![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organs of Respiratory System |
Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Lungs |
|
|
|
Purpose of Conchae |
^ SA. & air turbulence w'in nasal cavity |
|
|
|
Three regions of Pharynx |
Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
Larynx |
Plays role in speech Made of 8 rigid hyalin cartilages and epiglottis |
|
|
|
Trachea |
Connects larynx w. Bronchi Lined w. Ciliated mucosa |
|
|
|
Tracheostomy |
Incision in trachea below cricoid cartilage if larynx is obstructed |
|
|
|
Intubation |
Passing a tube from mouth/nose through larynx & trachea |
|
|
|
Left lung |
Two lobes |
|
|
|
Right lung |
3 lobes |
|
|
|
Covering of lungs |
Visceral Pleura Parietal Pleura |
|
|
|
Visceral Pleura |
Covers and is attached to the outside of lung surface |
|
|
|
Parietal pleura |
Lines internal walls of thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
Respiratory tree division |
Trachea Primary bronchi 2ndry bronchi 3tiary bronchi Bronchioli Terminal bronchioli ALL BUT THE SMALLEST BRANCHES HAVE REINFORCED CARTILAGE |
|
|
|
Bronchodilation |
Via adrenaline |
|
|
|
Bronchoconstriction |
Via histamine and acetylcholine |
|
|
|
Structure of alveoli |
Alveolar duct, " " sac, alveolus |
|
|
|
Type 1 alveolar cells |
Simple squamous cells where gas exchange occurs |
|
|
|
Type 2 alveolar cells (septal cells) |
Free surface has microvilli Secrete alveolar fluid containing surfactant |
|
|
|
Alveolar dust cells |
Wandering macrophages remove debris |
|
|
|
Events of Respiration |
Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Internal respiration |
|
|
|
Pulmonary ventilation |
Moving air in & out of the lungs |
|
|
|
External respiration |
Gas exchange b'ween alveoli and pulmonary deoxygenated blood 02 moves into blood |
|
|
|
Internal Respiration |
Gas exchange b'ween arterial/capillary (oxygenated) blood and cells of the body |
|
|
|
Mechanics of Breathing |
Inspiration Expiration |
|
|
|
Inspiration |
Flow of air into lung Diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract Size of thoracic cavity increases External air pulled into the lungs due to an increase in intrapulmonary vol. |
|
|
|
Expiration |
Air leaving lung (Quiet) largely a passive process which depends on natural ling elasticity As muscles relax, air is pushed out of lungs |
|
|
|
Intrapleural pressure |
Normal pressure w'in pleural space. Always negative Difference in lung and pleural space pressures, keep lungs from collapsing |
|
|
|
Nonrespiratory movements |
Can be caused by reflexes or voluntary actions |
E.g. cough/sneeze Laughing Yawn |
|
|
Eupnea |
Normal quiet breathing |
|
|
|
Apnea |
Temporary cessation of breathing |
|
|
|
Dyspnea |
Difficult or laboured breathing |
|
|
|
Tachypnea |
Rapid breathing |
|
|
|
Diaphragmatic breathing |
Descent of diaphragm causes stomach to bulge during inapiration |
|
|
|
Costal breathing |
Just rib activity involved |
|
|
|
Coughing |
Deep inspiration Closure of rima glottidis Strong expiration blasts air out to clear respiratory passages |
|
|
|
Hiccuping |
Spasmodic contraction of diaphragm Quick closure of rima glottidis prod. sharp inspiratory sound |
|
|
|
Residual volume |
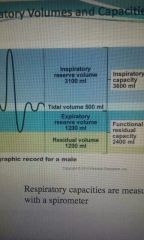
1200ml |
|
|
|
Expiratory reserve volume |
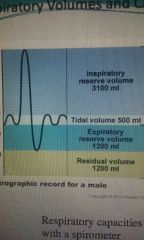
1200ml |
|
|
|
Tidal volume |
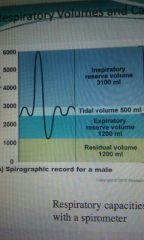
500ml |
|
|
|
Inspiratory reserve volume |
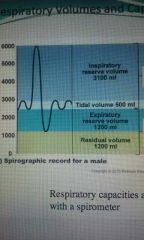
3100ml |
|
|
|
Inspiratory capacity |
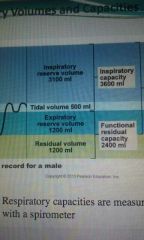
Inspiratory reserve vol. + tidal vol. |
|
|
|
Functional residual capacity |

Expiratory reserve vol. + residual vol. |
|
|
|
Vital capacity |
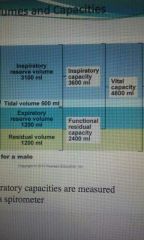
Inspiratory + Func. Resid. Capacity |
|
|
|
Total lung capacity |
6000 ml |
|
|
|
Normal breathing |
Moves ~ 500mL of air in breath |
|
|
|
Factors that affect respiratory capacity |
A person's size Sex Age Physical cond. |
|
|
|
Bronchial sounds |
Prod. By air rushing through trachea and bronchi |
|
|
|
Vesicular breathing sounds |
Soft sounds of air filling alveoli |
|
|
|
Neural reg. Of respiration |
- Activity of respiratory muscles is transmitted to the brain by the phrenic and intercostal nerves - Neural centres that control rate and depth are loc. In medulla - Pons appears to smooth out respiratory rate |
|
|
|
Hypernia |
Increased resp. Rate |
|
|
|
Role of resp. Centre |
(MEDULLA + PONS) 3 groups of neurons - medullary rhythmicity - pneumotaxic - apneustic centers |
|
|
|
Medullary Rhythmicity Area |
- Ctrls basic rythm of respiration - Inspiration for 2 sec, exp for 3 - Autorhythmic cells active for 2 secs then inactive - Exp. neurons inactive during most quiet breathing only active during H vent. rates |
|
|
|
Pneumotaxic area |
Constant inhibitory impulses to inspiratory area Neurons trying to turn off inspiration before lungs too expanded |
|
|
|
Apneustic Area |
Stimulatory signals to insp. area to prolong inspiration If pneumotaxic area is sick. |
|
|
|
Factors influencing respiratory rate/depth |
Physical factors Volition (conscious ctrl) Emotional factors Chem. Factors |
|
|
|
Physical factors |
^ BT Exercise Talking Coughing |
|
|
|
Chemical factors |
CO2 - ^ CO2 = ^ Resp. - Directly affects med. Obl. O2 - changes in c (O2) detected by chemoreceptors in aortic/carotid bodies - "" |
|
|
|
Adult resps. Normal |
12-18 resp/min |
|
|
|
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) |
Exemplified by chronic bronchitis Dyspnea becomes more severe Coughing/freq. Pulmonary inf. Pt. Hypoxic, has respiratory acidosis Will ultimately dev. resp. failure. |
|
|
|
Emphysema |
Alveoli enlarge as adj. chambers break through Chronic inflamm. promotes lung fibrosis Airways collapse during exp. Pt. Use large amounts of energy to exhale Overinflation of lungs leads to permanently exp. Barrel chest |
|
|
|
Chronic Bronchitis |
Mucosa of lower resp. passages becomes severely inflamed. Mucus prod. ^ Pooled mucus impairs vent. & gas exchange Risk of lung inf. ^ |
|
|
|
Ageing effects on breathing |
Elasticity of lungs ⬇ Vital capacity ⬇ Blood 02 ⬇ More risk of resp. Tract inf. |
|

