![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the six nutrients
|
inorganic:
water minerals organic: vitamins lipids carbohydrates protein |
|
|
Provide kcalories
Carbohydrate = Protein = Fat = |
Carbohydrate = 4 kcal/g
Protein = 4 kcal/g Fat = 9 kcal/g |
|
|
Minerals
-energy? -how many? |
Do not yield energy
Sixteen essential minerals Indestructible |
|
|
Estimated Average Requirements (EAR)
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) |
Estimated Average Requirements (EAR)
Average amount: sufficient for half of population Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) Recommendations to meet needs of most healthy people About 98% of population |
|
|
Basal metabolism how much of daily calories needed for baseline aliveness?
|
– 2/3 of calorie cumpsumption
|
|
|
Accumulation of lactate in muscles
Effects |
Accumulation of lactate in muscles
Effects misconception, not lactic burn, protons transfer coincide with it, causing the high acidity. Dificulty to contract the muscles |
|
|
Cori cycle-
purpose |
Cori cycle-
Way to convert lactate back to glucose |
|
|
Pyruvate enters mitochondria of cell, how does it become acetly CoA?
|
Carbon removed – becomes carbon dioxide
(two carbons left) this 2-carbon compound joins with CoA becoming acetyl CoA – irreversible |
|
|
Acetyl CoA’s options – 2 function
|
2 functions:
Synthesize fats Generate ATP through TCA cycle -Hydrogens – electron transport chain |
|
|
Amino acids-to-energy
|
Amino acids-to-energy
Several entry points in energy pathway Converted to pyruvate (glucogenic) Converted to acetyl CoA (ketogenic) Enter TCA cycle directly (glucogenic) |
|
|
for metabolism, which is perfered for storage
|
Metabolism favors fat formation
Regardless of excess from protein, fat, or carbohydrates Excess fat – most direct and efficient conversion |
|
|
ketone production on hunger
|
Ketone bodies-no longer hungry.
Slows the rate of body protein breakdown Ketosis induces a loss of appetite |
|
|
Satiation –
Satiety – |
Satiation – stop eating - - the reason why you stop eating
Satiety – not to start eating again?--?> the signal that prevents you from eating again - - if food has a high one, signal s to not want to eat for a very long time |
|
|
satiation and satiety of these:
Protein: High-fat foods: Low-energy density foods: High-fiber foods: |
Protein is most satiating (low satiety)
High-fat foods – weak satiation, strong satiety signals Low-energy density foods are more satiating High-fiber foods are more satiating |
|
|
measure Basal metabolic rate (estimate)
|
BMR Equations
Weight in kg, height in cm, age in years Men: (10 x wt(kg)) + (6.25 x ht) – (5 x age) + 5 Women: (10 x wt) + (6.25 x ht) – (5 x age) – 161 |
|
|
factors that a/effect Basal metabolic rate
|
age
height growth gender malnutrition stresses caffeine smoking sleep hormones fever environmental temperature |
|
|
High-protein foods vs. high-fat foods
-which takes more energy to digest? |
Higher proteins (thermic effect) higher if eat really fast, all at once instead of spread out
|
|
|
Healthy weight: BMI =
|
18.5 to 24.9
|
|
|
Yo-yo dieting
|
diet, stop gain a lot more, diet, stop gain even more
|
|
|
Three disorders of underweight
|
Anorexia nervosa- 1/200
Bulimia nervosa- 2-3/100 Binge eating disorder-higher Prevalence of various eating disorders |
|
|
Waist circumference measurements
Indicator of fat distribution & central obesity? |
Women: greater than 35 inches
Men: greater than 40 inches |
|
|
Waist-to-hip ratio
what should be smaller? |
Waist-to-hip ratio
-Compare whether or not degree of central obesity want waste to be smaller than hips |
|
|
which is the set method truely used to measure body fat percentage?
|
hydrodensitometry
|
|
|
Risks associated with being underweight
|
-Fighting against wasting diseases
-Menstrual irregularities and infertility -Osteoporosis and bone fractures |
|
|
Female Athlete Triad
|
-Disordered eating
Unsuitable weight standards Body composition differences Risk factors for eating disorders in athletes -Amenorrhea Characteristics: low estrogen, infertility, bone mineral loss -Osteoporosis Stress fractures |
|
|
Anorexia Nervosa
what are the problems with it? impact on body, and main cause of death? |
*Cannot be self-diagnosed* since Distorted body image
Central to diagnosis Protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) Malnutrition Impacts brain function and judgment Causes lethargy, confusion, and delirium Denial Levels are high among anorexics Impact on body Growth ceases and normal development falters Changes in heart size and strength Other bodily consequences -heart failure main reason why anorexics die |
|
|
which is more prevalent, bulimia nervosa or anorexia nervosa
|
bulimia nervosa
|
|
|
-ways bulimics purge
--physical signs of bulimics |
- fingers in throat
Cathartic – strong laxitive Emetic - throw up usually used for acute poisoning -Tooth erosion, red eyes, calloused hands |
|
|
treatments for bulimia
|
Treatment
Discontinuing purging and restrictive diet habits Learn to eat three meals a day-(refrain from dieting or skipping meals) Plus snacks record in food diary (association with eating less) Treatment team Length of recovery Five to ten years range |
|
|
Microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system (MEOS)
alcohol with it |
Alcohol interferes with drug metabolism
Microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system (MEOS) – 1/5 alcohol metabolism drugs too, so with tynenol, alcohol priority and toxin accumulates. May cause damage |
|
|
set point theory
|
set point theory is that each person has a set body weight determined by genetics and a feedback mechanism.
|
|
|
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
|
Storage of triglycerides - - it removes them from vLDL and to put in fat cells ( the vLDL then turns into LDL and recycles to the liver)
|
|
|
Obesity gene
|
Codes for the protein leptin
Acts as a hormone in hypothalamus Promotes negative energy balance Suppresses appetite Increases energy expenditure |
|
|
Essential amino acids:
|
Histidine,
leucine, isoleucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine valine |
|
|
Oristat
|
inhibits pancreatic lipase in g.i. tract-->blocking digestion side effects cramping, diarrhea, gas, frequent bowel movements *reduces absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (rare:liver injury)
|
|
|
Phentermine (diethylpropion) =
|
Phentermine (diethylpropion) = enhances release of neurotransmitter norepinephrine-->appetite suppression
|
|
|
what are the objective of surgery for obesity
|
Reduces food capacity of stomach
Effectively limits food intake Reduce production of ghrelin Health-related benefits Long-term safety and effectiveness |
|
|
two main types of surgery for obesity
|
gastric bypass (jujenum re-stapled to "small stomach" (cutting out the duodenum and much of the stomatch)
gastric banding- a band that pumps up to constrict the esophageal opening |
|
|
healthy weight loss strategies
|
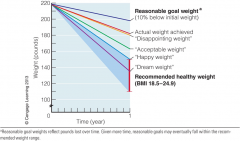
½ to 2 pounds per week
Or 10% weight loss within six months =good healthy weight loss rate *Goal: nutritional adequacy without excess Deficit of 500 to 1000 kcalories per day - - - - tips: Remember water Assistance with weight management Focus on fiber -Low in energy and high in nutrients, Require effort to eat Speed of food consumption Choose fats sensibly Energy density and satiation Watch for empty kcalories: Fat, sugar, and alcohol Saturated trans fats |
|
|
Successful strategies incorporate;
|
Small changes
Moderate losses Reasonable goals Reasonable rate of weight loss |
|
|
bad practices to avoid (dieting)
|
Avoid restrictive eating
Avoid rapid weight loss Breakfast frequency is Inversely related to obesity -in other words, eat breakfast |
|
|
Best approach to weight management besides diet content:
|
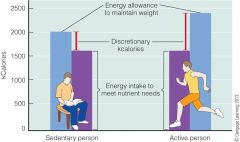
Moderate physical activity plus activities of daily life
Combination of diet and physical activity= Lose more fat Retain more muscle Regain less weight Reduction of abdominal fat (Metabolism Speeds up with activity Immediate and long-term benefits) |

