![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
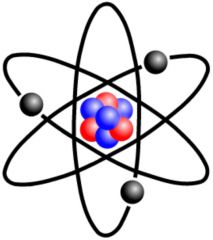
Atom
|
The basic unit of a chemical element
|
The Hydrogen atom has 1 proton.
|
|

Atomic Mass
|
The mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number) or to the average number allowing for the relative abundances of different isotopes.
|
The atomic mass of Lithium is 6.941.
|
|

Atomic Mass Unit
|
The weighted average of an elements naturally occurring isotopes (always a decimal)
|
The atomic mass unit of C-12 is 1/12 of 12.011.
|
|
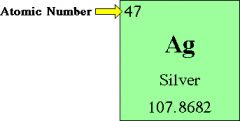
Atomic Number
|
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
|
The atomic number of an element determines it's placement on the Periodic Table.
|
|
|
Atomic Symbol
|
?
|
?
|
|
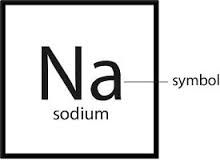
Chemical Symbol
|
A notation using one to three letters to represent an element
|
The chemical symbol of Phosphorus uses just the first letter and is "P".
|
|
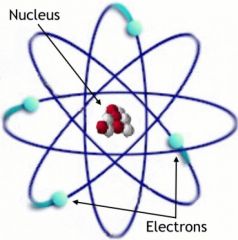
Electron
|
An elementary particle with a negative charge
|
Electrons can be found in the Electron Cloud.
|
|
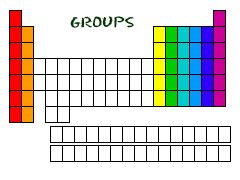
Group
|
The elements of a vertical column in the Periodic Table
|
Group 1 on the Periodic Table starts with Hydrogen and go down to end at Francium
|
|
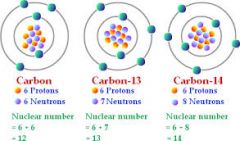
Isotope
|
One of two or more atoms having the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
|
C-12 is the most naturally occurring Carbon isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
|
|
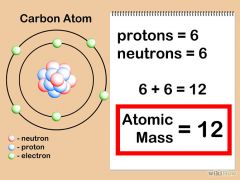
Mass Number
|
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
|
The mass number of Carbon is 12.
[6 (protons) + 6 (neutrons) = 12 |
|
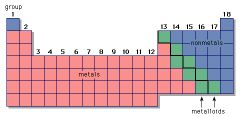
Metal
|
An element that tends to lose electrons in chemical reactions
|
|
|
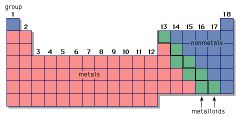
Metalloid
|
An element that has property characteristics of a metal and a nonmetal.
|
|
|
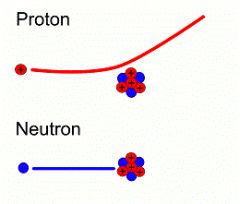
Neutron
|
A neutral subatomic particle; a hadron. (has no charge) Located in the nucleus.
|
The number of neutrons can be calculated/found by subtracting the number of protons from the mass number.
|
|
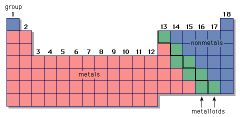
Non-Metal
|
An element that tends to gain electrons in chemical reactions.
|
Helium is an example of a nonmetal
|
|
|
Period
|
A horizontal row of elements
|
|
|

Proton
|
Located in the nucleus, a proton is a positive charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
|
Subatomic Particles
|
Protons, neutrons and electrons that make up the atom.
|
|
|
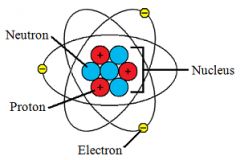
Nucleus
|
Made of protons and neutrons and the center of the atom.
|
|

