![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocrine system |
Hormonal glands secrete chemicals to send messages between body cells |
|
|
Excretory System |
Removes waste from the blood and regulates fluid level (blood pressure) chemical content of the blood |
|
|
Nervous system |
Allows the body to respond to both internal and external stimuli Includes brain, spinal cord, nerves. |
|
|
The endocrine and nervous systems work together to... |
regulate the functions of other body systems |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The body works to maintain a relatively constant internal env within a range despite changing external env's Imp bc the humna nody can only survive within a narrow range of conditions |
|
|
Conditions the human body can survive in: temp, blood glucose, and blood pH |
Temp: 37 degrees Blood glucose: 100mg/mL Blood pH: 7.4 |
|
|
Feedback system |
Mechanism for maintaining homeostasis |
|
|
3 parts of a feedback system |
Sensor, control centre, effector |
|
|
Sensor |
Part of the body that detects a change in the internal env; sends a signal to the control centre |
|
|
Control centre |
Part of the body that sets the range of values within which a variable should be maintained; receives info from sensor and sends signal to effectors if needed |
|
|
Effector |
Part of the body that responds to signals from the control centre to effect/ correct the change in a variable |
|
|
Negative feedback system |
Reverses a change in a variable |
|
|
Positive feedback system |
Change in the system is strengthened or increased |
|
|
Negative feedback loop example |
Body temperature dropping below 37 degrees causes the body to work and try to increase your body temperature. |
|
|
Positive feedback system example |
Blood clotting. Platelets begin the clotting and signal for more platelets to come as well. |
|
|
Monitor |
Sends a message (chemically, electrically, or both) to a control centre. |
|
|
Spinal cord structure |

|
|
|
White Matter |
Formed from myelinated neurons Inner region of some areas of the brain Outer area of the spinal cord |
|
|
Myelin |
Insulation around nerves which speed up nerve impulses |
|
|
Grey matter |
Contains mostly cell bodies, dendrites, and short + unmyelinated axons Around the outside area of the brain Forms the H-shaped core of the spinal cord |
|
|
Spinal cord |
A column of nerve tissue that extends out of the skull from the brain and downward through a canal within the backbone Vital communication link between the brain and the peripheral nervous system |
|
|
Brain and spinal cord are protected by... (3) |
Meninges, vertebrae, skull |
|
|
Meninges |
3 layers of tough, elastic tissue within the skull and the spinal column that directly enclose the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Vertebrae |
Bony structure which protects the spinal cord |
|
|
Blood-brain barrier |
Protective barrier formed by glial cells and blood vessels that separates the blood from the CNS selectively controls the entrance of substances into the brain from the blood (ex: caffeine) |
|
|
Good substances that can cross the blood-brain barrier |
Oxygen Glucose Nutrients |
|
|
Bad substances that can cross the blood-brain barrier |
Nicotine, caffeine, alcohol |
|
|
What cannot cross the blood brain barrier?? |
Toxins and infectious angents |
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid |
Transports hormones, white blood cells, and nutrients across the blood-brain barrier to the cells of the brain and spinal cord. Acts as a shock- absorber to cushion the brain. |
|
|
Where is cerebrospinal fluid found? |
Ventricles of the brain and in the central canal of the spinal cord, is associated with meninges. |
|
|
Largest part of the brain |
Cerebrum |
|
|
Neuron |
(nucleus, cell body, dendrites, axon) Nerve cell specialized to respond to physical/ chemical stimuli Conducts electrochemical signals~ releases chemicals that regulate body processes |
|
|
Dendrite |
Short-branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses are received |
|
|
Axon |
Long thread-like part of a nerve cell along which impulses travel |
|
|
Schwann cells |
Wraps around nerve cells, forming the myelin sheath |
|
|
Myelin |
Soft + white fatty material in the membrane of Schwann cells |
|
|
Synaptic Cleft |
Space between neurons @ a nerve synapse across which a nerve impulse is transmitted by a neurotransmitter |
|
|
3 parts of your brain |
Reptilian, limbic, neocortex |
|
|
Reptilian part of your brain |
Brain stem, back of brain Very old- 300 million yrs old Instinctive brain Functions: feeding, flight, fight, reproduction- OVERALL it's needed for SURVIVAL |
|
|
Limbic part of your brain |
100 m yrs old Emotional part and short term memory Works best when you socialize, never isolate yourself or your brain will not work properly We learn best when we learn with passion-- limbic connects w neocortex |
|
|
Components of the limbic part of your brain |
Amygdala: emotion centre Hippocampus: short term memory, info stored here first |
|
|
Neocortex |
Top of brain 4 mill yrs old Largest part, INTELLECT Used to UNDERSTAND Long term memory, planning and predicting, reasonable and rational decisions, free will, creativity, imagination |
|
|
Temporal lobe function |
Shares in processing visual info AUDITORY RECEPTION |
|
|
Parietal lobe function |
Receives and processes sensory info from skin Helps process info about body's position + orientation |
|
|
Occipital lobe function |
Receives and analyzes visual info Visual recognition |
|
|
Frontal lobe function |
Integrates info from other parts of the brain |
|
|
Central Nervous system |
Brain + spinal cord Integrates and processes info |
|
|
Peripheral NS |
Involves nerves Sends sensory info to CNS Receives motor info from CNS Subdivided into somatic and autonomic NS |
|
|
Somatic NS |
voluntary movement |
|
|
Autonomic NS |
Involuntary control (controls muscle contractions) |
|
|
Neurons |
Receive physical/chemical stimuli, conduct electrochemical signals, and release chemicals to regulate processes in the body |
|
|
Glial cells surround neurons to: |
Nourish neurons Remove their wastes Defend against infection Provide a supporting framework for all the NS tissue |
|
|
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic NS often work in opposition of each other ... |
to regulate involuntary processes of the body |
|
|
Neuron Diagram |

|
|
|
Dendrite |
Short branching terminals that receive nerve impulses from other neurons or sensory receptors Send impulses to the cell body |
|
|
Cell body |
Contains nucleus Transmits a signal through the axon IF the signal from the dendrites is strong enough |
|
|
Axon |
Conducts impulses |
|
|
3 functions of neurons |
Sensory, Integration, Motor output |
|
|
Sensory neurons (PNS) |
receive stimuli from SENSORY receptors |
|
|
Integration neurons (CNS) |
Receive signals from the sensory neurons Send signals to motor neurons |
|
|
Motor output neurons (PNS) |
Receive signals from the interneurons to signal effectors to respond (muscles/ glands/ organs) |
|
|
Reflex arc |
Responsible for reflexes Simple connection of neurons that results in a reflex action in response to a stimulus
Involves neurons to signal from the SKIN RECEPTORS ---> sensory neurons ---> spinal interneuron (which signals motor neurons to react) |
|
|
Action potential |
In an axon, the change in the charge that occurs when the gates of the K+ channels close and the gates of the Na+ channels open after a wave of depolarization is triggered |
|
|
A nerve impulse consists of... |
A series of action potentials |
|
|
How does one action potential stimulate another? |
Nodes of Ranvier contain enough voltage-gated sodium channels to depolarize the membrane and elicit an ACTION POTENTIAL |
|
|
Urine (3) |
Waste from your blood Water Urea |
|
|
Nephron |
Filters within kidney, more than a million within the renal cortex |
|
|
Which molecules do not pass through the Bowman's Capsule? |
Rbc Wbc Proteins Large molecules |
|
|
Blood flows _______ efferent arteriole |
Out of |
|
|
Blood flow ___ afferent arteriole |
Into |
|
|
Which substances carry on through the collecting duct? |
Urea, H2O, K+, Na+, uric acid, HCO3 -, CL - |
|
|
___ & ____ diffuse out of the loop of Henle |
Na+ and H2O |
|
|
Permeability of the distal tube is controlled by... |
ADH= anti-diuretic hormone |
|
|
If H2O in a nephron is low, ____is high. |
reabsorption |
|
|
Diuretic examples |
Alcohol caffeine |
|
|
Glomerelus |
Bundle of capillaries FILTRATION |
|
|
From the collecting duct, waste goes... |
Urine---> urinal pelvis Ureter---> bladder |
|
|
Stuff from glomerelus ---> Bowman's Capsule |
Forced filtration |
|
|
Bowman's Capsule |
Plasma w dissolves solutes diffuses and is passed on to tubule FILTRATION |
|
|
Proximal Tubule |
REABSORPTION Active transport pumps glucose, sodium, and amino acids back onto capillaries: most urea stays inside tubule |
|
|
Henle's loop |
+ [H2O] inside tubule than blood REABSORPTION |
|
|
Distal tubule |
REABSORPTION Final adjustment of H2O +solutes Permeability controlled by anti-diuretics |
|
|
Collecting duct |
SECRETION Ammonia + K move from capillary network into duct by active transport REABSORPTION: H2O moves by osmosis from duct into surrounding blood |
|
|
Urinary System Diagram |
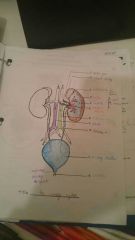
|
|
|
Adrenal Medulla Hormone |
Secretes Epinephrine + Norepinephrine Fight or flight hormones |
|
|
Ovaries produce which hormone? |
Estrogen- stimulates uterine lining growth and promotes development of the female 2ndary sexual characteristics Progesterone- promotes growth of the uterine lining and prevents uterine muscle contractions |
|
|
Testes produce which hormone? |
Testosterone- promotes sperm formation and development of the male 2ndary sexual characteristics |

