![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Metbolism |
Sum of chemical reactions occuring in a living organism Controlled by enzyme Controlled in metabolic pathways Can be coupled - Energy from 1 reaction to drive another |
|
|
Anabolism |
Metbolic pathways of synthesis Small energy molecules (precursors) to complex high energy |
|
|
Catabolism |
Metabolic pathways of breakdown Release energy and low energy products |
|
|
Boomolecules |
Molecules present in living things |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Most are polymer Consist of small units linked by covalent bonds |
|
|
Condensation polymer |
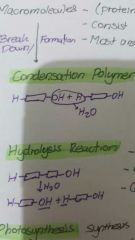
Water loss for each covalent bond Must have 2 functional groups for linking Catalyzed by enzyme polymerases |
|
|
Hydrolysis reaction |

A water molecule added for every covalent bonds broken
During chemcal digestion Catalyzed by enzyme, pH, heat |
|
|
Photosynthesis Respiration |
CO2 reduce to sugar 6CO2 + 6H20 = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Oxidation -oxidize sugar to CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O = 6H2O + 6CO2 |
|
|
Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration |
Aerobic = Use O2 Completely oxidizes glucose to cO2 Release more energy Anaerobic = Absence of O2 Release less energy |
|
|
Fibrous protein and globular protein difference |
Fibrous protein. Structural components Elongated molecules, Dominant 2ndary structure Insoluble in water Globular protein: Drive metabolism reactions Compact spherical structure, dominant 3triary structure Soluble in water |
|
|
Amino acids |
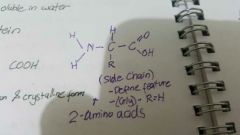
Building blocks of protein Monomer NH2 and COOH |
|
|
Zeiterrion amino acid in aq solution and crystalline form |
Internal salts Amphoteric and ampiprotic Accept and donate H+ according to pH High pH Low H Needs to be hoven H by zwiterrion Zwiterrion anion |
|
|
Isoelectric point |
PH at which the charge carried by amino acid is electrically neutral Not move Least soluble |
|
|
Peptide bond |

Cnnected by condensation reaction of amino acid Chain of peptide bond -poly peptide |
|
|
Primary structure |
Amino acid sequence Amino acid number Dictated by DNA genetic info |
|
|
Secondary structure of proteins
2types |

Hydrogen bond between peptide bonds along its length (co, and nh) Folding of polypeptide chain B pleated sheet Side by side polypeptide Flexible inelastic Fiber A helix Flexible and elastic (like spring) (like spring) Hair skin claw |
|
|
Tertiary structure of protein |
Interaction between r-group side chain of amino acid Further folding Intramolecular interaction Globular protein Interactions: Hydrophobic interaction H-bond Ionic bonding Disulfide bridges |
|
|
Quantenary structure of proteins |
Different polypeptifes Same interaction as tertiary Ex. Collagen Hemoglobin |
|
|
4 interactions of tertiary and quantenary structure of protein |
Hydrophobic interactionH bondIonic bondDisulfide bridges |
|
|
Enzymes |
Protein that are biological catalyst Form enzyme substrate complex E+s = e-s = e-p = e+p |
|
|
Enzyme sometime require non protein molecule for activity |
For organic Coenzymes (like vitamins) For inorganic Metal ions |
|
|
Formation of enzyme complex depends on |
Side xhain of amino acid at active site Non covalent interactions (4 like in tertiary and quantenary) |
|

Enzyme rate of reaction and substrate concentration graph
|
a) at low substrate concentration Rate of reaction prop to substrate conc 《Enzyme available to bind with substrate》 b) as substrate conc increase Rate lower 《Some enzyme have its active site occupied by substrate/ not available》 c) at high substrate conc Constant rate 《Enzyme saturated with substrate》 |
|
|
Enzyme influenced by |
Temperature pH Heavy metal ions |
|
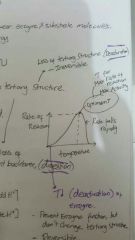
T influence on enzyme
T optimum |
T^ increase frequency of collision Between enzyme and substrate molecules. Rate of reaction ^
Optimum T is T when max rate of reaction KE change conformation of protein 《Denaturation》- Loss of tertiary structure (irreversible) - Enzyme cannot bind with substrate
If T is low, 《deactivation》 Dont change tertiary structure so recersible |
|
|
pH influence on enzyme activity ... |
Influence state of ionization of acid base group in side chain Change in ionization = alter shape, ability to recognize substrate Ectrene pH denatures enzyme |
|
|
Heavy metal ions affect on enzyme activity |
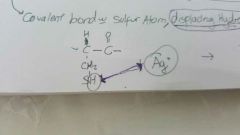
Disrupt protein folding, change shape of active site Inability to bind with substrate Bond with sulfur aton displacing hydrogen. |
|
|
Analysis of protein Amino acid composition Protein concentration |
1st step -break amino acid's peptide bond (hydrolysis) Seperation of resulting amino acid is by: 1. Chromatography 2. Electrophoresis |
|
|
Chromatography |

Mixture component have different affinities for 2 phase. Stationary and mobile phase Component seperate when mobile p move to stationary phase Locating reagent - needed for idnetification. Amino acid is colorless |
|
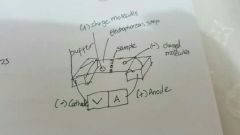
Electrophoresis |
Movement of charge particles in electric field ( amino acid have different charge at different pH buffer solution) pH - isoelectric point... Not move Ph > isoelec .. amino acid is anion. Move to anode Ph < isoelec .. amino is cation. Move to cathode Require agent ninhydrin to detect |
|
|
Lipids |
More reduced than carbohydrate. More oxidize and produce more energy Energy released slowly die to insolubility Triglyceride Phospholipid Steroid |
|
|
Use of lipids |
- Heart disease. Low soluble and accumulate in walls Cholestrol LDL - saturated unhealthy HDL = unsaturated fats healthy Steroid abuse Increase hormones. Testosterone promote todsue growth |
|
|
Triglycerides |
Fats and oils Glycerol + 3 fatty acids (COOh) Eliminate OH of glycerol with OH woth H of COOH to produce water (esterification)
|
|
|
Esterification |
Cndensation that release water |
|
|
Saturated and unsaturated fatty acid of triglycerides |
Saturated - CnH2n+1 COOH Molecules Packed closely. London force ^ MP^ solid LDL : ( Fats Unsaturated = have kinks in chain Difficult to pack molecules close. Intermolecular force v MP v liquid OILS |
|
|
Test degree of unsaturation |

Addition reaction with iodine Molmass of I2 * #of C=C Divide Molmass of acid *100g Iodine # down more saturated |
|
|
2 types of rancidity of fats |
Undergo chem change 1. Hydrolytic rancidity Water present in food Break down glycerol and fatty acid in triglyceride 2. Oxidative rancidity Unsaturated C=C react with O2 Produce volatile aldehyde or ketone Controlled by antioxidants |
|
|
Phosoholipid |

2 fatt acid,1 glycerol, phosphate group Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic head Phospholipid bilayer - maximize interaction of polar group like water |

