![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Vascular Plants |
Plants that have evolved to move water and nutrients throughout the plant |

An example of a ____ is a flowering plant.
|
|
|
Lignin |
Binds to cellulose fibers and strengthens the cell walls of plants |
____ provide rigidity and don't rot easily. |
|
|
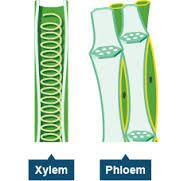
Xylem |
Carry water and minerals from roots to the rest of the plant |
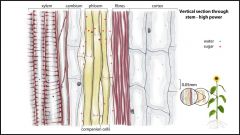
Hollow, tube-snapped cells are known as ____. |
|
|
Phloem |
Tubes of streaming cytoplasm that carry organic nutrients via active transport |
____ are elongated cell. |
|
|
Tracheids |
Have pointed ends, thick cell walls, and pits to connect to adjacent cells |

____ help in the transport of water. |
|
|
Vessel Elements |
Less pointed, wider and shorter, thinner cell walls |
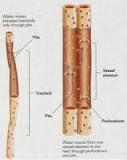
____ have openings at the ends of the cell. |
|
|
Cohesion |
A property of water that makes its molecules attracted to each other |
____ deals with similar substances coming together. |
|
|
Adhesion |
Non-similar particles that are attracted to one another |
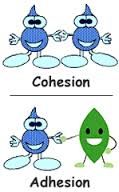
____ deals with different substances coming together. |
|
|
Sieve Tubes |
Phloem cells have openings at cell ends to create long channels |
____ are arranged in chains. |
|
|
Endosperm |
Tissue that transfers nutrients from the parent plant to the developing embryo |
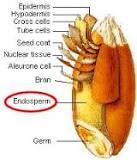
____ is produced inside the seed of most flowering plants. |
|
|
Cotyledons |
"Seed leaves" that develop before true leaves to perform photosynthesis and store nutrients from the endosperm |

The number of ____ present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants |
|
|
Apical Meristems |
Continuously divide to make new cells that become differentiated |
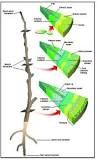
____ is a zone of plant cells at the tips of the shoot and root. |
|
|
Seed Coat |
Tissue formed by parent flower surrounding the endosperm and embryo, protecting the new plant until it sprouts |
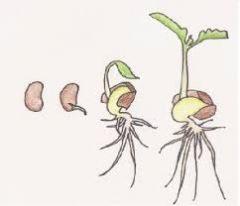
The ____ ____ is one of three parts of a seed. |
|
|
Germination |
Sprouting of seeds occurs when conditions are right |

____ is the process by which a plant grows from a seed. |
|
|
Primary Growth |
Growth that occurs at the meristems |

____ ____ grow in the opposite direction of secondary growth. |
|
|
Node |
Points where leaves emerge from stem |
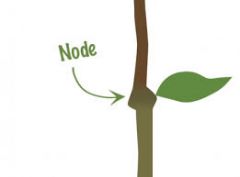
____ is where the leaf meets the stem. |
|
|
Root Cap |
Protective covering of cells over the root apical meristem |
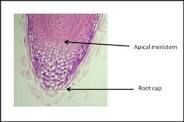
____ is also called calyptra. |
|
|
Epidermis |
Outer layer of cells |
The layer below the ____ is the Dermis. |
|
|
Cuticle |
Helps prevent water loss |

Water stays out due to the ____. |
|
|
Vascular Tissue |
Xylem and Phloem. Used in transport |
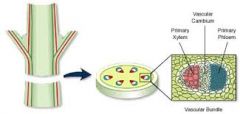
____ ____ is made of more than one cell type. |
|
|
Ground Tissue |
Provide internal support and shape |
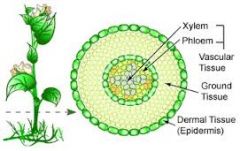
The ____ ____ of plants includes all tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular. |
|
|
Secondary Growth |
Horizontal growing that occurs as a result of cell division in the vascular cambium |
____ ____ grows in the opposite direction of primary growth. |
|
|
Vascular Cambium |
Meristem tissue layer near the other surface of roots and stems |
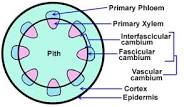
The ____ ____ is a plant tissue located between the xylem and the phloem in the stem and root of a vascular plant. |
|
|
Pericycle |
Cylinder of meristem tissue surrounding the xylem and phloem in the root; source of secondary roots ("root branches") |
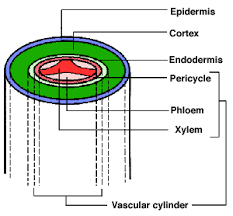
The ____ lies just inside the endodermis. |
|
|
Plant Growth Regulators (PGR's) |
Compounds in plants that are produced by genes and act similarly to hormones in animals; influence plant growth and development |
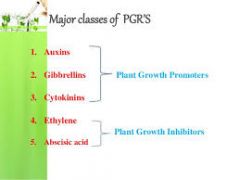
____ ____ ____ are AKA plant hormones. |
|
|
Auxins |
A growth stimulant PGR Produced in apical meristems and seeds, move through plant via active transport. |
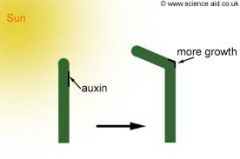
The ____ effect depends on the concentration. |
|
|
Gibberellins |
A growth stimulant PGR Produced in fungi and plants' apical meristems and germination embryos. |
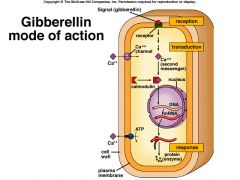
____ promotes stem elongation. |
|
|
Cytokinins |
A growth stimulant PGR Work with auxins and other PGR's to regulate the growth pattern of the plant. |
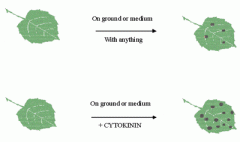
____ is produced mainly in roots and developing fruit. |
|
|
Abscisic Acid |
A growth inhibiter PGR Promotes closing the stoma, dormancy in buds and seeds, synthesis of storage proteins in seeds |
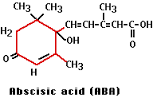
____ ____ is produced in response to dry conditions. |
|
|
Ethylene |
A growth inhibiter PGR Promotes aging of tissues(i.e. ripening fruit) |

____ inhibits effects of auxins and cytokinins. |
|
|
Tropism |
Growth toward or away from a stimulus as a result of differences in growth between parts of plant organs |
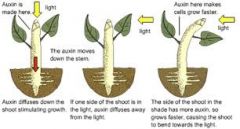
There are a few forms of this that include the prefixes photo- and Gravi-. |
|
|
Phototropism |
Growth toward light source as a result of higher auxin concentrations on the dark side of stems |

____ is growth toward light. |
|
|
Gravitropism |
Growth toward or away from Earth's gravitational pull as a result of auxins, other PGR's, and calcium ion concentrations |

____ grows with or against gravity. |
|
|
Photoperiodism |
Response to the relative length of light and darkness in a 24 hour period |

____ helps promote cross pollination. |
|
|
Phytochrome |
Pigment that "measures" length of darkness |
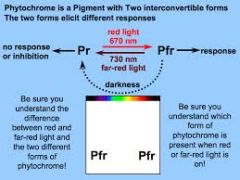
____ is a photoreceptor. |

