![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is DNA? |
~Deoxyribonucleic Acid ~1/2 from mom 1/2 from dad ~blue print" of life |
|
|
What are genes? |
~Covers a wider characteristic or trait ~Codes for hair color |
|
|
What are alleles? |
~A specific part or "variety" of a gene ~Are different "versions" or varieties of the genes that code for hair color. |
|
|
What does DNA do? |
The genetic code gets transcribed into the nucleotide code of mRNA. |
|
|
What does DNA look like? |
~structured in a "double helix" where two strands of nucleotide face each other and pair up ~Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytosine ~Genetic material that codes for genes |
|
|
Where does DNA come from? |
~inside the nucleus |
|
|
What does dominance mean? |
~Means that a particular trait for an allele "covers over" or dominates another form of that trait or allele. ~ALWAYS SHOW UP and are the visible trait that people observe- phenotype |
|
|
What are Recessive Alleles? |
~For a trait are "covered over" or "hidden" ~ONLY be visible when there are 2 copies of them in a genome ~Still expressed but their expression is "hidden over" by the dominant gene and are invisible |
|
|
Consequences of Inheritance: |
~BB: Black hair alleles- dominant ~bb: Blond hair alleles- recessive |
|
|
What is RNA? |
~Ribo Nucleic Acid ~Chemically very similar to DNA but structurally is different (not double helix) ~RNA comes in 3 "flavors" mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
|
|
|
What is Messenger RNA (mRNA)? |
~Single stranded molecule |
|
|
What is Transfer RNA (tRNA)? |
~Complex secondary structure |
|
|
What is Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)? |
~Complex secondary structure |
|
|
What is RNA composed of? |
~Composed of adenine, guanine, and uracil. |
|
|
How does the DNA "Genetic Code" or "Blueprint of Life" work? |
~Has three main functions ("RER"): 1. replication, 2. Gene Expression, 3. Gene Regulation |
|
|
What is replication? |
~DNA makes a "copy" of itself when the cell divides. This way each cell gets an exact copy of the DNA from the "mother" cell. |
|
|
What is Gene expression? |
~The nucleotide "letters" of DNA contains genes that provide the instructions to make all the proteins that the cell needs to function. ~Here the nucleotide letter code of DNA gets transcribed into mRNA which then translates the "message" into making a protein. |
|
|
What is the Gene expression that flows the genetic information? |
~DNA-RNA-Protein |
|
|
What is gene regulation? |
~DNA contains "genetic switches" which are region of DNA responsible for turning genes "on" or "off" and telling the cells WHICH PROTEINS to make, WHEN to make them and HOW MUCH. ~Explains it part how the cells of the embryo can become all the different cell types in the body. |
|
|
How does a protein like hemoglobin get made from the hemoglobin gene encoded by DNA? |
~ |
|
|
What is hemoglobin gene? |
~DNA double stranded- nucleotide pairs (A loves T, C loves G) ~One of the 2 DNA strands get transcribed into mRNA |
|
|
Define translate? |
~tRNA and rRNA are involved in translating mRNA into protein. ~Work together with tRNA and rRNA to get mRNA code into protein |
|
|
What is hemoglobin? |
~Genetic disease that affects the red blood cell protein. ~Found in red blood cells ~Carries oxygen to tissue |
|
|
What is sickle cell anemia? |
~Results from a defective hemoglobin. ~Hemoglobin molecules stick together. ~Sickle RBCs are damaged and have decreased longevity in the blood stream. |
|
|
What are complications from low oxygen supply to tissues? |
~Pain, organ damage, stroke, increase chance of infections. |
|
|
What is "Normal Hb" mean? |
~Normal blood flow |
|
|
What does Sickle cell Hb cause? |
~Causes RBC to misshape or "sickle". |
|
|
What are the results of RBC? |
~as a result the ____ of sickle cell patients becomes "sticky" and blood flow becomes blocked. |
|
|
What are the hemoglobin structures? |
~Multi-sub-unit protein (tetrameter) ~2 alpha and 2 beta subunits ~Heme |
|
|
What is heme? |
~One per sub-unit ~has an iron atom ~carries O2 in red blood cells. |
|
|
What are red blood cells? |
~Bags of hemoglobin that transport oxygen to tissues and organs. |
|
|
What is normal Hb gene? |
~Hb A |
|
|
What is sickle Hb gene? |
~Hb S |
|
|
What is normal Hb protein? |
~HbA |
|
|
What is sickle Hb protein? |
~HbS |
|
|
What is sickle cell hemoglobin a result of? |
~Change or mutation in only ONE nucleotide in the Hb gene. ~Change in the gene translates into ONE amino acid difference in a critical part of the Hb molecule |
|
|
What is sickle cell hemoglobin? |
~One nucleotide difference in the hemoglobin gene causes a change in the amino acid sequence during translation. ~This mutation causes a significant change in the hemoglobin structure. |
|
|
Is sickle cell anemia a recessive or dominate disease? |
~Recessive disease |
|
|
What is sickle cell anemia? |
~Recessive disease ~RBC have all normal Hb-A ~This person got 2 normal copies of the hemoglobin gene. ~Expresses only Hb-A (normal Hb) |
|
|
What happens if you have enough "normal" HbA? |
~They are carriers of sickle cell anemia but are asymptomatic b/c ____ is normally expressed in their RBC so they do not misshapen or sickle and cause symptoms. |
|
|
A is dominant over S and therefore the deleterious affects of sickle Hb-S do not surface. |
~They are "masked" |
|
|
What is Malaria? |
~Carried by mosquito ~Carrying mosquito inject the infection parasite into a host that has all normal Hb- A ~The infection parasite grows and multiplies well in normal blood cells and this person becomes infected w/ the disease. |
|
|
What do people with sickle cell carry? |
~They express both kinds of Hb (A & S) |
|
|
What happens when recessive genetic diseases occur? |
~Need TWO copies of the mutant allele to get the disease ~If both parents are carriers there is a 25% Chance that a boy or girl will be affected, a 50% chance that a child will be carried and a 25% chance that the child will not carry the gene. |
|
|
What happens in a dominant genetic disease? |
~Can be caused by a single abnormal gene from either parent ~Even though one member of the gene pair is normal, the abnormal gene overrules the normal gene. ~If one parent has the disorder, there is a 50% chance that it will be passed to each child. |
|
|
What are sex linked genetic diseases? |
~Mutations carried on the X chromosome. |
|
|
What happens if women carry an x-linked disorder? |
~There is a 50% chance that ____ will pass the disorder to their son and a 50% chance that their daughter will be a carrier. |
|
|
What happens if a man carries an x-linked disorder? |
~All the daughters will be carriers and none of the sons will be affected. |
|
|
What is Hemophilia? |
~ A medical condition in which the ability of the blood to clot is severely reduced, causing the sufferer to bleed severely from even a slight injury. The condition is typically caused by a hereditary lack of a coagulation factor, most often factor VIII. |
|
|
What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy? |
~A genetic disorder characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakness. It is one of nine types of muscular dystrophy. |
|
|
What is turner syndrome? |
~chromosomal condition that affects development in females. ~An early loss of ovarian function (ovarian hypofunction or premature ovarian failure) is also very common. The ovaries develop normally at first, but egg cells (oocytes) usually die prematurely and most ovarian tissue degenerates before birth. Many affected girls do not undergo puberty unless they receive hormone therapy, and most are unable to conceive (infertile). |
|
|
What is Huntington's disease? |
~ A hereditary disease marked by degeneration of the brain cells and causing chorea and progressive dementia. |
|
|
What is Familial hyper-cholesterolemia? |
~ Is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, "bad cholesterol"), in the blood and early cardiovascular disease. |
|
|
What is cystic fibrosis? |
~ A hereditary disorder affecting the exocrine glands. It causes the production of abnormally thick mucus, leading to the blockage of the pancreatic ducts, intestines, and bronchi and often resulting in respiratory infection. |
|
|
What does DNA look like? |
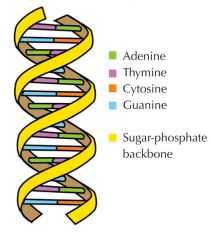
|
|
|
Where does DNA come from? |
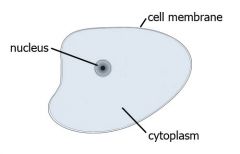
|
|
|
What is the difference between genes and alleles? |
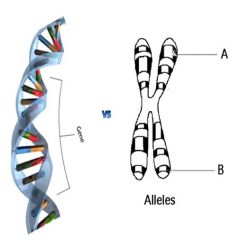
|
|
|
What is the difference between DNA and RNA? |
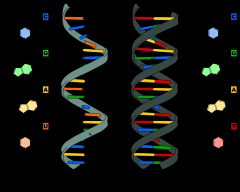
|
|
|
What does mRNA look like? |
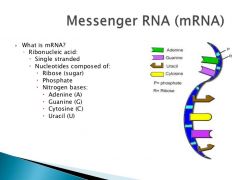
|
|
|
What does tRNA look like? |
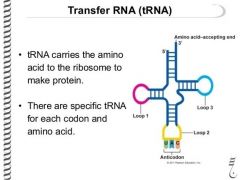
|
|
|
What does rRNA look like? |
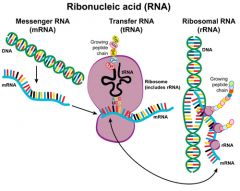
|
|
|
What does DNA replication look like? |
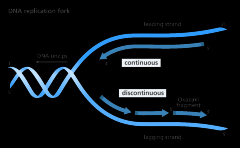
|
|
|
What does gene expression look like? |
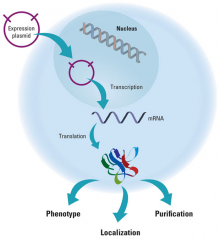
|
|
|
What does gene regulation look like? |
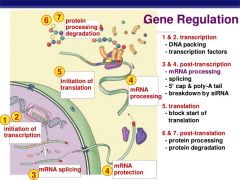
|
|
|
What does normal v. sickle blood look like? |
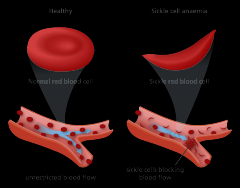
|
|
|
What does the hemoglobin structure look like? |
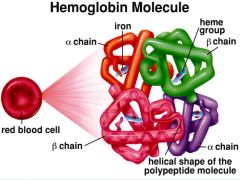
|

