![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
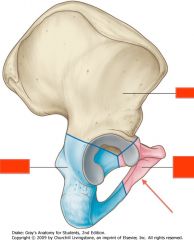
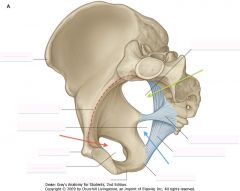
Identify the structure shown by the red arrow.
|
Pubis
|
|
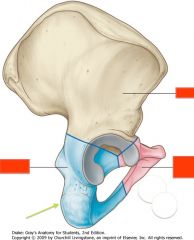
Identify the structure shown by the green arrow.
|
Ischium
|
|
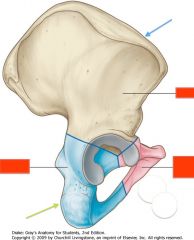
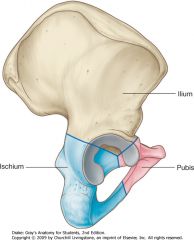
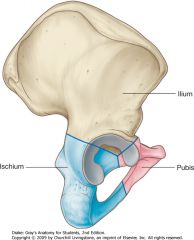
Identify the bone shown by the blue arrow.
|
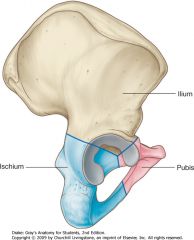
Ilium
|
|
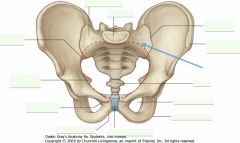
What is the bone indicated by the blue arrow?
|
Sacrum
|
|
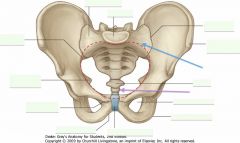
What is the bone indicated by the purple arrow?
|
Coccyx
|
|
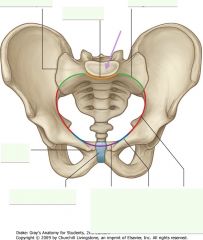
What bony structure is indicated by the purple arrow. It forms the posterior boundary of what structure?
|
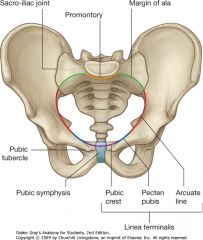
Sacral Promontory.
Pelvic brim or inlet. |
|
|
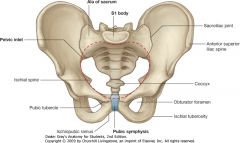
What is the difference between the true and false pelvis?
|
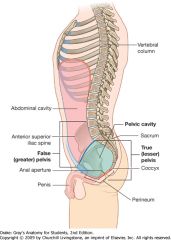
The false (greater) pelvis is bordered superiorly by the anterior superior iliac spine, and inferiorly by the pelvic brim.
The true (lesser) pelvis contains the pelvic cavity between the pelvic brim and the perineum. |
|
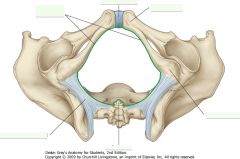
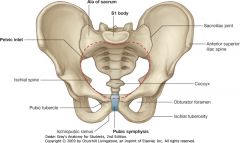
Is the structure indicated by the green outline the pelvic inlet or the pelvic outlet.
|
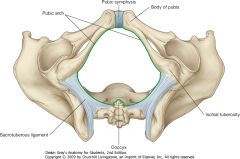
The pelvic outlet. The namings follow the direction of a fetus into and out of the pelvic cavity.
The pelvic inlet is another name for the pelvic brim. |
|
|
What is the only diameter that can be measured intravaginally? How do you find it?
|
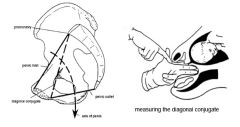
The diagonal conjugate is the distance between the lower margin of the pubic symphysis and the sacral promontory.
|
|
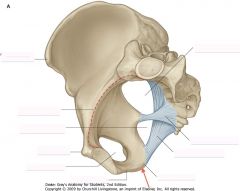
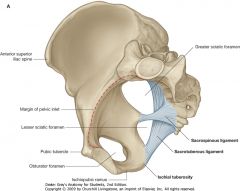
Identify the bone indicated by the arrow.
|
Pubic symphysis
|
|
What bony structure is indicated by the red arrow.
|
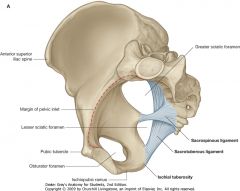
Ischial Tuberosity
|
|
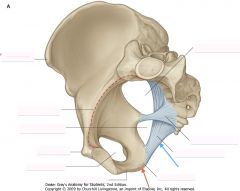
What ligament is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
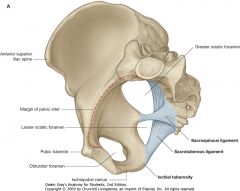
Sacrotuberous Ligament
|
|
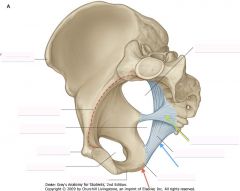
What ligament is indicated by the green arrow?
|
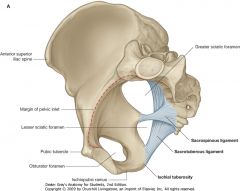
Sacrospinous ligament
|
|
What are the spaces indicated by the arrows called?
|
Obturator foramen
|
|
What is the structure indicated by the arrow called?
|
The Rectum
|
|
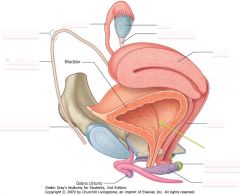
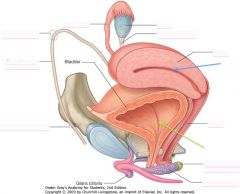
What is the structure indicated by the green arrow?
|
Bladder
Ah poop... |
|
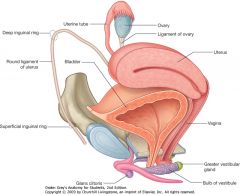
What is the structure indicated by the blue arrow?
|
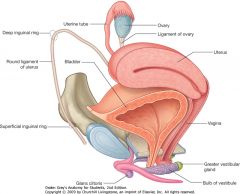
Uterus
|
|
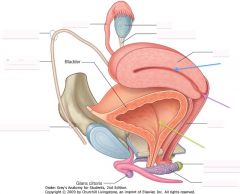
What is located at the tip of the purple arrow?
|
Cervix
|
|
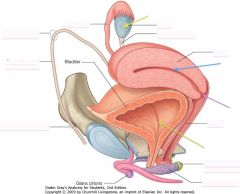
What is the organ indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
Ovary
|
|
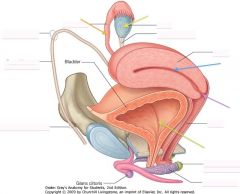
What is indicated by the orange arrow?
|
Uterine (Fallopian) tube
|
|
What is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The vagina.
|
|
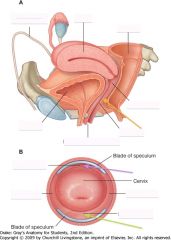
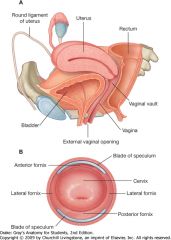
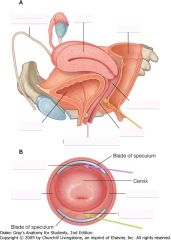
What is indicated by the purple arrow?
|
The anterior fornix of the vagina.
|
|
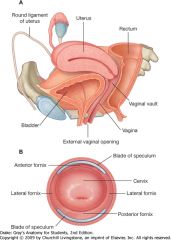
What is indicated by the green arrow?
|
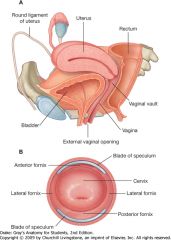
The posterior fornix of the vagina.
|
|
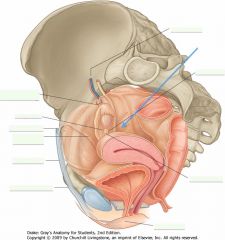
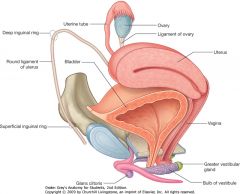
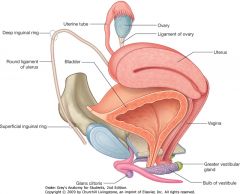
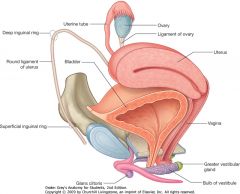
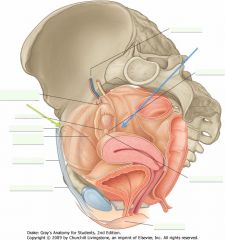
What is the (transparent) structure indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The broad ligament of the uterus.
|
|
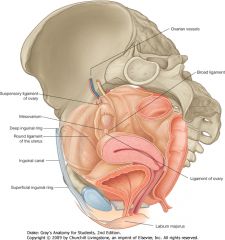
What is the (long) structure indicated by the green arrow?
|
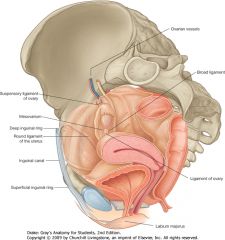
The round ligament of the uterus, you can see it coming out of the deep inguinal canal.
|
|
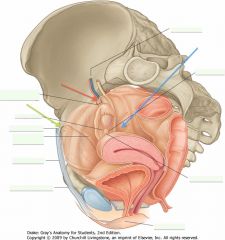
What is the ligament indicated by the red arrow?
What does it enclose? |
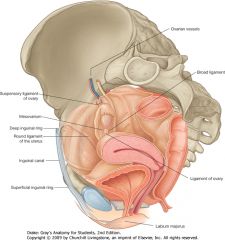
The suspensory ligament of the ovary. The enclosed ovarian vessels are indicated above.
|
|
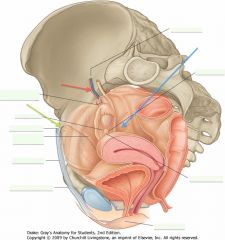
What are the vessels indicated by the red arrow?
|
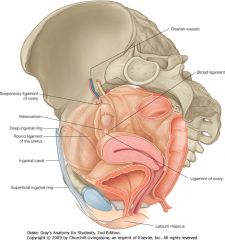
Ovarian vessels.
You can see them entering the suspensory ligament of the ovary. |
|
|
What is the extension of the peritoneal cavity between the rectum and back wall of the uterus called?
|
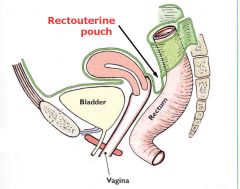
The rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas).
|
|
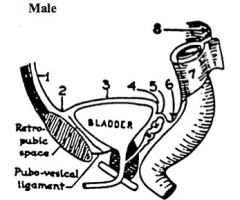
Identify the points on the peritoneal reflection 1-through 8 in the diagram.
|
Male: Peritoneum:
1. Covering the anterior abdominal wall. 2. Reflecting from the anterior abdominal wall to bladder. 3. Covering the superior surface of urinary bladder. 4/5. Reflecting from the superior surface of bladder to rectum. 6. Forming the Rectovesicular Pouch. 7. Covering the rectum 8. Covering the posterior abdominal wall |
|
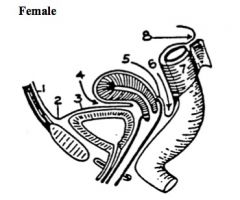
Identify the points of the peritoneal reflection labelled on the diagram.
|
Female: Peritoneum:
1. Covering the anterior abdominal wall. 2. Reflecting from the anterior abdominal wall to the bladder. 3. Covering the superior surface of the urinary bladder. 4. Forming the Vesicouterine Pouch. 5. Covering the posterior upper third of the vagina. 6. Forming the Rectouterine pouch (of Douglas). 7. Covering the rectum. 8. Covering the posterior abdominal wall. |
|
|
Distinguish between the Rectovesicular Pouch, the Vesicouterine Pouch and the Rectouterine Pouch.
|
The three pouches are all reflections of the peritoneum around pelvic structures.
The Rectovesicular Pouch is found only in males, between the rectum and bladder (Green arrow). The Vesicouterine Pouch is between the uterus and the bladder (Orange). The Rectouterine Pouch is between the rectum and the uterus (purple arrow). |
|
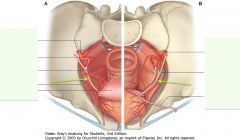
What is the structure indicated by the arrows (in both women (A) and men (B))
|
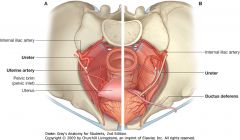
Ureter
|
|
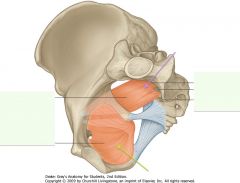
What muscle is indicated by the green arrow?
|
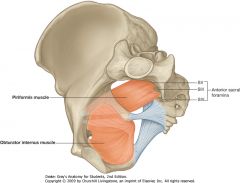
Obturator internus muscle.
|
|
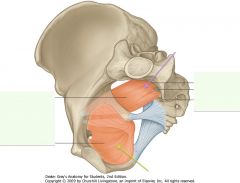
What is the muscle indicated by the purple arrow?
|
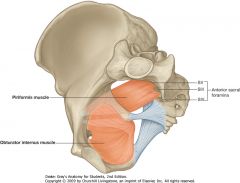
Piriformis muscle.
|
|
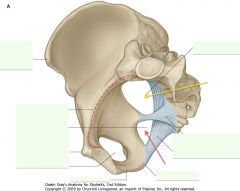
What is the space indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
Greater Sciatic Foramen
|
|
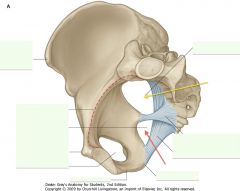
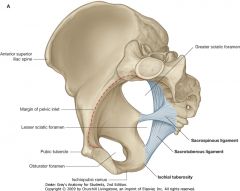
What is the opening indicated by the red arrow?
|
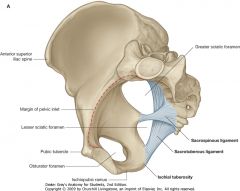
Lesser Sciatic Foramen
|
|
|
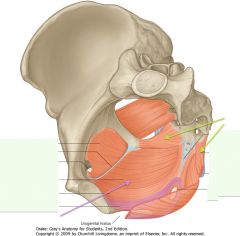
What two muscles form the Pelvic Floor (also called Pelvic Diaphragm)?
|
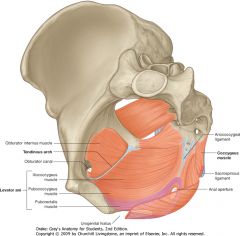
Levator Ani and Coccygeus Muscles.
|
|
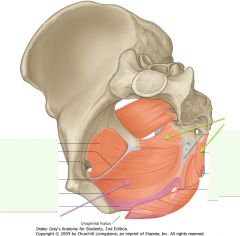
What muscle is indicated by the green arrows?
|
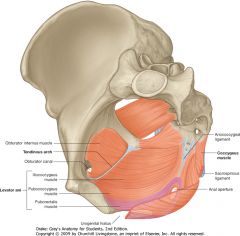
Coccygeus muscle.
|
|
What is the muscle indicated by the purple arrow?
|
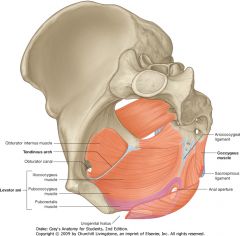
Levator Ani
|
|
|
What is the Tendinous Arc?
|
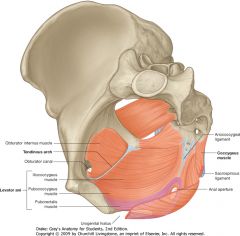
The Tendinous Arc is a local thickening of the fascial covering of the Obturator Internus. It gives origin to two components of the Levator Ani muscle, the Pubococcygeus and Iliococcygeus.
|
|
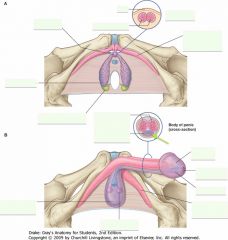
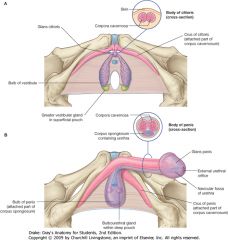
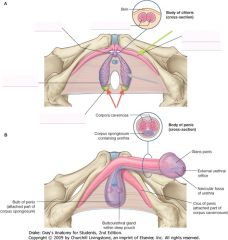
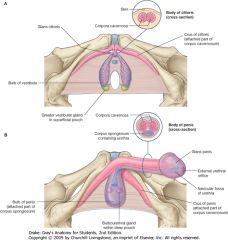
What is the erectile tissue indicated by the green arrow? What does it contain?
|
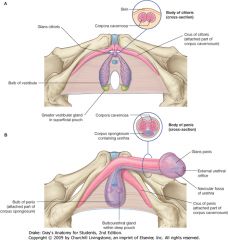
Corpus Spongiosum.
It contains the Urethra. |
|
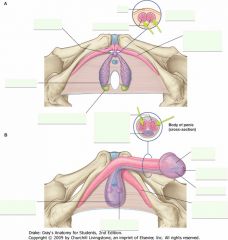
What is the erectile tissue indicated by the arrows?
|
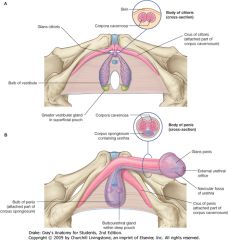
Corpus Cavernosum.
|
|
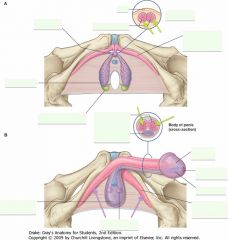
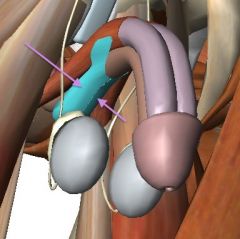
What are the structures indicated by the purple arrows?
|
Left and right crura of the penis (singular crus).
|
|
What are the structures indicated by the purple arrows?
What functions do they perform? |
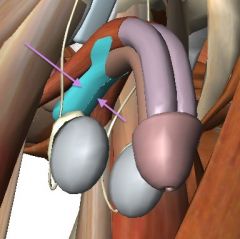
Bulbospongiosius muscle (right and left).
Empty Urethra and compresses the veins of the penis. |
|
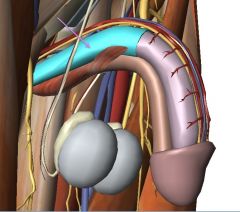
What muscle is indicated by the purple arrow?
What role does the muscle play? |
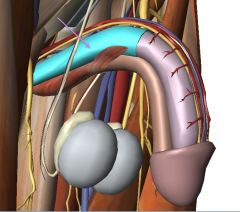
Ischiocavernosus Muscle (Right)
It aids in maintaining the penile erection. |
|
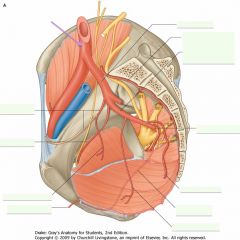
What vessel is indicated by the purple arrow?
|
Internal Iliac Artery.
|
|
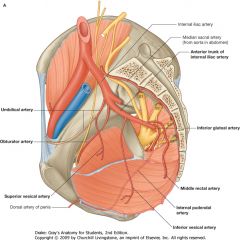
What is this vessel?
|
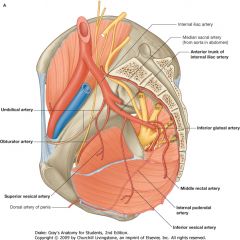
Umbilical Artery, from the anterior branch of the Internal Iliac.
The lateral branch of the umbilical artery is called the Obliterated Umbilical Artery. |
|
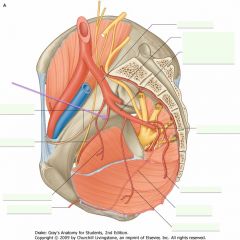
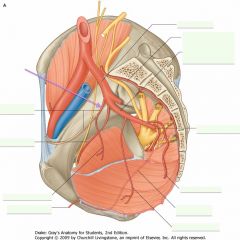
What is the vessel indicated by the arrow?
Where does it exit the pelvic cavity? |
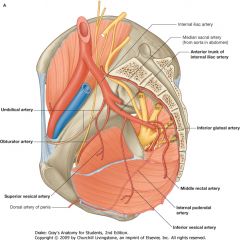
The Obturator Artery, off of the Anterior Branch of the Internal Iliac Artery.
It exits the pelvic cavity through the obturator foramen, along with the obturator nerve. |
|
|
How do you have to identify the branches of the anterior division of the Interior Iliac Artery?
|
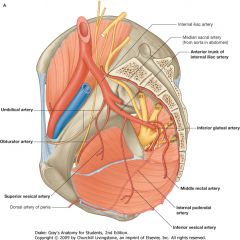
You have to identify by the structure they supply, not by the branching pattern, which can be highly variable.
|
|
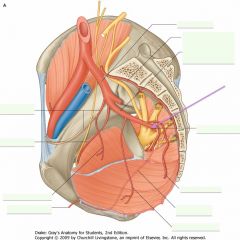
What is the vessel indicated by the arrow?
What does it supply? |
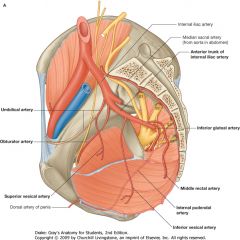
Inferior Gluteal Artery.
It supplies the gluteal region after it exits the pelvis below the S1 (S2 shown) nerve. |
|
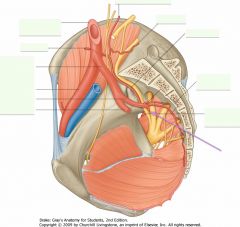
What is the artery indicated by the arrow?
|
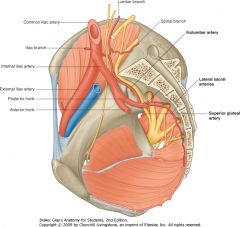
The Superior Gluteal Artery, the largest artery in the posterior division of the Internal Iliac.
It exits the pelvic cavity above the piriformis muscle and the S1 spinal nerve root. (To distinguish from the Inferior Gluteal Artery) |
|
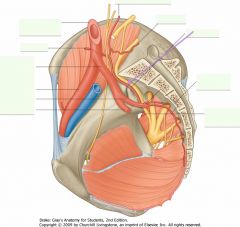
What is the artery indicated by the arrow?
|
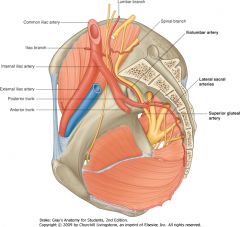
The Iliolumbar Artery off of the posterior division of the Internal Iliac.
It runs upwards, lateral to the lumbar vertebral bodies. |
|
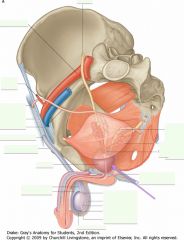
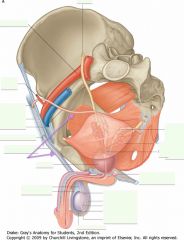
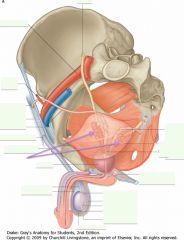
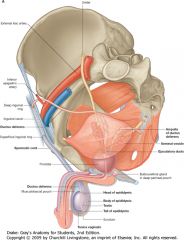
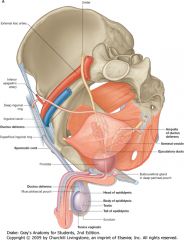
What is the structure indicated by the arrow?
|
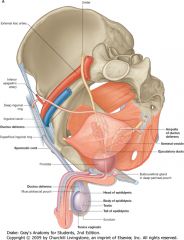
The Prostate gland.
|
|
What is the tube indicated by the arrows called?
|
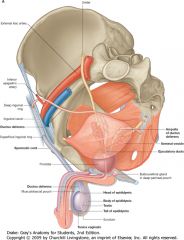
The Ductus (Vas) Deferens
|
|
What are the structures indicated (behind the bladder)?
|
The Seminal Vesicles.
Don't confuse them with the Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens. |
|
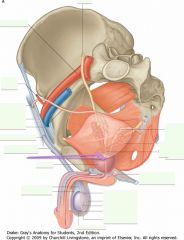
What structure in the Prostate is indicated by the arrows?
|
The Ejaculatory Ducts, where fluid from the Seminal Vesicles are merged with the business from the Ductus Deferens.
|
|
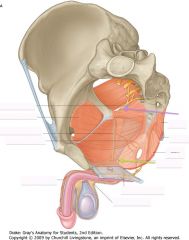
Identify the nerve indicated by the green arrow.
What does it supply? |
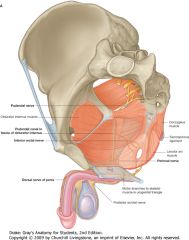
The Perineal Nerve (right).
It supplies the urogenital region (sensory and motor), except for the skin of the penis |
|
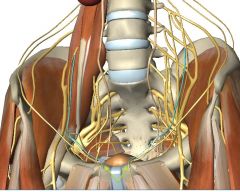
What is the nerve indicated by the green arrows (and coloured green)?
|
The Genital Branch of the Genitofemoral Nerve (From L1,2). It provides both motor(to Cremaster muscle) and sensory innervation (to the skin of the thigh).
|
|
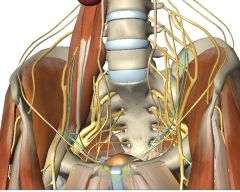
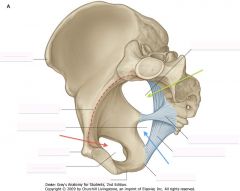
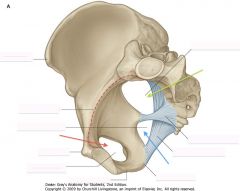
What is the space indicated by the green arrow?
|
Greater Sciatic Foramen
|
|
What is the space indicated by the blue arrow?
|
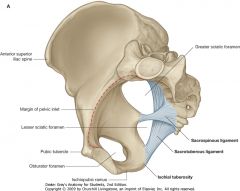
The Lesser Sciatic Foramen
|
|
What is the space indicated by the red arrow?
|
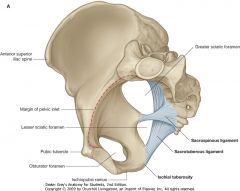
The Obturator Foramen.
|
|
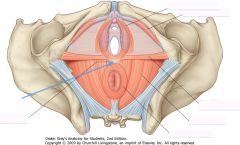
What is the structure indicated by the blue arrow?
|
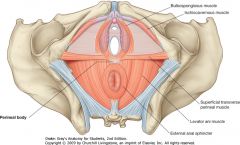
The Perineal Body
|
|
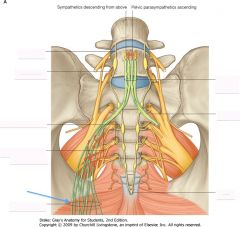
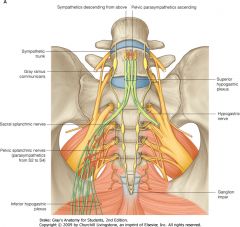
What is the group of nerves indicated by the blue arrow?
|
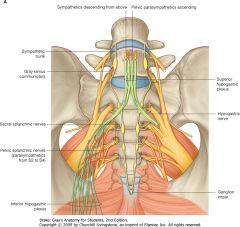
The Pelvic Plexus (Inferior Hypogastric Plexus).
|
|
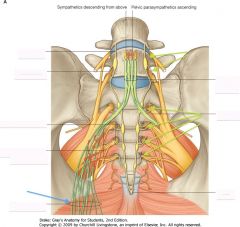
What are the structures indicated by the green arrows?
|
Ventral Rami of L4, L5 and S1-S4.
|
|
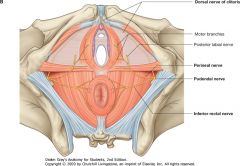
What nerve is indicated by the red arrows?
|
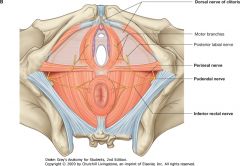
Dorsal Nerve of Clitoris
Branch off of the Pudendal Nerve |
|
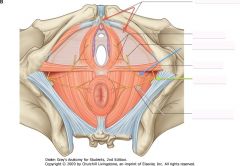
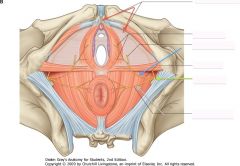
What nerve is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Perineal Nerve
|
|
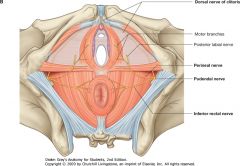
What nerve is indicated by the green arrow?
|
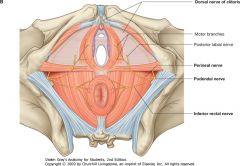
Pudendal Nerve.
|
|
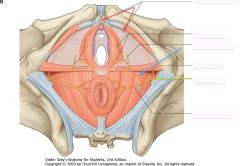
What nerve is indicated by the grey arrow?
|
Inferior Rectal Nerve.
|
|
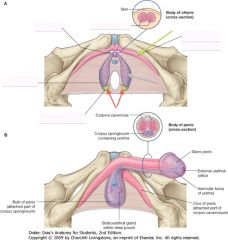
What structure is indicated by the green arrow?
|
The Left Crura.
|
|
What structure is indicated by the grey arrow?
|
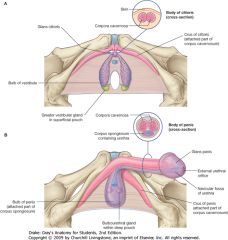
The Bulb of the Vestibule of the Vagina.
|
|
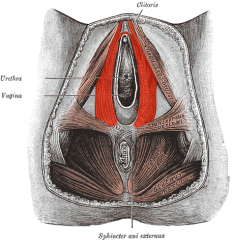
Name the red-highlighted muscle.
|
The Bulbospongiosus Muscle in Female.
|
|
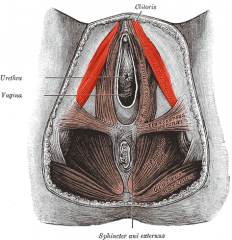
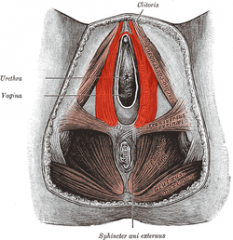
What is the muscle highlighted in red?
|
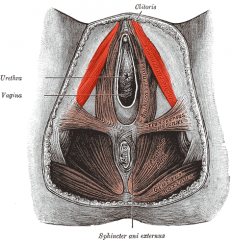
Ischiocavernosus muscle
|
|
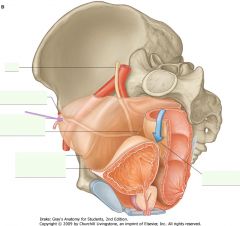
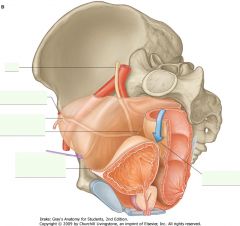
What is the structure indicated by the purple arrow?
|
Lateral Umbilical Fold
|
|
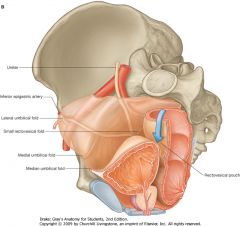
What structure is indicated by the purple arrow.
|
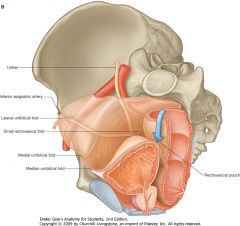
Medial Umbilical Fold
|
|
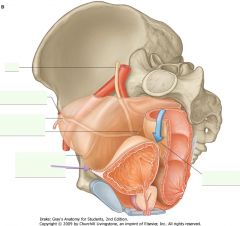
What structure is indicated by the purple arrow?
|
Median Umbilical Fold.
|
|
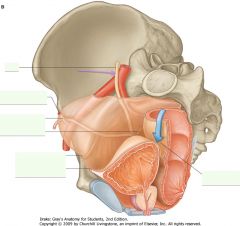
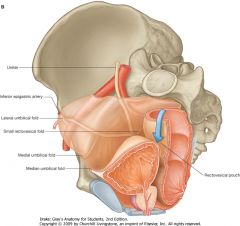
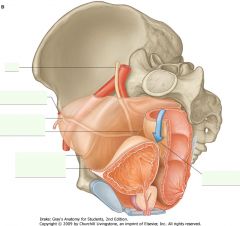
What structure is indicated by the purple arrow?
|
Ureter
|
|
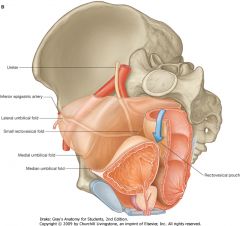
What is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
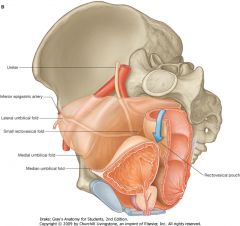
Rectovesicular Pouch
|
|
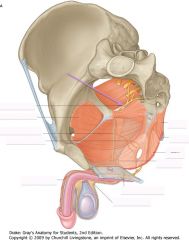
Identify the nerve indicated by the purple arrow.
|
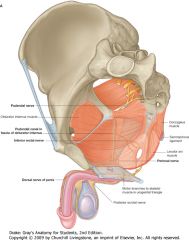
Pudendal Nerve.
It's origin is from the Ventral Rami of S2,3,4. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, into the gluteal region, then enters the perineum through the pudendal canal. |

