the work assignment, can be greatly helped by competent supervisor. |
|
|
Maintenance stage |
Ages 45-64. Try to protect themselves and secure their positions in the organizations. Have to take another look at goals, mid life crisis time. |
|
|
Decline stage |
Ages 65+. Aporoach retirement. |
|
|
Stages of development- professional careers model's four stages |
Apprenticeship(new employees dependent on mentor and following directions), independent contributor(gain independence success depends on innovation), mentor(train and direct others), sponsor(involved in strategic decision making success determined by making wise decisions) |
|
|
Career pathing |
Identifying a sequence of jobs through which individuals can expect to progress toward higher levels of management |
|
|
Dual career ladders |
Usually found in technical fields. Becoming manager but still doing technical work. |
|
|
Mommy track/daddy track |
Flexibility needed due to family. Trade career growth and compensation for freedom from working long hours and weekends. |
|
|
Management development program |
Succession planning. Must ID high potential replacements, analyze that person's developmental needs, provide relevant learning opportunities. |
|
|
First step to creating effective management development plan |
Assessing career interests and promotion potential of current leaders. Survey or send to assessment center or performance reviews then give them special activities or assignments to develop them. |
|
|
Potential for promotion grid |

|
|
|
Hierarchy of managerial skills |
Technical and professional skills, interpersonal skills, conceptual and administrative skills. All managerial positions require different skills though. |
|
|
Hierarchy of management skills chart |

|
|
|
Double loop learning aka model II strategies |
Developed by Chris Argyris. Trains mangers to change their assumptions about behavior by making them aware of the difference between what they actually do versus what they think they do. Encourage openness of communicating and feedback. |
|
|
Model I strategies aka single loop learning |
By Argyris. 95% of managers Strive to attain four primary values: achieve their defined purposes, win, stores negative feelings, maximize rationality and minimize emotionality. Have to have control over these which makes them defensive and thus ineffective. |
|
|
Expatriate training |
Problems with adjustments, cross cultural training and culture shock |
|
|
Important issues for expatriates managers chart |

|
|
|
Culturegram |
Contains info about the country. Presented in a culture assimilator. |
|
|
Culture assimilator |
Presents information in a programmed learning format or video |
|
|
Effective cross cultural training is based on |
Social cognitive theory. Learner must attend to the new info, remember it, visualize how they can demonstrate it, learn vicariously from the experience of others, and receive reinforcement for behaving right. |
|
|
Three phases of culture shock |
Feeling of excitement and curiosity, disillusionment when they discover comforts of home are gone, adjustment. |
|
|
OSHA mandated training |
Training in hazardous materials, blood borne pathogens, safety. |
|
|
Is sexual harassment and discrimination training mandatory |
No but you should give it because it shows a good faith effort to prevent harassment and discrimination |
|
|
Significant issues associated with demonstrating effective training for harassment and discrimination |
Did they provide formal training, was the training endorsed and supported by top management, was training thorough, did all employees get training, did supervisors get training on how to respond to a complaint, was training repeated, were supplemental materials given to staff to review later. |
|
|
Under socialization |
Behavior violates social norms or they rebel against the organization |
|
|
Over socialization |
Behavior is exceedingly rigid and confirming, they lose creativity |
|
|
Performance management |
The process if improving job performance through performance planning, performance evaluations, mentoring and continuous feedback. |
|
|
2012 American national standards instititute |
Approved set of guidelines on how performance management should be administered. |
|
|
Three processes of effective performance management |
Goal setting, performance reviews, performance improvement plans |
|
|
Elements of effective goal setting |
Both managers and individuals participate in the development of goals, document the goals, be specific, be measurable, challenging but attainable, reasonable, identified time frame for completion, flexible, monitored with progress shown, flows from top down and is aligned with org's mission |
|
|
Performance reviews |
Suggested that a numerical or descriptive rating scale is used with 4 recommended processes: feedback should be continuous and timely, performance discussion should give specific feedback measured against preestablished goals, review acknowledged by emp and manager, face to face conversation at least once yearly |
|
|
Performance improvement plans |
Individual performance improvement plan documents deficiencies and outlines what they need to do to improve. Should include what the job should be, the job the person is doing, explanation of discrepancy, plan of action with dates for completion, signed by emp and manager with periodic review dates after initial meeting |
|
|
Five important org functions served by performance evals |
They guide hr decisions such as promotions, reward and motivate employees, promote personal development, identify training needs, and integrate hr functions such as forming hris system. |
|
|
Performance criteria |
What the employee is evaluated on. Can use competency models, dimensions of performance, production data, personnel data and judgements of others |
|
|
Dimensions of performance |
Scales that are summed to form a composite evaluation for each employee. Can simplify promotion decisions but can actually distort the eval if some areas are actually more important than others. |
|
|
Three basic types of behavior that should be included in performance appraisals |
Attracting and holding people in the org (absenteeism tardiness length of service), dependable task accomplishment (minimal levels of quantity and quality), organizational citizenship behaviors (spontaneous and innovative behavior) |
|
|
Types of spontaneous and innovative behavior |
Cooperation, protective acts against hazards/threats, constructive ideas, self training, favorable attitudes |
|
|
Three major categories of performance measurement data |
Production data, personnel data, and judgement of others |
|
|
Production data |
Evaluates the degree of dependable task accomplishment by measuring quantity and quality of performance. Ex units per hour. Best source of data because directly observable, but shouldn't be the only data used. |
|
|
Examples of indirect production data |
Ex training can't be directly observed so you would use these factors instead: number of training programs conducted, total number of participants, improvements in the participants test scores, ratings by participants of how well they enjoyed the training, increases in profitability of departments, amount of grievances absences and tardiness in trained programs vs untrained programs. Gather this info then compare against historical data since many factors can contribute to the above in addition to the training. |
|
|
Criterion (criteria) problems |
Deficiency, contamination, biases |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of evaluating outcomes |
Advantage: attention is focused on producing specific results. Disadvantage: outcomes can be achieved by unethical means and can burn out employees thus increasing turnover |
|
|
If evaluations are used for compensating employees they should focus on |
Outcomes |
|
|
If performance evaluations are used for personal development they should focus on |
Behaviors |
|
|
Possible contaminates of performance evals |
Economic conditions, material shortages, poor equipment |
|
|
Inter rater reliability |
The extent to which different evaluators produce consistent evaluations. |
|
|
The following are necessary for an evaluator toakr a good performance evaluation. |
Must know job responsibilities of subordinates, must have accurate info re performance, must have a standard by which to judge the adequacy of the perf, must be able to communicate the evals to the subordinates and explain the basis on which they were made. |
|
|
Calibration |
The process of overcoming leniency/strictness biases |
|
|
Two best methods for helping managers gain perf feedback skills |
Role playing and behavior modeling |
|
|
Some major criticisms of performance evaluations |
Individual threat (reduces self esteem), threat to supervisors (don't like to give evals), defining performance (hard to do), halo/horn effect (rate too high or too harshly based on one characteristic of the emp), leniency-strictness effect (a manager who gives all emps good or bad evals across the board), central tendency effect (gives everyone avg ratings), inter rater reliability, sequencing effect(an eval being influenced by the one before it), zero sum problem (above avg ratings equal below), numbers fetish(gives everything a number even when something can't really be given a number), recency effect(recent events effect eval), biased subjective evals (eval is based solely on opinion of the supervisor so emps similar to sup get better ratings) |
|
|
Classification procedures |
Categorize individuals into one of several categories (high vs low, outstanding fair poor etc). Easy to produce but unreliable and biased unless costly monitored and carefully developed. Hard to define categories so rating tends to be inflated. Give guidelines of how a particular distribution of evaluations should look. |
|
|
Classification procedure example chart |

|
|
|
Forced distribution |
Placing quotas on the number of individuals who can be put in each category |
|
|
Card stacking method |
Each employees name is written on a separate card. Evaluator chooses 30% for top. 30% for bottom and 40% for middle. Then 1/3 of high and low groups are selected address vet best and poorest. |
|
|
Ranking procedure objective |
To order a group of employees from highest to lowest along some dimension, usually overall performance |
|
|
Three different methods for rank ordering a group of employees |
Straight, alternate, paired |
|
|
Straight ranking |
Ranking the best, then second best, then third etc etc |
|
|
Alternate ranking |
The evaluator is given the list of individuals to be ranked and is asked to alternate identifying the best and the worst, then remove those two, then repeat until all employees are sorted |
|
|
Paired comparison ranking |
Asking an evaluator to consider only two individuals at one time andnto decide which of the two is better. Get paired with everyone and the best emp is determined by how many times they're chosen as better than their pair. |
|
|
Paired comparison chart |

|
|
|
Paired comparison equation |
N(N-1)/2 where N isnthe total number of employees in the group |
|
|
Intransitive relationships |
A is better than b, b is better than c, c is better than a. Means either all 3 individuals are essentially equal or the evaluator made a mistake |
|
|
Graphic rating scales |
Evaluate performance related characteristics and personality characteristics by selecting characteristics and scaling the characteristics |
|
|
Graphic rating scale chart |
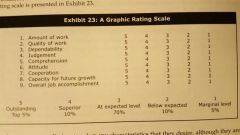
|
|
|
Examples of characteristics used in evaluating |
Hourly workers- quantity, quality cooperativeness, knowledge, dependability, initiative, creativity, performance. Managers-leadership, communication, decision making, planning delegation consideration initiative leadership mental ability knowledge. |
|
|
How to choose the characteristics |
Choose what relates to the organizational effectiveness. Omit difficult to change things such as intelligence and personality characteristics. |
|
|
Rated ranking |
Combines ranking and rating by ranking the employees first (usually by alternate ranking) and then rate on selected scales |
|
|
Examples of rating scales for evaluated job knowledge chart |
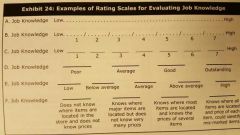
|
|
|
Scaling the characteristics |
Use a continuous scale (evaluator can choose any point between two points) or discrete scale(must choose one of a specified number of categories). Optimal number of choices for both is 7. |
|
|
Civil service reform act of 1978 emphasizes the importance of using |
Behavioral descriptions that accurately assess the performance of employees. |
|
|
Advantages of graphic rating scales |
Easybto understand, simple to develop and convenient to use. Permit a ready comparison of scores that reveal merit of every employee. |
|
|
Disadvantages of rating scales |
Can have poorly chosen characteristics, can be incorrectly scaled, total score can be incorrectly combined |
|
|
Forced choice |
A number of statements arranged in pairs. For each pair the evaluator must check the one statement that is most descriptive of the performance of the employee, or if it's a negative statement choose the one least like the employee. Weighting of the choices kept secret from the evaluator so they can't choose the end rating. Hr does the scoring. |
|
|
Advantage of forced choice |
Less bias and greater objectivity |
|
|
Disadvantage of forced choice |
Takes a lot of time and skill to develop and are difficult to discuss with the subordinates since the manager doesn't know how it's scored |
|
|
Forced choice evaluation sample chart |

|
|
|
Weighted checklist |
A list of behaviors that evaluators use to describe the performance of employees. Created by gathering statements of emp performance from critical incident descriptions. A group of judges then evaluates each statement from 0-10 based on contribution to organizational effectiveness. If they can't agree that statement is eliminated. Evaluator doesn't know the weighting and is asked to choose which statements best describe and employees behavior. |
|
|
Advantages of weighted checklist |
Less biased because weighting is unknown to evaluator and good because the statements refer to observable behaviors |
|
|
Disadvantage of weighted checklist |
Lots of time and effort to develop and complete. Jobs have to be stable and have several employees performing each job or the weighted checklist is useless. |
|
|
Narrative appraisal method of evaluating advantage and disadvantage |
Very useful for personal development but essays can't be easily compared so not good for hr comparisons |
|
|
Critical incidents |
Descriptions by qualified observers of behavior that are especially effective or ineffective. One of the best techniques for identifying the most important aspects of a job. |
|
|
How to gather critical incidents |
Have managers write a short summary at thenend of week to describe very favorable or unfavorable things the subordinates have done. |
|
|
How to use critical incidents |
Identify what categories of behavior are related to effective performance and then give each evaluator a list of the general categories to use in evaluating performance along with sample behaviors that describe each category. The evaluator then records in a free form essay any incidents that occur that match a category. |
|
|
Behaviorally based appraisal methods |
Management by objectives, behavioral anchored rating scales, behavioral expectation scales, behavioral observation scales |
|
|
Management by objectives |
A philosophy of management that espouses a positive proactive way ofanaging rather than reactive. Focuses on predicting and shaping the future through long range objectives and plans, accomplishing results, improving individual competence and organizational effectiveness, and increasing participations and involvement of employee's in the affairs of the organization. |
|
|
Series of management functions of MBO |
Development of clear organizational objectives, formulation of coordinated individual objectives to acheive overall objective, systematic measurement and review of performance, taking corrective action when needed. |
|
|
Peter drucker's MBO |
Each manager has clear objectives that support the objectives of higher management, all managers participate in goal setting and then exercise self control over their own performance, their performance is measured and compared with objectives. |
|
|
Three phases of MBO |
Evaluating performance against measurable objectives (hr clarifies responsibilities and focuses and achieving results), programs are integrated into the org's planning and control process- now managers get involved and training of subordinates begins, MBO system is fully implemented- all major organizational functions and management processes are integrated logically and consisitently (ex perf evals, strategic plans, staffing, compensation, training) emphasis on teamwork being flexible to acheive goals frequent perf reviews and individual growth |
|
|
Four principles of MBO |
Goal setting , delegation, feedback reviews, evaluations |
|
|
MBO- goal setting |
Central mission and long range plans formed, then cascading process (lower depts and individual goals formed based off main org goals) |
|
|
MBO- delegation |
Focuses on delegating results not activities to increase personal responsibility. When delegating, results should be specified in detail. |
|
|
MBO- feedback reviews |
Should be done periodically and prescheduled. Self review should be encouraged. Written feedback should be provided. |
|
|
MBO- evaluations |
Done when a project is completed or periodically. Focus on problem solving and growth. Then give new project and establish new results. |
|
|
Advantages of MBO |
Produces job positive attitudes, positive changes in performance and behavior, employees more likely took take action |
|
|
Performance contracts |
Employees identify measurable objectives which are then appended by supervisor. Increases motivation by rewarding behavior such as getting a raise. |
|
|
Employee performance Management system |
Computer software that monitors employee performance. Record personal goals and objectives, performance, suggest raises etc |
|
|
Behaviorally anchored rating scales |
Similar to graphic rating scales except that the scales are described more accurately by specific behaviors. Developed usual critical incidents. |
|
|
Example of behaviorally anchored rating scale chart |

|
|
|
Advantage of bars |
Less biased, characteristics more carefully selected, inspire agreement among evaluators since they evaluate observable behavior. More reliable less ambiguous and less biased than graphic rating scales. |
|
|
Disadvantage of bars |
Takes a lot of effort to develop, focuses only in behavior soanagers should have a separate eval for results oriented appraisal |
|
|
Behavioral expectation scales |
Similar to BARS except anchors are described in term of behavior the employees would be expected to do. Raters just check the behavior that employee could be expected to do. The expectation is based on what the emp has done over a period of time. Good at identifying training needs. |
|
|
Behavioral observation scales |
Similar to BARS. Asks the rater only to describe the frequency of the behavior rather than to evaluate the quality of the performance. Scores obtained by assigning numerical value to frequency judgements and possibly weighting some behaviors greater than others. Scored are then summed and translated to an overall score. |
|
|
Behavior observation scales chart |

|
|
|
Beh obs scale advantage |
Good personal feedback for emps, contributes to improved productivity through individual goal setting- goal clarity acceptance and commitment. |
|
|
Different types of appraisers |
Supervisor, peer, client, self, team subordinate, 360 |
|
|
Peer appraisal research |
Shown to be predictive of success and correlated with both objective and subjective ratings of success. Popular for professional and technical jobs. Increases interaction and coordination of peers |
|
|
Conditions required for good peer analysis |
High level of trust, noncompetitive reward system, opportunities for peers to observe each other's performances |
|
|
Arguments in favor of self evals |
More satisfying and constructive eval process, less defensiveness, improved job performance through greater commitment to organizational goals. |
|
|
Arguments against self evals |
Employee and supervisor don't typically agree. Biased. Not good for promotions or raises. |
|
|
The two evals used in team appraisals |
One measures hope well each member contributes through peer evals the second measures how well the team accomplished it's goals |
|
|
Three good reasons for using subordinate evals |
Provides unique info, creates incentive to change, reduces power differential which increases flow of communication |
|
|
Limitations of subordinate evals |
Based only on interactions with them, not the organizational effectiveness |
|
|
360 degree appraisals |
Contain evals from many different sources that are then combined by by hr and given to the evaluated person along with suggestions for improvement. Lots of issues with these types of evals. |
|
|
Simple guidelines to enhance evaluation effectiveness |
Develop your own style so you're comfortable, both parties should prep, evaluator should clarify the reason for the review (yearly, disciplinary etc) and possible consequences of the review |
|
|
Sandwich interview |
Bad news sandwiched in between good. Actually a negative experience. |
|
|
What should you use instead of sandwich interview |
Problems and praise- identify all problems up front and then discuss problems individually, talk about future improvements, then express appreciation for good behaviors. Allow the employee time to talk. |
|
|
What happens when you tell someone they're average |
Significant drop in organizational commitment. |
|
|
Two separate appraisals approach |
Providing an eval for contributions and an eval for personal development. Should conduct at separate times. |
|
|
Contributions appraisal |
Focus is on past performance with objective of improving future performance through effective reward contingencies. What they have contributed to the company and usually determines pay increase. |
|
|
Personal development appraisal |
Supportive eval. Focus on improving future performance through self learning and growth with the evaluator offering guidance and counsel along with feedback. Usually determines advancement and promotion. |
|
|
Employment decisions that should be linked to performance appraisals |
Pay increases, incentive compensation, personal development and training, disciplinary action and performance improvement, promotion and replacement planning |
|
|
Two most important factors when making promotion decisions |
Seniority and merit |
|
|
Real promotion vs quasi promotion |
Real is change in title and duties, quasi is just title change |
|
|
What factors are most often used to determine a promotion |
Not performance evals. Usually informal evals and personal knowledge along with broad experience and visibility |
|
|
Advantage of informal eval system |
Takes less time |
|
|
Advantage of a formal eval system |
Less biased, more defensible, more open to inspection |
|
|
Should you give a good rating to someone doing poorly |
No can be used against you in a wrongful termination suit. |
|
|
Five criteria a defensible system should satisfy |
Identify objective and job related criteria(assess against important job related aspects), document performance events especially those that will lead to disciplinary action, communicate performance standards, use reasonable care (give honest eval but don't be viscous), train evaluators and provide clear guidelines for writing evals |
|
|
Change agent |
Someone who acts as a catalyst for change in an org |
|
|
Some reasons change fails |
Wasnt tied to org strategy, was seen as fad or quick fix, involved ridiculous and unattainable expectations, inadequate leadership, lack of measurable goals asked timetable, fear of the unknown, lack of commitment |
|
|
7 factors crucial to success of change effort |
Having a change sponsor (someone responsible), creating a shared need(why it's important), shared vision, mobilizing commitment (involving others), changing rusted and structures (integrating into org's structure), monitoring progress and measuring success, making change last through short term and long term planning |
|
|
Common mistake when initiating change |
Assuming an org can beer changed by changing each individual. Can't change everyone. |
|
|
Forces of change chart |

|
|
|
Three kinds of organizational change |
Developmental, transitional, transformational |
|
|
3 kinds of org change chart |

|
|
|
Developmental change |
A gradual improvement in skills methods or processes to help an org function more efficiently. Fine tuning and improving what's already happening. Usually a training program. |
|
|
Transformational change |
Most dramatic kind of change. A radical reconceptualization of the organisation's mission, culture, products, leadership or structure. Usually done by a stagnant or threatened company experiencing paradigm change (new pattern or view, forces need to change out you'll become obsolete). Described as punctuated equilibrium-alternation between long periods of small changes then revolutionary upheaval. |
|
|
Transitional change |
Having an org slowly evolve from an old state to a new state. Includes defined transition steps. |
|
|
7 most common targets of change |
Individual personality(especially key admins), dyad(relationship between two people), group, work teams aka family groups, the entire org and its divisions (getting all departments to work together), org structure, org strategy |
|
|
Theory of change- Kurt Lewin's force field analysis |
Change occurs when the forces pushing in one direction are greater than the forces pushing in the opposite direction. Planned change occurred in three stages: unfreezing(see a need for change), change and refreezing(stabilizes the change and solidifies new patterns of behavior through reinforcement). Managers create planned change by adjusting the restraining and driving forces. |
|
|
Kurt Lewin's force field analysis chart |

|
|
|
Theory of change- creating lasting change: Dalton change model |
Likelihood change will last more than 6 months is slim. Dalton says charge won't occur unless there's sufficient pain and tension to motivate it and needs to be supported by credible source. Then four sub processes occur to help facilitate change: change generalized goals to specific objectives, transition from former social ties to new relationships (suggested you find a whole new peer group), change self doubt to heightened self esteem, charge external motive for change to internal motive for change (create new belief system). Four theories why change occurs: education, reinforcement, peer group influences, inspiration of ones own example. |
|
|
Rational empirical change |
People are rational and will follow their self interest once this is identified for them. Happens with education and communication. |
|
|
Methods for overcoming resistance to change chart part one |

|
|
|
Methods for overcoming resistance to change chart part two |

|
|
|
Power coercive change strategy |
Involves the application of power in which people with less power are forced to comply with the plans, directions, and leadership of those with great power. Ex reinforcement and coercion |
|
|
Normative re educative change strategy |
Based on the assumption that change occurs as people learn new normative orientations that result in new attitudes values and interpersonal relationships. Ex peer group influence aka peer pressure |
|
|
Four reasons group discussions are so effective in changing attitudes |
People contemplating change are reinforced by others making the change, discussion forces a decision point, members are forced to make public commitment to the change, the decision making process itself helps the person accept the change |
|
|
Advanced change theory |
Relies on the inspiration of a change agent who creates change in others by modeling the appropriate kind of behavior. Emphasizes need for change agent, people charges by the attraction and inspiration. Ex inspiration of one's personal example aka it worked for me so it will work for you |
|
|
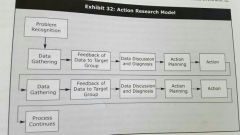
Action research model |
Basic approach most of most org change activities. Six basic steps: data gathering, give data feedback to target group, discussion and diagnosis of data, action planning, action, and recycling. |
|
|
Action research model chart |
|
|
|
Four methods of data gathering |
Interviews, observation, questionnaire surveys, and archival data |
|
|
Target of change |
Those involved in the problem. Can be an individual, group, or the total org. |
|
|
To reduce likelihood of misdiagnosing problem groups should |
Consider alternative causes of the problem if there are any |
|
|
Recycling stage |
Keep going through change prices and fine tuning or correcting what didn't work |
|
|
Learning organization |
An org skilled at creating, acquiring, and transferring knowledge and at modifying it's behavior to reflect new knowledge and insights. |
|
|
What five building blocks contribute to a learning organization |
Systematic problem solving, experimentation, learning from past experience, learning from others, transferring knowledge. |
|
|
Benchmarking is used to identify |
Best industry practices |
|
|
Four stages of an org |
Entrepreneurial stage(need for creativity), collectivity or growth stage (need for leadership, delegating and giving clear direction), formalization or maturity (est of formal procedures, delegation and control), and elaboration stage (control inefficiencies, reducing bureaucratic procedures) |
|
|
Five stages of revitalizing mature organizations |
Restructuring(downsizing or delayering the org), bureaucracy bashing(removing with that doesn't add value to customers), employee empowerment(let emp ID better work procedures and implement them), continuous improvement, cultural change |
|
|
Two problems that limit effectiveness if org development interventions |
Transfer of training and intervention diffusion |
|
|
The following increases transfer of training |
The new skills/attitudes/beh are supported and modeled by others, new learning is percieved as being useful in their work, participants are allowed to practice their new behaviors in the training, and new behaviors are evaluated and rewarded on the job. |
|
|
Diffusion of org development |
The extent to which the initial change spreads throughout the org and produces complementary changes in other individuals or programs. |
|
|
Factors that contribute to the problems of diffusing org development interventions |
Lacks support of top management, other depts are OK with status quo or don't feel pain that would motivate them to change, reward system doesn't recognize or reinforce the change, structural and technological changes aren't made, other problems perceived as more pressing |
|
|
Major barriers to change success |
Employee resistance and change in management, employees distracted by day to day, actions of people don't change |
|
|
Org development intervention |
A set of structured but adaptable activities designed to improve some aspect of org functioning |
|
|
4 targets of org development interventions |
Interpersonal relationships, group processes, intergroup processes, total org |
|
|
Interpersonal interventions |
Aimed at individual learning and skill building. Designed to improve effectiveness of individuals and to contribute to personal growth |
|
|
Types of interpersonal trainings |
Coaching and counseling(ID problem and suggest new beh), sensitivity training aka T-groups(unstructured group discussion on the here and now, talk about feelings, either improves interpersonal skills or destroys self confidence, instrumented t group involves questionnaire), process consultation (consultant helps org understand and alter it's processes/interactions, teaches the client how to diagnose group activities and interpersonal relationships) |
|
|
Characteristics of an effective work group |
Norm of cooperation and teamwork, open communication, no defensiveness, task relevant discussions, listening, decisions based on group consensus, conflict and disagreement based on ideas and method not personality, help each other satisfy personal needs whole working together to achieve work goals |
|
|
Four most popular group interventions |
Team building method, group diagnostic meeting, role analysis technique (RAT), responsibility charting |
|
|
Group diagnostic meetings |
Supervisor and their subordinates, ID problems and prioritize. Open discussion of problems and sharing of feelings. Can divide into smaller groups if too large or hostile. Have a separate session to come up with solutions to problems. |
|
|
Team building meetings |
Meant to build better functioning team through goal accomplishment, improved group processes (communication, decision making, interactions, problem solving). Usually help away from the workplace for an extended period of time. ID problems and come up with solutions and action steps assigned to specific individuals. Shouldn't be dominated by one leader. |
|
|
Role analysis technique RAT |
Org role= task assignment and responsibilities of a particular job and relationships with other jobs. RAT designed to reduce uncertainty surrounding an employees task assignments and responsibilities. Typical for manager positions. Defines requirements of focal role (role being examined). Intervention has two steps: person in role defines essential functions then clarifies expectations the focal role has of others. Continue this process for each separate role. |
|
|
Responsibility charting |
Clarifies who is responsible for which decisions and actions. First construct matrix of decisions and actions then divvy out by using RA-VSI (responsibility to initiate action, limited approve or veto, provide supporting resources, inform about decision). |
|
|
Responsibility chart example chart |
|
|
|
Innovative work teams |
Engines of innovating and creativity that generate future products and services. Must encourage an environment that fosters creativity. |
|
|
Five core values work teams and individuals require for innovating to occur |
Curiosity and ability to question status quo, risk taking and willingness to learn from failure, openness and willing to share info, patience tenacity and willingness to give ideas a chance, trust and sense of security and knowing some ideas will fail. |
|
|
Intergroup interventions |
Finding a common outside enemy, joint activities, rotating membership(swapping group members), conflict resolution meetings (bringing leaders of both groups together to gain commitment, the two groups meet alone and generate lists about their feelings about the other group and what they think that group is saying about them, then groups come together and share lists, discussion limited to questions for clarification no justifications allowed, finally groups move toward problem solving) |
|
|
Ex of substantive issues that cause group conflict |
Disagreements over policy and procedure, competition over scarce resources, differing expectations about role relationships |
|
|
If conflict exists over substantive issues, meeting should include |
Problem solving and negotiation |
|
|
If conflict exists over emotional issues |
Meeting should focus on restructuring attitudes and discussing negative feelings |
|
|
Two most common company wide interventions aka comprehensive interventions |
Survey feedback and structural interventions |
|
|
Two major activities of survey feedback |
Administering the attitude survey and then reporting the info back to the emps to facilitate problem solving. Everyone participates in both parts. Success depends on commitment of members to share and participate, support of top management and creation of open environment, questionnaire must address key issues and accurately assess emp feelings |
|
|
Knowledge management programs |
Help members of a company share relevant info among each other and from external resources on an ongoing basis. |
|
|
Strategies used to facilitate sharing of knowledge |
Memos, seminars, luncheons, bulletins, email, phone, chat boards, web based info centers, imbedding knowledge into the work flow of the job(ex articles from online store in an accessible system) |
|
|
Structural change |
Easiest and fastest way to charge an org. Ex moving job to another Dept, reducing supervisors span of control, dividing Dept, transferring Dept to another division, creating new Dept to take over a function, reorganizing entire org |
|
|
Quality and performance management aka total quality management TQM |
Reduce errors to zero and improvev quality of service. Made by W Edward Demings 14 PT philosophy (starts with commitment by top management) and Philip Cosby zero defects approach to prevention through statistical process control. Most are customer focused, invoice strategic planning, continuous improvement and empowerment |
|
|
TQM characterized by what 3 goals |
Doing things right the first time, striving for continuous improvement, and being responsive to interests of customer |
|
|
Continuous improvement |
Working with suppliers to improve quality of incoming parts and ensuring that manufacturing processes are capable of consistently high quality. |
|
|
Statistical process control |
Popular TQM TECHNIQUE. Involves carefully measuring the production process and using the data to identify problems and to monitor quality improvement. |
|
|
Major steps in implementing a TQM intervention |
Defining major functions and services to be performed, determine customers and suppliers, ID customer requirements and develop measures to assess satisfaction, ID requirements and criteria for suppliers to meet, map or flow chart the processes to occur in each Dept and between depts, continuously improve |
|
|
Benchmarking |
Studying the productivity and practices of industry leaders and using them as a performance standard. |
|
|
Induction |
Process of teaching what is right and why |
|
|
Obsolescence |
Reduction in ability or effectiveness caused by lack of knowledge or skill due to difference forgetfulness or creation of new knowledge and tech |

