![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of muscle tissue |
1. Motion 2. Maintain posture 3. Heat production |
|
|
Functional of skeletal muscle |
Action is a movement produced by a muscle - Skeletal muscle rarely acts independently or alone. They act in groups. |
|
|
Functional groups of skeletal muscle 1. Agonist |
Prime movers; produce most of the work
|
|
|
Functional groups of skeletal muscle 2. Antagonist |
Opposes, reverses, or steadies a movement |
|
|
Functional groups of skeletal muscle |
Agonist and antagonist can switch. Example: Biceps brachii and triceps brachii. Biceps are the agonist when flexing the arm but triceps are the agonist when doing a pull up. |
|
|
Functional groups of skeletal muscle 3. Synergists |
Assist prime movers by: - Adding extra force -Stabilizing movement -Modifying movement direction
Example: Brachioradialis to the biceps brachii |
|
|
Functional groups of skeletal muscle 4. Fixators |
Immobilize bone or muscle's origin Example: The abdomen and back muscles act to stop you from falling off your bike |
|
|
Skeletal muscle terminology 1. Origin |
Area where muscle attaches to bone that does not move (remains stationary). Usually more proximal. |
|
|
Skeletal muscle terminology 2. Belly |
Thick region of the muscle |
|
|
Skeletal muscle terminology 3. Insertion |
Area where muscle attaches to bone that moves. Usually more distal. |
|
|
Origin and Insertion may switch |
Example: Biceps brachii. When picking something up, the insertion is in the radius, but when doing a pull up, the insertion is the shoulder. |
|
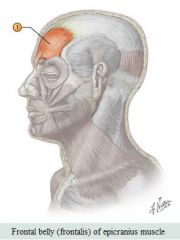
Facial muscles |
Muscle: Epicranius (frontalis) Action: Elevates eyebrows & wrinkles forehead |
|
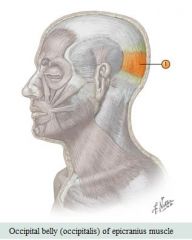
Facial muscles
|
Muscle: Epicranius (occipitalis) Action: Elevates eyebrows & wrinkles forehead |
|
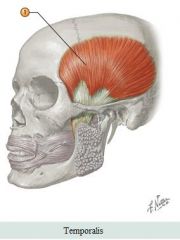
Facial muscles |
Muscle: Temporalis Action: Elevates/retracts jaw |
|
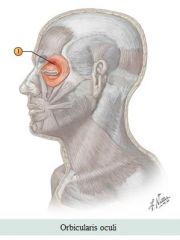
Facial muscles
|
Muscle: Orbicularis oculi Action: Closes eyelids |
|
Facial muscles
|
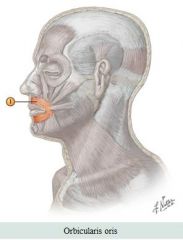
Muscle: Orbicularis oris Action: Closes lips |
|
Facial muscles
|
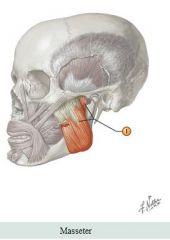
Muscle: Masseter Action: Clenches jaw - mastication |
|
Facial muscles
|
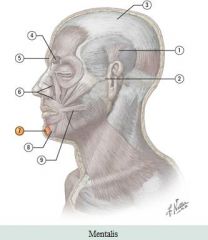
Muscle: Mentalis Action: Lower lip pouts |
|
Facial muscles
|
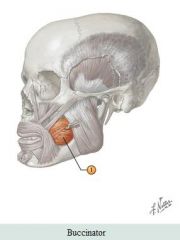
Muscle: Buccinator Action: Compresses cheek, whistles, sucks, and blows air |
|
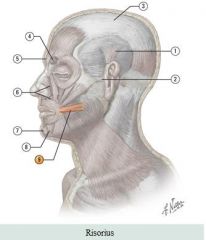
Facial muscles
|
Muscle: Risorius Action: Contract lips laterally for smiling or laughing |
|
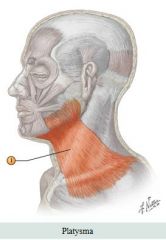
Neck muscles
|
Muscle: Platysma Action: Tenses skin of neck, draws down lip and angle of mouth in surprise expression |
|
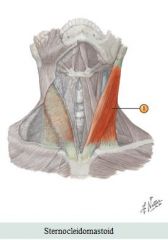
Neck muscles
|
Muscle: Sternocleidomastoid Unilateral action: Flexes and laterally rotates head to look over shoulder Bilateral action: Draws the head forward and down for reading/eating
Origin: Manubrium and medial end of clavicle Insertion: Mastoid process
Antagonist: Splenius capitis |
|
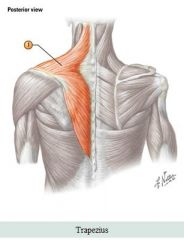
Neck muscles
|
Muscle: Trapezius Action: Extend & laterally flex neck; Elevates or Depresses scapula; Retracts and Rotates the scapula
From superior to inferior: Clavotrapezius, Acromiotrapezius, Spinotrapezius
Origin: Occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae & spinous processes of C7 to T12 Insertion: Acromion, spine of scapula and clavicle |
|
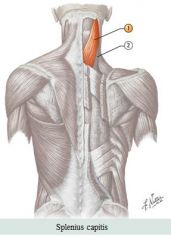
Neck muscles
|
Muscle: Splenius Unilateral action: Roates head to look over shoulder Bilateral action: Extends head and neck
Origin: Ligamentum nuchae and spinous processes C7 to T6 Insertion: Mastoid process and occipital bone for Splenius capitis and transverse processes of C1-C3 for Splenius cervicus
Antagonist: Sternocleidomastoid |
|
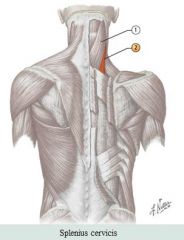
Neck muscles
|
Muscle: Splenius Unilateral action: Roates head to look over shoulder Bilateral action: Extends head and neck
Origin: Ligamentum nuchae and spinous processes C7 to T6 Insertion: Mastoid process and occipital bone for Splenius capitis and transverse processes of C1-C3 for Splenius cervicus
Antagonist: Sternocleidomastoid |
|
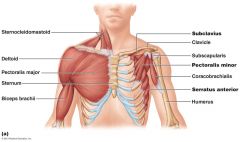
Torso muscles
|
Anterior torso (chest, abdomen, back) muscles In general are flexors |
|
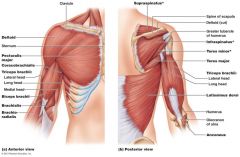
Torso muscles
|
Posterior torso (chest, abdomen, back) muscles In general are extensors |
|
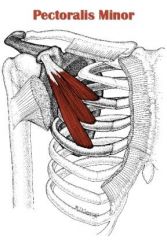
Torso muscles
|
Anterior. Muscle: Pectoralis minor Action: Draws scapula anterior (forward) and inferior (down).
Origin: Anterior surface of ribs 3-5 Insertion: Coracoid process of scapula |
|
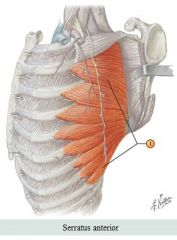
Torso muscles
|
Anterior Muscle: Serratus anterior Action: Rotates/protract scapula
Origin: Anteriorlateral surface of ribs 1-8 Insertion: Portion of the anterior surface of the scapula |
|
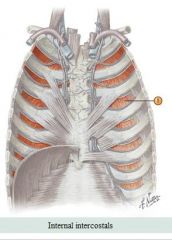
Torso muscles
|
Anterior Muscle: Internal intercostals Action: Elevate ribs during inspiration, depresses the rib cage during forceful expiration
Origin: Superior border of below rib Insertion: Inferior border of above rib |
|
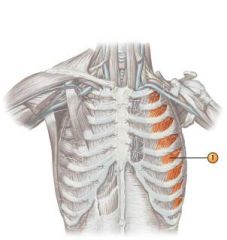
Torso muscles
|
Anterior Muscle: External intercostals Action: Elevate ribs during inspiration
Origin: Inferior border of above rib Insertion: Superior border of below rib |
|
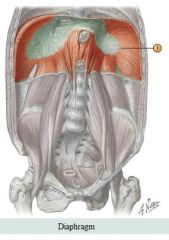
Torso muscles
|
Anterior Muscle: Diaphragm Action: Prime mover of inspiration by increasing volume of thoracic cavity
Origin: Inferior-internal surface of sternum, costal cartilages and lumbar vertebrae Insertion: Diaphragm central tendon (aponeurosis) |

