![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Family life cycle |
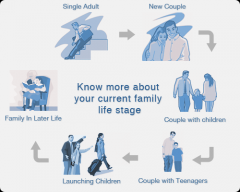
|
|
|
authoritarian parenting |
strict rules, harsh punishments, high obedience low happiness and self-esteem, parents fail to explain rules |
|
|
authoritative parents |
rules guidelines, parents respond to questions, more nurturing, forgiving punishments, happy successful capable children |
|
|
permissive parents |
few rules, rarely discipline, more of a friend, low happiness, problems with authority |
|
|
uninvolved parents |
low demands, low communication, low responsiveness, detached patents, lowest self-estem, low self-control, low competent |
|
|
events that can lead to trauma |
may threaten life or safety make them feel overwhelmed, unexpected, no preparation, feelings of being powerless to prevent it, happened repeatedly, someone was intentionally cruel, happened in childhood |
|
|
emotional and psychological symptoms of trauma |
shock, denial, disbelief, anger, irritability, mood swings, guilt, shame, self-blame, feeling sad or hopeless, confusion, difficulty concentrating, anxiety and fear, withdrawing from others, feeling disconnected or numb |
|
|
physical symptoms of trauma |
insomnia, easily startled, racing heartbeat, aches and pains, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, defines and agitation, muscle tension |
|
|
various signs of abuse |
suspicious injury, somatic complaints without reason, behavioral presentations, controlling partner |
|
|
Human genetics autosomal dominant |
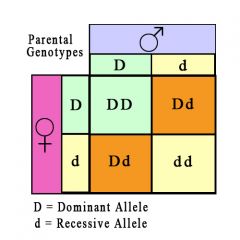
|
|
|
human genetics autosomal recessive |
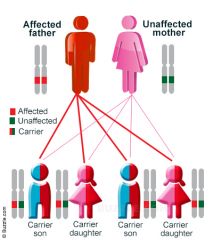
|
|
|
human genetics x-linked |
rarely affects females, always passes to males, females are carriers |
|
|
human genetics |
there is a specific gene that mutated causing a disorder |
|
|
Person in Environment theory |
behavior cannot be understood without considering various aspects (social, political, family, environment, spiritual, physical, economic) |
|
|
Oral Stage |
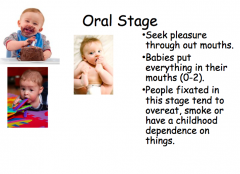
|
|
|
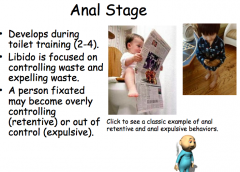
Anal Stage |
|
|
|
Phallic stage |

|
|
|
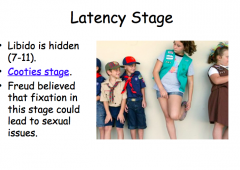
Latency stage |
|
|
|
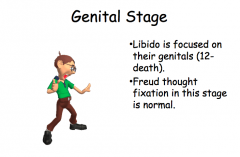
Genital stage |
|
|
|
Individual psychology
|
emphasizing the drive to overcome feelings of inferiority by compensation and the need to achieve personal goals that have value for society.
|
|
|
self psychology |
the self is the central organizing and motivation force in personality, objective is to develop a sense of self-cohesion
|
|
|
self-object needs |
mirroring-validates child sense of perfect self idealization- child borrows strength from others and identifies with some more capability Twinning- child need alter ego for a sense of belonging |
|
|
ego psychology |
focus on the rational and conscious process of the ego, manage stress and effects |
|
|
ego psychology treatment addresses |
how clients behave in situations, client perception of situations, coping ability, capacity for relating to others |
|
|
psychoanalytic theory |
resolve unconscious sexual and aggressive impulses and societal demands to restrain impulses |
|
|
levels of awareness |
preconscious- ready available thoughts and feelings
conscious- all information that is being paid attention to unconscious- thoughts and feelings that one is unaware of |
|
|
id |
operates on the pleasure principle- achieve pleasure and avoid pain |
|
|
ego |
prevents id from impulses |
|
|
superego |
moral standards from society and parents. Causes people to feel guilty when they go against societies rules |
|
|
psychosexual stages |
oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital |
|
|
Fixation |
inability to move from one stage to that next. Shows up in adults |
|
|
oedipus complex |
during the phallic stage, males sexual desire is to his mother and hostility towards his father |
|
|
psychoanalytic therapy |
primary technique is analysis |
|
|
alder- compensation |
attempt to shed normal feelings of inferiority |
|
|
psychosocial stages |
looked at identity crisis, stages can be resolved at later dates |
|
|
Trust V Mistrust |
birth to one year, is my world loving, stable, trusting? is it predictable and supportive? |
|
|
autonomy V shame and doubt |
1-3, can i do things by myself or do i rely on others? |
|
|
Initiative V Guilt |
3-6, am i good or bad? tell others how they feel. |
|
|
Industry V Inferiority |
6-12, am i successful or worthless? kids want to be encouraged and acknowledged |
|
|
Identity V Role Confusion |
early teens, Who am i? trying to decide who they are |
|
|
Generatively V stagnation |
middle adult, will I succeed in life? Will I find a career I love? |
|
|
Intamacy V Isolation |
young adult, will I share my life with someone or life alone? |
|
|
ego Integrity V Despair |
Older adult, Have I live a full life? Did I have a life of meaning? |
|
|
Attachment theory |
Children are programmed to attach to someone, first attachment is to the caregiver, critical in the first 5 years |
|
|
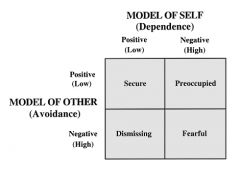
Attachment Styles |
|
|
|
social development micro |
learning how to behave and interact with other, Relies on emotional development |

