![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CSF
Ventricles |
Made by choroid plexus
Openings of middle of brain.. |
|
|
Arachnoid villi
|
site where CSF
gets RE-absorbed into blood drains back to systemic circulation |
|
|
Blood Brain Barrier
|
- a selectively permeable barrier
created by astrocyte glia cells - induces endothelial cells to form tight junctions (paracrine) less fenestrations -Brain metabolism |
|
|
Spinal Cord –
Gray matter- White matter- |
-consist of sensory and motor nuclei
-myelination |
|
|
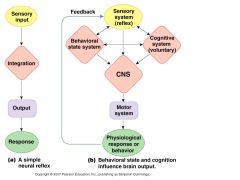
General CNS organization
Sensory input Cognitive system behavioral state |
|
|
|
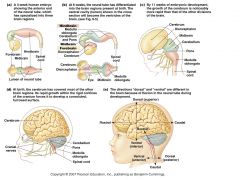
Development of CNS
|
|
|
|
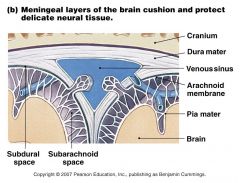
3 Meningial Layers
Dura matter Arachnoid membrane Pia mater |
|
|
|
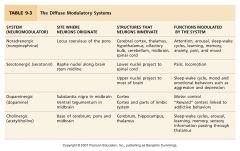
Neuromodulators:
1.Noradrenergic 2.serotonergic 3.dopaminergic 4.cholinergic |
|
|
|
gray matter
|
OUTSIDE part of cerebral crtx
cluster of neurons in the middle. |
|
|
white matter
|
Basal Ganglion
cluster of neurons between the cerebral crtx and the thalamus. responsible for motion. |
|
|
Hippocampus
|
Big center of leanring,
lots of connections in here for remembering things. Memories - based on emotions. |
|
|
Integration.
|
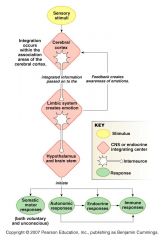
|
|
|
Hippocampus
|
Famous inverted C.
Learning and memory |
|
|
Amygdala
|
Involved in emotion and memory
|
|
|
Cingulate gyrus
|
role in emotion.
|
|
|
Left vs right dominance.
plasticity |
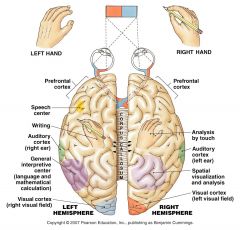
Ability to change and adapt from left side of brain to specific functions of the right, and vice versa.
|
|
|
2 forms of Long term memory
Implicit Explicit |
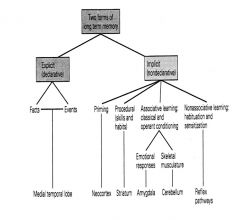
–(non declarative) – once the skill is learned, you don’t have to think about it anymore, its all automatic (driving). Cerebellum (ALWAYS) involved in movements.
facts and events. Medial temporal lobe. |
|
|
Reflexive
|
Implicit
doesnt require conscious attention motors skills, procedures |
|
|
Declarative
|
Explicit
recall requires conscious attention higher level thinking - inference, comparison, evaluation, memories can be reported verbally |
|
|
Hippocampus
|
Long term potentiation
|
|
|
Frontal lobe-
|
Cognition
|
|
|
Premotor
|
developing what programs you want to use to move, or what you want to modify.
|
|
|
Primary motor cortex
|
sends info down spine to like the fingers.
|
|
|
Premotor
|
developing what programs you want to use to move, or what you want to modify.
|
|
|
Frontal lobe-
|
Cognition
|
|
|
sensory
|
all sensory input ends up on cortex.
|
|
|
Occipital input –
|
map neurons, and specific neurons is fired for specific visual stimuli.
|
|
|
The musculoskeletal system
|
the muscle spindle, golgi organs, those are sensory organelles. They also use them to control muscle movements.
|
|
|
Gray
white |
nerve cells,
myelinated axons |

