![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is human resource management? |
It refers to the activities an organisation carries out to use its human resources effectively |
|
|
Goals of human ressource management |
Provide hr necessary for achieving organisational goals: Right.. Quantity Quality Time Place --> economic goals --> social goals |
|
|
Major activities of HRM |
Recruiting job candidates Selecting j c Orienting and training new employees Training and Development Appraise Performance Provide monetary and non monetary incentives Discharge (entlassen) personnel Planning manpower needs |
|
|
Who is responsible? |
- Executive board: control budget, set goals, guidelines - Line Managers: eg sales manager, request for staff, promotions, appraisal - Staff managers: support line managers, eg controlling,legal,hr - Employees |
|
|
Current trends in HRM |
-Globalisation -demographic trends (skills shortage) -socio cultural trends (generation y) -change in nature of workforce -technological trends (e-hrm) -strategic role of hrm -human capital and added value of hrm -corporate social responsibility |
|
|
International Human Resource Management |
IHRM is the study and application of all hrm activities as they impact the process of managing hr in enterprises in the global environment |
|
|
Different settings of ihrm |
Headquarters of mne Subsidiaries of foreign owned firms Domestic firms |
|
|
Headquarters of mne |
-Develop and oversee ihrm practices in all foreign operations -Administer movement of employees between headquarters and foreign locations -International assignments -Strategic partner in global planning |
|
|
Subsidiaries of foreign owned firms |
- implement hr policies and practices coming from the foreign headquarter - integrate local culture and organisational culture |
|
|
Domestic firms |
-hiring employees coming from another country -recruiting talent “overseas“ - going global, eg with a small office |
|
|
Types of international employees |
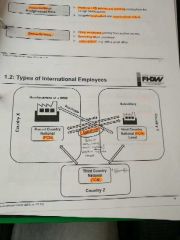
Parent country national (pcn) Host country national (hcn)/ local Third country national (tcn) |
|
|
Parent country national (pcn) |
-Citizen of country of the headquarter of a mne - if transferred to foreign subsidiary for > 1year --> expatriate - if transferred back to HQ --> repatriate |
|
|
Host Country National (HCN) / local |
-citizen of the country of a foreign subsidiary hired to work in a subsidiary in their home country (locals) - if transferred to HQ --> inpatriate |
|
|
Third country national (tcn) |
Citizens of a country other than the parent country or the country of a subsidiary |
|
|
Expatriate Management |
-selcecting expatriates for international assignments - orienting and training expatriates on i.a. - administer the comps and bens packages - appraise performance - repatriation |
|
|
Difference between hrm and ihrm |
Ihrm is more complex and demanding due to: - more hr functions and activities - broader expertise and perspective - more involvement in people's life - dealing with and managing a much wider mix of employees - more external factors and influences - greater Level of risk with greater exposure to problems and difficulties |
|
|
Dilemma of ihrm strategy formulation |
- Pressure for centralisation: most of authority and decising making is at the HQ --> standardisation/integration - need for decentralisation: dispersion of authority and decision making to operating units --> differentiation
But: a complete standardisation is impossible for HR (legal etc.) |
|
|
Mne ihrm strategies |

-receptive = standardise ( high integration, low local responsiveness) -autonomous = let subsidiaries decide (low integration, high local responsiveness) -active = balance control and freedom (high integration, high local responsiveness) |
|
|
HQ international orientation |
=mindset Degree of domination the HQ has over the subsidiary management and hr practice, compared to degree of localisation of subsidiary practices -Ethnocentrism -Polycentrism/Regiocentrism -Geocentrism |
|
|
Ethnocentrism |
-home country standards used as reference in international activities - centralised decision making and high control over operations |
|
|
Polycentrism/regiocentrism |
-Host country standards increasingly used as reference in international activities - more de-centralised and autonomous operations in wholly owned subsidiaries |
|
|
Geocentrism |
Ihrm practices being more eclectic, borrowing best practivces from around the world |
|
|
Staffing policy |
-ethnocentric: all key management positions are filled with parent country nationals -polycentric: all kmp are filled with host-country nationals -Geocentric: kmp are filled with managers regardless their nationality |
|
|
Pros of Ethnocentric staffing policy |
-transfer and control of company strategy -maintain unified corporate culture -transfer of core competencies -suitable managers not available locally (????? Ist das nicht ein contra?) |
|
|
Cons of ethnocentric staffing policy |
-lack of local familitary/contacts -little development opportunities for hcn -pcn/ family adaption problems -high costs |
|
|
Pros of polycentric staffing policy |
- familiarity with culture, procedures, language, politics etc - firm acts local, develops hcn - likely to be less costly |
|
|
Cons of polycentric staffing policy |
-lack of integration between corporate HQs and foreign subsidiaries -less firm-wide integration - possible conflict of interest |
|
|
Pros of geocentric staffing policy |
- company makes best use of its human resources - ability to build up a cadre of international managers being able to work in differenr cultures |
|
|
Cons of geocentric staffing policy |
- national immigration laws may limit implementation - expensive to implement |

