![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
types of active transport (old)
|
-Pumps
Sodium Potassium Pump: (3 Na+out/2 K+ into the cell; important in nerve transmission) -Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis -Exocytosis |
|
|
types of passive transport (old)
|
-Diffusion
-Osmosis -Facilitated Diffusion- usage of a membrane spanning protein (to help move larger molecules?) |
|
|
active transport (old)
|
movement of a substance
across a membrane against its concentration gradient, helped by transport proteins that REQUIRE ENERGY |
|
|
passive transport (old)
|
diffusion of a substance
across a biological membrane using no energy |
|
|
enzyme action (old)
|
speeds up chemical reactions
|
|
|
activation energy (old)
|
energy needed to start a reaction
|
|
|
catalysts (old)
|
increases rate of a chemical reaction without permanent chemical changing of itself
|
|
|
Hypotinic (old)
|
-less solute outside than in
-a solution causing a cell to take in water |
|
|
isotonic (old)
|
equal amount of solute
(on both sides of the membrane) |
|
|
hypertonic (old)
|
-more solute inside than out
-solution causing a cell to lose water |
|
|
reactants and products of
photosynthesis in general |
light + water + CO2 = Glucose + Oxygen
|
|
|
reactants and products of
each stage of cellular respiriation |
1. Glycolysis - cytoplasm
Reactants: glucose, 2ATP, 4ADP Products: 2 pyruvate, 4ATP, 2NADH, 2H+, 2ADP 2. Pyruvate Oxidation - mitochondrial matrix Reactants: 2 pyruvate, 2NAD+, 2CoA Products: 2acetyl-CoA, 2NADH, 2H+, 2CO2 3. Krebs cycle - mitochondrial matrix and inner mitochondrial membrane Reactants: 2 acetyl-CoA, 2 oxaloacetate, 6NAD+, 2ADP, 2Pi, 2FAD Products: 2CoA, 4CO2, 2 oxaloacetate, 6NADH, 6H+, 2FADH2, 2ATP 4. Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis - inner mitochondrial membrane and intermembrane space Reactants: 6NADH, 2NADH, 2FADH2, 2FADH2, 32ADP, 32Pi, 6 O2, 12H+ Products: 8NAD+, 4FAD+, 24H+, 32ATP, 6H2O |
|
|
reactants and products of
cell respiration in general |
Oxygen + sugar = CO2 + H2O + ATP
|
|
|
reactants and products of
each stage of photosynthesis |

|
|
|
equation for photosynthesis
|
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
|
|
|
equation for cell respiration
|
C6H12O6 + 6CO2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
|
|
|
Effects of temperature on photosynthesis
|
more as the temperature rises until it hits 33 degrees C, then it drops rapidly
|
|
|
Effects of light on photosynthesis
|
more when there's more light until 9,000, then it's constant
|
|
|
energy storage in ATP
|
Energy stored in unstable covalent bonds between phosphates
ADP + Phosphate + Energy ➡ ATP |
|
|
final electron acceptor in cell respiration
|
O2
|
|
|
Electron carriers of cell respiration
|
NAD+
FAD |
|
|
Electron carrier of photosynthesis
|
NADP+
NAD+ |
|
|
Lactic acid fermentation
|
Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+
|
|
|
Alcoholic fermentation
|
glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to ethyl alcohol, regenerating NAD+ and releasing CO2
|
|
|
Anaerobic cell respiration
|
not requiring oxygen
|
|
|
Aerobic cell respiration
|
requiring oxygen
(or sometimes uses oxygen) |
|
|
Parts of mitochondrion
|
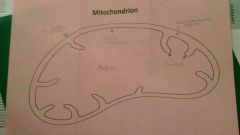
inner & outer membrane
inner membrane space matrix- where the CAC takes place, cristae- folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane, ETC and chemiosmosis here |
|
|
Parts of chloroplast
|
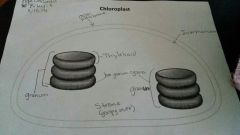
outer & inner membrane
granum- stack of membrane-bounded thylakoids (plural: grana) thylakoid- sac-like structures; light energy ➡ chemical energy (during light reactions of photosynthesis) stroma- goopy substance in chloroplasts |
|
|
Pigments
|
light absorbing molecules
|
|
|
calvin cycle
|
plants use ATP and NADPH to build high-energy compounds that can be stored for long time periods
|
|
|
electron transport chain
|
uses high-energy electrons from the krebs cycle
|
|
|
krebs cycle
|
pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
|
|
|
light dependant reactions
|
oxygen gas is produced and ADP & NADP+ are converted to ATP and NADPH
|

