![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Terminology- Structure of Words |
High school Biological terminology , continously adding.... |
This flashcard can be also use as Fill in the blank. Textbook: Physics Chemistry Biology Mathematics. |
|
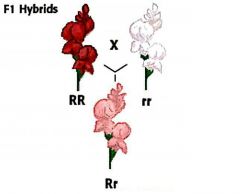
Hybrid |
(general) Any of mixed origin or composition, or the combination of two or more different things. (biology) An offspring resulting from the cross between parents of different species or sub-species. (molecular biology) A complex formed by joining two complementary strands of nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
Caudal (adj) |
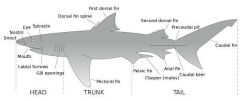
of or like a tail. ▪ at or near the tail or the posterior part of the body.
|
Fish (rohu) caudal fin acts as steering during swimming. |
|
|
Apoptose |
DNA Cellular |
|
|

Xero- |
Means dry |
Gr word |
|
|
Inhabit (v) |
(of a person, animal, or group) live in or occupy (a place or environment) |
The birds inhabit on tree. |
|
|
Inhabit (v) |

(of a person, animal, or group) live in or occupy (a place or environment) |
The birds inhabit on tree. |
|
|
Xerocole (n) |
commonly referred to as a desert animal, an animal adapted to live in the desert. |
Camel is xerocoles animal adapted to desert conditions. |
|
|
Domestication |
It is a process of a bringing a species under human management. For centuries humans have believe that dogs are domesticated wolves, but DNA testing reveals that they are in fact a different species. |
All our major food crops represent domestication varieties. |
|

Mating |
The act of pairing a male and female for reproductive purposes; "the casual couplings of adolescents. |
"the mating of some species occurs only in the spring" |
|
|
Hybridisation or Hybridization |
1.genetic science, genetics - the branch of biology that studies heredity and variation in organisms 2.hybridisation - (genetics) the act of mixing different species or varieties of animals or plants and thus to produce hybrids |
crossbreeding, hybridization, hybridizing, interbreeding, crossing, cross |
|
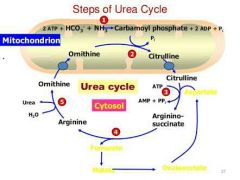
Ureotelic |
Describing animals that excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of urea. Most terrestrial vertebrates are ureotelic, converting ammonium ions formed during the breakdown of amino acids into urea. |
Compare Ammonotelic , Uricotelic. |
|
|
Ammonotelic |
Describing animals that excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of ammonia. |
Most aquatic animals are ammonotelic. Compare ureotelic ; uricotelic. |
|
|
Uricotelic |
Uricotelic Describing animals that excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of uric acid. |
Uricotelic animals include birds and reptiles. Compare ammonotelic; ureotelic. |
|
|
Plant Breeding (Breed To produce offspring/young one ; give birth to or hatch.) |
Changing and improving the heredity of plants in order to create a desired types. |

Heredity means ^ |
|
Trait |
In science, trait refers to a characteristic that is caused by genetics. Having green eyes or being shorter than average are traits a person might have. In more general use, a trait is an important part of someone’s personality or appearance. Try to describe your favorite teacher in three words and you’ll probably come up with a list of her essential traits — such as compassionate, calm, and kooky. |
A trait is something about you that makes you "you." When your mother says that you get all your best traits from her, she means you have the same charming smile and the same brilliant mind as she has. |
|
|
Offspring |
In biology, offspring is the product of reproduction of a new organism produced by one or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two parents. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way. |
Brood, Spawn, Progeny :- (of a fish, frog, mollusc, crustacean, etc.) release or deposit eggs. |
|
|
Inherit |
Inherit may refer to: Inheritance, passing on of property after someone's death Heredity, passing of genetic traits to offspring |
|
|
|
Systematic |
Systematic is the scientific study of similarities and differences among different kinds of organisms and it also includes their identification, nomenclature, and classification. |
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
It branch of biology which deals with the collection, identification, nomenclature, descriptions and classification of plants and animals. |
|

